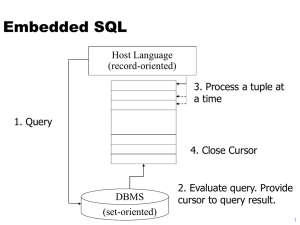
here
advertisement

CIS 270—App Dev II
Big Java Chapter 22
Relational Databases
22.1.1 Database Tables
• A relational database (DB) stores information in
tables
_________.
columns
• Tables contain data in rows and __________.
fields such as SSN,
• Columns represent data ________
Name, DateOfBirth, etc.
entities such as
• Rows represent individual _________
students (which have SSN, Name, DateOfBirth, …).
• Data in relational databases are accessed using
language
SQL (structured query ___________).
• Java can be used to send SQL commands to a DB.
22.1.1 SQL Examples
• SQL command to create a product table:
CREATE TABLE Product
(
Product_Code CHAR(11),
Description CHAR(40),
Price DECIMAL(10, 2)
)
row in a table:
• Insert a _____
INSERT INTO Product
VALUES (‘257-535’, ‘Hair dryer’, 29.95)
• Remove a table from the DB:
DROP TABLE Product
22.1.2 Linking Tables
instance fields that
• A Customer class can have _________
directly relate to columns in a relational table.
– Customer table: customerId, name, address,
city, state, zip
• However, an Invoice class may have a Customer
object as an instance field (more complicated).
• This situation would require an Invoice table:
– Invoice table: invoiceId, customerId, payment
• These two tables are linked by the customerId
field, which is the primary _____
key of Customer and
foreign key of Invoice.
a __________
22.1.3 Implementing Relationships
• Each invoice has exactly one customer, which is a
1:1 relationship (single-valued).
_____
1:n or
• But an invoice can have many line items (____
multi-valued relationship):
– private ArrayList<LineItem> items;
• This requires two more tables.
– LineItem table: invoiceId, productId,
quantity
– Product table: productId, description, price
• Tables and relationships:
1:1 Product
Customer 1:1
--- Invoice 1:n
--- LineItem ---
22.2 Queries I
• Use the SELECT command to _______
query a database:
–
–
–
–
SELECT city, state FROM Customer
SELECT * FROM Customer WHERE State = ‘CA’
SELECT * FROM Customer WHERE Name LIKE ‘_o%’
SELECT * FROM Product
WHERE Price < 100
AND Description <> ‘Toaster’
one character’ and
• Above, the _ means ‘match ____
the % means ‘match any number of characters’
• Calculations:
– SELECT AVG(Price) FROM Product
22.2 Queries II
• Joins
– SELECT LineItem.invoice_number
FROM Product, LineItem
WHERE Product.description = ‘Car vacuum’
AND Product.product_code =
LineItem.product_code
• Updating and Deleting Data
– DELETE FROM Customer WHERE State = ‘CA’
– UPDATE LineItem
SET quantity = quantity + 1
WHERE invoice_number = ‘11731’
22.4 Create a DB and a DSN
• Create a database using Access and save to a folder
source name) for the database
• Create a DSN (data ________
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
In Windows, click Start, Settings, Control Panel
Double-click Administrative Tools
Double-click Data Sources (ODBC)
Click User DSN tab
Click Add button
Select Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb, *.accdb), click Finish
Enter a Data Source Name (your choice)
Click the Select button, navigate to the folder containing
the database, select the database, click the database file
– Click OK, OK, and OK
22.4 Write the Java Program I
• Create a Connection object
import
import
import
import
java.sql.Connection;
java.sql.Statement;
java.sql.DriverManager;
java.sql.ResultSet;
public class Test
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
try
{
Class.forName( "sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver" );
String dataSourceName = "mdbTEST";
String dbURL = "jdbc:odbc:" + dataSourceName;
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(
dbURL, "","" );
22.4 Write the Java Program II
• Create an SQL Statement object and use it to
execute various SQL commands
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
stmt.execute( “CREATE TABLE Table1 ( aColumnName integer )” );
stmt.execute( “INSERT INTO Table1 VALUES( 77 )” );
stmt.execute( “SELECT aColumnName FROM Table1” );
22.4 Write the Java Program III
• Create a ResultSet object and use it to display
results
ResultSet rs = stmt.getResultSet();
if ( rs != null )
while ( rs.next() )
{
System.out.println( "Data from first column: " +
rs.getString( 1 ) );
}
stmt.execute( “DROP TABLE Table1" );
stmt.close();
con.close();
} // end try
22.4 Write the Java Program IV
• Finish up
catch ( Exception err )
{
System.out.println( "ERROR: " + err );
} // end catch
} // end main
} // end class
• Install the database, compile the Java program
and run
• See http://www.planet-sourcecode.com/vb/scripts/ShowCode.asp?txtCodeId=2
691&lngWId=2#SECTION_SQL for more discussion