Yes
advertisement

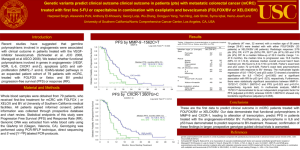
DOES THE NEW EPOC TRIAL ELIMINATE ANTI-EGFR ANTIBODIES AS PART OF PRE-OP THERAPY FOR CURABLE LIVER-ONLY MCRC? YES! Cathy Eng, M.D., F.A.C.P. Associate Professor Associate Medical Director, Colorectal Center Director of Network Clinical Research, GI Med Onc March 28, 2014 Department of GI Medical Oncology Disclosures: The presenter is the first of the sessions so please be kind . In this setting, it is presumed we will be providing neoadjuvant chemotherapy regardless In the perspective of the actual clinical setting, it is recommended that each patient is evaluated on a individual basis. Cancers of the Colon and Rectum International Statistics Colorectal cancer is the 3rd most Worldwide common cancer in men and the 2nd in women. Incidence Mortality 1.2 Million 609,000 per annum USA (2014) Incidence 136,830 Mortality 50,310 Jemal et al: Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev; 19(8) August 2010; Siegel et al: CA Cancer J Clin 2014 Facts about mCRC: There is NO standard approach to surgically resect patients with liver metastases. The liver is the most common site of metastatic disease. Approximately, 20% of patients will have surgically resectable disease at presentation Approximately, 20% of patients after neoaduvuant chemotherapy will be downsized to be potentially resectable. The expected 5-yr OS of a surgically unresectable patient is 13%. The 5-yr OS of a patient with surgically resectable disease is 33-58%. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html Management of MCRC: An Evolving Treatment Algorithm Diagnosis of MCRC Resectable (20%) Neoadjuvant/ Preoperative Therapy Unresectable Borderline/ Potentially Resectable (20%) First-Line Second-Line Surgery +/- Adjuvant Therapy NCCN, 2010. Palliation MDACC Algorithms: The complexity of treating mCRC Pivotal Trials of mCRC with Surgically Resectable Liver Metastasis • Keep in mind, there are limited studies overall • Most studies have been small single institution phase II studies or retrospective analyses. Original EPOC Trial: Phase III EORTC 40983 FOLFOX4 Surgery FOLFOX4 6 cycles 6 cycles (3 months) (3 months) Surgery N=364 patients Nordlinger et al: Lancet 2008; Lanc Onc 2013 Primary endpoint: PFS EORTC 40983: PFS in Eligible Patients HR= 0.77; CI: 0.60-1.00, p=0.041 100 90 +8.1% At 3 years 80 Periop CT 70 60 50 36.2% 40 30 Surgery only 28.1% After a median follow-up of 8.5 yrs, no difference in 5-yr OS (51% vs. 48%, p=0.34) 20 10 0 (years) 0 O N 125 171 115 171 1 2 3 Number of patients at risk : 83 57 37 115 74 43 4 5 22 8 21 5 6 Why consider anti-EGFR therapy in the neoadjuvant setting? Incorporate biologic therapy Hope for additional benefit when using enriched pt pop KRAS WT patients may have increased benefit from an EGFR inhibitor to optimize outcome Avoid class effect toxicities of anti-VEGF therapy: Long t1/2 requiring dose to be held prior to surgery GI perforation Wound healing Original EPOC study showed ~8% improvement in 3-yr PFS with neoadjuvant FOLFOX in mCRC patients with operable liver metastases Nordlinger et al, Lancet 2008 New EPOC Phase III Study: Chemotherapy ± Cetuximab in Operable KRAS-WT mCRC FOLFOX4 + Cetuximab Surgery FOLFOX4 + Cetuximab 6 cycles 6 cycles (3 months) (3 months) FOLFOX N=621 patients Nordlinger et al: Lancet 2008; Lanc Onc 2013 Surgery FOLFOX Primary endpoint: PFS New EPOC Phase III Study: Chemotherapy ± Cetuximab in Operable KRAS-WT mCRC FOLFOX4 + Cetuximab Surgery FOLFOX4 + Cetuximab 6 cycles 6 cycles (3 months) (3 months) FOLFOX Surgery FOLFOX Primary endpoint: PFS N=272/621 patients Nordlinger et al: Lancet 2008; Lanc Onc 2013 Proportion progression free New