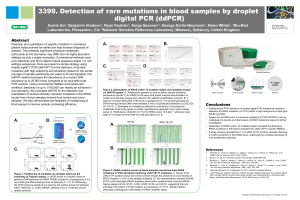
Accompanying Powerpoint Presentation
advertisement

KRAS testing in colorectal cancer Philippe Taniere Birmingham Targeted therapy in colorectal cancer (CRC) Two anti EGFR monoclonal antibodies are licensed for CRC Cetuximab (Erbitux, Merck Serono) first line treatment in combination with irinotecan-based chemotherapy or FOLFOX4 2nd or 3rd line treatment as a single agent Panitumumab (Vectibix, Amgen) monotherapy after failure of fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin and irinotecan-containing chemotherapy regimens. Mandatory molecular testing KRAS mutation testing is mandatory prior to prescription since trials have clearly shown that KRAS mutated tumours will never respond to the drug Negative predictive marker KRAS mutation KRAS gene mutated in 40 to 45% of CRC 2 main hotspots in exon 2 at codons 12 and 13 1 rarely mutated site in exon 3 at codon 61 1 even more rarely mutated site at codon 146 Licensing for wild type codons 12 and 13 Sources of material Sections from paraffin blocks Stained sections Cytology specimens DNA extraction and PCR Scraping from slides Tissue in DNA extraction buffer Direct sequencing (Sanger) Substitution Pyrosequencing G to T codon 12 GGT Codon 12 GGC Codon 13 Real time PCR View: All Wells View: Control (3A) and 12 Val mix (3G) Exogenous Control and Single Mutation: 12 Val Positive all 7 K-RAS Mutation Mixes Exogenous Control. Well 3A 12 Val: Positive. Well 3G Others, … HRM Snapshot Etc,.. KRAS and CRC In practice, tests to be performed within 3 to 5 working days In practice Who is paying for testing? How much does it cost? NHS Merck Serono Very cheap! When to start on the testing? Who can do the testing? Perspective Only a proportion of patients with wild-type KRAS respond to anti EGFR monoclonal antibody A more advanced assessment of tumour cells may become justified in the near future ?More codons of KRAS (61 and 146) ?BRAF, PIK3CA, pTEN, etc,.. Need for platforms, kits, etc,..for cheap and quick multiple screening


![Evaluating my own performance [Toolkit]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/005903020_1-474985eeb46266732dcf984d4f4c9a09-300x300.png)