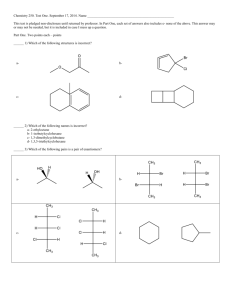
Review Sheet and Study Guide
advertisement

Notes for Chapter 4: Preparing for the Future Economists categorize the kinds of work people do into 4 main sectors: 1.) Primary 3.) Tertiary 2.) Secondary 4.) Quaternary Primary - This is work involving the harvesting and extracting of natural resources - For thousands of years, this was the main type of work - Technology has changed the primary sector as well as the number of people working in the primary sector - Examples include: farming, fishing, forestry, mining Secondary - Work in this sector is mostly construction or manufacturing - Construction involves building things such as homes, bridges, and offices - Manufacturing involves turning raw materials into useful products - Examples include: packaging foods, clothing, furniture Tertiary - People working in this sector provide services to others - Examples include: sales people, bus drivers, actors, teachers, government workers, doctors, electricians Quaternary - This is the most recent sector and involves working with ideas and information technology - Examples include working in labs to research new ideas and products and working with communication and information technologies to create, store and transmit information electronically Diversified Economies - An economic system that has a good balance of jobs in all sectors is called a diversified economy - A diversified economy usually has most jobs in the tertiary and quaternary sectors. Some jobs are in the secondary sector and the fewest are in the primary sector - Canada is an example of a diversified economy (see map page 68-69) Statistics - Statistics are information in the form of numbers - There are a number of ways stats can be presented (see pages 65-66): 1.) Circle graphs 3.) Bar graphs 2.) Line graphs 4.) Pictographs Following the trend - Most countries are moving toward a diversified economy, but at different rates. - Economies first become industrialized, then diversified - Note the global trends on the map on page 68-69 Demographics - demographics are statistics about a certain population - they include topics such as the number of people in each age group and of each sex, whether people are single or married, etc. - these statistics are analyzed so that over time we can identify certain trends in society (example: studying demographics to determine if Canada has an aging population) Social Trends - Social trends are important ideas in society that start to shape the ways people do things - An example would be using alternative energy sources such as wind and solar instead of oil and gas. This would have many economic effects, such as: 1.) increase use of alternative energy 2.) new jobs in these areas 3.) loss of jobs in oil and gas 4.) less pollution The Global View - no country’s economy is separate from the economies of other countries - almost all countries make goods that are sold to other countries and buy goods made in other countries - there are many benefits and downfalls to global trade for Canada, such as: 1.) Being able to trade with other countries gives us a much bigger market for our products 2.) Global trade also means that Canada doesn’t totally control its own economy. Why? 3.) Global trade also affects politics. Countries that are trading partners need to stay on good terms Forecasting the Future - To forecast the economy, economists look at things such as social trends and demographics. - In order for you to plan your economic future, you need to analyze what is happening now, and forecast how it will affect the economy over time Study Guide Chapter 4 1.) Be able to identify to which sector a list of jobs would belong. For example, a chef would be in the tertiary industry while a computer analyst would be in the quaternary sector (page 61-62) 2.) Be able to take statistical data and present it in a particular type of graph (page 65-66) 3.) Be able to create a cause and effect chain relating to forecasting the future (page 70-71) 4.) Be able to predict future trends based on demographic information 5.) Be able to briefly define the four types of economies on page 68 (diversified, newly industrialized, industrializing, agricultural) 6.) Know the following terms: - Sector p. 61 - Circle graph p. 65 - Primary sector p. 61 - Line graph p. 65 - Secondary sector p. 61 - Bar graph p. 66 - Tertiary sector p. 62 - Pictograph p. 66 - Quaternary sector p. 62 - Forecast p. 70 - Diversified economy p. 64 - Social trends p. 70 - Statistics p. 65 - Demographics p. 71