EPOC: Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy ± Cetuximab in Operable KRAS-WT mCRC: PFS Median PFS 1.00 HR: 1.49 (95% CI: 1.04-2.12); P = .030 0.75 0.50 0.25 Chemo alone Chemo + cetuximab 0.00 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 Time to progression or death (months) Number at risk Chemo alone 116 89 Chemo + Cetuximab 117 87 60 65 38 23 12 5 2 1 1 0 54 24 15 5 3 2 1 0 0 Primrose JN, et al. ASCO 2013. Abstract 3504. significantly worse with cetuximab: 14.1 months vs 20.5 months with chemotherapy alone Study stopped at predefined futility analysis Immature data, but more events unlikely to change result Why did the new EPOC study fail? KRAS is a predictive marker of potential benefit for EGFR inhibition. Cetuximab does not have a role in the adjuvant setting Phase III N0147: FOLFOX +/- cetuximab failed to demonstrate improvement in DFS in stage III colon cancer 3-yr DFS: 74.6% vs 71.5% with the addition of cetuximab (HR, 1.21; 95% CI, 0.98–1.49; P=.08) Or is it the chemotherapy backbone of FOLFOX and cetuximab? Alberts et al: JAMA. Apr 4, 2012; 307(13): 1383–1393. Pivotal trials in mCRC of EGFR inhibition CRYSTAL Study Phase III Patients • Previously untreated mCRC, EGFR + pts FOLFIRI + Cetuximab • Tumor tissue from primary tumor or metastasis available for biomarker analysis 1:1 Randomization • ECOG PS 0-2 FOLFIRI • N=1198 Primary Endpoint: PFS Van Cutsem et al: NEJM, 2009; Van Cutsem et al: JCO 2011 CRYSTAL STUDY - Cetuximab and Chemotherapy as Initial Treatment for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer • The PFS was 8.9M vs. 8.0M. • HR = 0.85 (95% CI: 0.72 to 0.99; P = 0.048). • The PFS for KRAS WT tumors was 9.9M vs. 8.7M • HR = 0.68 (95% CI, 0.50 to 0.94) • There was no initial significant difference in OS (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.81 to 1.07; P = 0.31). • UPDATE: Improved median OS for the investigational arm of (23.5 v 20.0 months; HR: 0.796; P = .0093) • The ORR in each arm was 46% (95% CI, 42-50) and 38% (95% CI, 3442). • Rate of surgery and R0 resection (7.9% v 4.6%; odds ratio, 1.823; 95% CI, 0.957 to 3.472; P = .0633 and 5.1% v 2.0%; odds ratio, 2.650; 95% CI, 1.083 to 6.490; P = .0265, respectively). Van Cutsem et al: NEJM, 2009; Van Cutsem et al: JCO 2011 COIN Study Phase III Patients • Previously untreated mCRC • Tumor tissue from primary tumor or metastasis available for biomarker analysis • ECOG PS 0-2 XELOX 1:1 Randomization • N=2445 XELOX + Cetuximab Primary Endpoint: OS Maughan et al Lancet 2011: OS (primary analysis) and PFS among KRAS wild-type patients Progression-free Survival Arm A Arm B Diff. Median OS : mo 17.9 17.0 -0.92 2-year survival rates 36.1% 34.4% -1.66% 0.75 1.00 Overall Survival Arm A Arm B Diff. Median PFS: mo 8.6 8.6 +0.07 2-year survival rates 8.83% 9.55% +0.72% HR point estimate = 1.038 95% CI = (0.90, 1.20) Χ2 = 0.18; p = 0.68 0.00 0.25 Survival 0.50 HR point estimate = 0.959 95% CI = (0.84, 1.09) Χ2 = 0.27; p = 0.60 0 Arm A (OxFp) Arm A (OxFp) Arm B (OxFp + cetux) Arm B (OxFp + cetux) 6 12 18 24 Time (months) 30 36 42 0 6 12 18 24 30 Time (months) 36 42 N patients at risk: A 367 316 250 154 83 44 19 1 367 245 92 41 18 11 6 1 B 362 306 238 149 80 42 17 3 361 249 103 42 22 9 6 0 CELIM: Phase II Patients • Previously untreated, surgically unresectable mCRC FOLFOX + cetuximab • ≥5 liver metastases • Tumor tissue from primary tumor or metastasis available for biomarker analysis • ECOG PS 0-2 1:1 Randomization FOLFIRI + cetuximab • N=114 Primary Endpoint: RR . Folprecht; Lancet Onc, 2010; Annals of Onc, 2014 CELIM STUDY – Tumor response and resectability of colorectal liver metastases following neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cetuximab Results: RR in 36 (68%) of 53 patients in group A, and 30 (57%) of 53 patients in group B (p=0.23). In a retrospective analysis of response by KRAS status, RR was noted 47 (70%) of 67 patients versus 11 (41%) of 27 patients with KRASmutated tumors (OR 3.42, 1.35-8.66; p=0.0080). Update: The median OS was 35.7M vs 29M HR 1.03 [95% CI: 0.66-1.61], p=0.9). • The median PFS was 10.8M vs. 10.5M, HR 1.18 [95% CI: 0.79-1.74], p=0.4). • Patients who underwent R0 resection (n=36) had a better median OS 53.9M vs. 21.9M, p<0.001). • The median disease-free survival for R0 resected patients was 9.9 [95% CI: 5.8-14.0] months, and the 5-year OS rate was 46.2 [95% CI: 29.5-62.9]%. New Data to Support EGFR Inhibition as Neoadjuvant Therapy Does it change my current opinion about the role of EGFR in neoadjuvant chemotherapy? No Update on PRIME Study Phase III Patients • Previously untreated mCRC • Fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy allowed if PD occurred ≥6 mo after completion; no oxaliplatin • Tumor tissue from primary tumor or metastasis available for biomarker analysis • ECOG PS 0-2 Panitumumab 6.0 mg/kg q 2 wk FOLFOX4 q 2 wk 1:1 Randomization FOLFOX4 q 2 wk Primary Endpoint: PFS • N=1183 Douillard JY, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4697-4705. PRIME (FOLFOX +/- Panitumumab) PFS by KRAS Mutation Status WT KRAS MT KRAS 100% 90% 80% RR: 55% vs. 48%, P = .068. 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 Proportion Event-Free Proportion Event-Free 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 Months Months Median (mos) (95% CI) Median (mos) (95% CI) Panitumumab + FOLFOX4 10.1 (9.3-12) Panitumumab + FOLFOX4 7.4 (6.9 – 8.1) FOLFOX4 7.9 (7.2-9.3) FOLFOX4 9.2 (8.1 – 9.9) HR = 0.72 (95% CI: 0.58 – 0.90) HR = 1.27 (95% CI: 1.04 – 1.55) Log-rank p-value = 0.004 Log-rank p-value = 0.02 Douillard et al: JCO, 2010; NEJM 2013 PRIME Biomarker Analysis: Analysis of KRAS/NRAS and BRAF Mutations RAS and BRAF Status WT MT WT KRAS exon 2 tumors tested for RAS and BRAF WT KRAS exon 2/MT other RAS, n (%) WT KRAS exon 3 (codon 61), n (%) MT Failure WT KRAS exon 4 (codons 117/146), n (%) MT Failure WT NRAS exon 2 (codons 12/13), n (%) MT Failure WT NRAS exon 3 (codon 61), n (%) MT Failure WT NRAS exon 4 (codons 117/146), n (%) MT Failure WT BRAF exon 15 (codon 600), n (%) MT Failure KRAS exon 2 (codon 12/13) FOLFOX4 Alone 331 219 (n = 321) 57 (18) 306 (95) 14 (4) 1 (0) 296 (92) 15 (5) 10 (3) 307 (96) 14 (4) 0 (0) 305 (95) 14 (4) 2 (1) 313 (98) 0 (0) 8 (2) 280 (87) 29 (9) 12 (4) Panitumumab + FOLFOX4 325 221 (n = 320) 51 (16) 308 (96) 10 (3) 2 (1) 288 (90) 21 (7) 11 (3) 308 (96) 8 (3) 4 (1) 305 (95) 12 (4) 3 (1) 316 (99) 0 (0) 4 (1) 286 (89) 24 (8) 10 (3) Oliner J, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(Suppl): Abstract 3511. Oliner J, et al. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(Suppl 2): Abstract 2275. Revised PRIME Consort Diagram Douillard et al: NEJM, 2013 PRIME: Updated OS Analysis Proportion Alive (%) Overall Survival in the Primary-Analysis Population No.at Risk Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 FOLFOX4 alone Events Median Mo no./total no. (%) (95% CI) Panitumumab- 128/259 (49) FOLFOX4 26.0 (21.7–30.4) FOLFOX4 alone 148/253 (58) 20.2(17.7–23.1) Hazard ratio, 0.78 (95% CI, 0.62–0.99) P=0.043 Months 259 253 189 174 88 65 0 0 Overall Survival in the Updated-Analysis Population Proportion Alive (%) Events Median Mo no./total no. (%) (95% CI) Panitumumab- 204/259 (79) FOLFOX4 FOLFOX4 alone 218/253 (86) 20.2(17.6–23.6) Hazard ratio, 0.77 (95% CI, 0.64–0.94) P=0.009 Months No.at Risk Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 FOLFOX4 alone Douillard et al, 2013. 25.8 (21.7–29.7) 259 253 189 176 129 104 83 60 49 30 14 8 FIRE-3 Phase III Study Design Patients • mCRC FOLFIRI + Cetuximab (Cetuximab: 400 mg/m2 loading dose; 250 mg/m2 weekly) • KRAS wild-type • ECOG PS 0-2 • 1st line therapy; prior adjuvant chemotherapy allowed if completed >6 mo before inclusion • N=592 1:1 Randomization FOLFIRI + Bevacizumab (Bev: 5 mg/kg every 2 weeks) Primary endpoint: Response Rate Heinemann V. ASCO 2013. Abstract LBA3506. FIRE-3: Overall Response Rate FOLFIRI + Cetuximab FOLFIRI + Bevacizumab OR P Value 62.0% 58.0% 1.18 (0.85-1.64) 0.183 Complete response 4.4% 1.4% Partial response 57.6% 56.6% Stable disease 17.5% 28.8% Progressive disease 7.1% 5.4% Not evaluable 13.1% 7.8% 72.2% 63.1% 1.52 (1.05-2.19) 0.017 Endpoint ORR, intent-to-treat (ITT) population (N=592) ORR, Evaluable (N=526) Heinemann V. ASCO 2013. Abstract LBA3506. Consort FIRE-3 Diagram N=752 mCRC 1st-line unselected patients N=592 KRAS exon 2 wild-type ITT population KRAS unknown= 30 No treatment= 13 No treatment KRAS mt = 4 N=113 KRAS exon 2 mutant population* N=407 (69%) RAS evaluable population N=342 RAS wild-type N= 171 FOLFIRI + Cetuximab N= 171 FOLFIRI + Bevacizumab N=65 (16%) ‘New’ RAS mutant N= 34 FOLFIRI Cetuximab N=58 FOLFIRI + Cetuximab N=55 FOLFIRI + Bevacizumab N= 31 FOLFIRI + Bevacizumab Stinzing et al: ESMO, 2013 FIRE-3: Overall survival RAS* all wild-type Events n/N (%) Median (months) 95% CI ― FOLFIRI + Cetuximab 91/171 (53.2%) 33.1 24.5 – 39.4 ― FOLFIRI + Bevacizumab 110/171 (64.3%) 25.6 22.7 – 28.6 1.0 Probability of survival 0.75 HR 0.70 (95% CI: 0.53 – 0.92) p (log-rank)= 0.011 0.50 Δ = 7.5 months 0.25 0.0 12 No. at risk 171 171 128 127 Stinzing et al: ESMO, 2013 48 36 24 months since start of treatment 71 68 39 26 20 9 60 72 6 1 * KRAS and NRAS exon 2, 3 and 4 wild-type FIRE-3 Update: Overall Survival by All-RAS Mutation Status FOLFIRI + Cetuximab FOLFIRI + Bevacizumab HR P Value ITT (N=592) 28.7 months 25.0 months 0.77 0.017 RAS WT (n=342) 33.1 months 25.6 months 0.70 0.011 RAS MT (n=65) 16.4 months 20.6 months 1.20 0.57 BRAF MT (n=48) 12.3 months 13.7 months 0.87 0.65 Study Population Stintzing S. European Cancer Conference 2013. Abstract LBA17. Pending Trials CALGB/SWOG 80405: Pending results Study amended: Wild-type KRAS tumors only • First-line mCRC • Amended accrual; N=2300 wild-type patients R A N D O M I Z E FOLFOX or FOLFIRI* + cetuximab FOLFOX or FOLFIRI* + cetuximab + bevacizumab FOLFOX or FOLFIRI* + bevacizumab BOS-2 (EORTC 40091): Phase II KRAS WT Resectable Liver Mets Study amended: Wild-type KRAS tumors only • First-line mCRC • N=360 R A N D O M I Z E FOLFOX FOLFOX + bevacizumab FOLFOX + panitumumab Primary Endpoint: PFS http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01508000?term=BOS-2&rank=1 BOS -3 (EORTC-1207) Phase II/III Study Design (Pending) Patients • mCRC FOLFOX + Aflibercept (Aflibercept: 4 mg/m2) • KRAS MT • ECOG PS 0-1 1:1 Randomization • 1st line therapy; prior adjuvant chemotherapy allowed if completed >12 mo before inclusion FOLFOX Primary endpoint: PFS http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01646554?term=BOS-2&rank=2 Conclusions: The data from the new EPOC trial indicates FOLFOX/cetuximab can be deleterious in surgically resectable KRAS WT patients Due to the rare RAS MT? Does EGFR inhibition require macroscopic disease for efficacy ~ irinotecan? Is it the backbone? CELIM was underpowered The use of FOLFOX/FOLFIRI + anti-EGFR therapy in a KRAS WT patient does not result necessarily in superior RR vs. anti-VEGF therapy. Pending final results of FIRE-3, CALGB 80405, BOS-2 and BOS- 3 If you are considering EGFR inhibition, must consider all RAS MT testing.