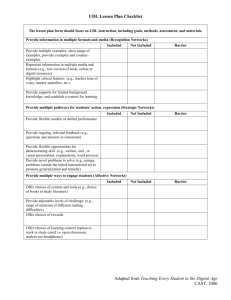
File
advertisement

CSIT 120 DIVERSITY NOTES Diversity- refers to all the ways in which people are different. This includes individual, group, and cultural differences. Cultural landscape- referring to the different lifestyles, traditions, and perspectives that can be found in the US and throughout the world. Also for example: we have a lot of immigration, different languages, and religion, workplace. Included in work place jobs now are translators, flexible work schedules for mother and fathers with children. Work/life policies, including paid and unpaid time, dependents care, flextime, and telecommuting are becoming huge considerations for men and woman work flexibility. Millennials are people born from 1980 to 2000. They are not uniformed about technology. Globalization – the growing interdependence of people and cultures has accerlated in the twenty first century. Globalization impacts all individuals. Technological advances have transformed our social world into what Marshall Mcluhan termed a global village. No such thing as an “American Job” in a flat world, factors such as immigration contribute to this. Cultural cruise control- acting as though our own values, beliefs and experiences are universal. DIVERSITY MYTHS: 1) diversity= woman+minorities….no diversity includes everyone. 2) Diversity is a new phenomenon….no there has always been diversity but now it has been receiving more attention. 3) Diversity= Deficiency…..this is a myth based on the premise that diversity results in standards being lowered. Today, professionals increasingly view diversity as a resource rather than a deficit. 4) Diversity= Divisiveness….being exposed to diversity can bring people together. 5) Diversity is to be feared……..how we approach diversity can make all the difference. If we approach it with a sense of humility and a sincere desire to learn more about others and ourselves, it will not be something to be feared or avoid. Diversity Skills : Flexible Thinking, Communication, Teamwork, Leadership, And social networking and the ability to overcome social and personal barriers. Diversity Consciousness- it is the awareness, understanding, skills that allow us to think through and value human differences. DEVELOPING OUR DIVERSITY CONSCIOUSNESS can help us become successful at school for example, learning styles, appreciating your heritage, ability to deal effectively with barriers, to balance “fitting in” and “being yourself” IT CAN bring success at work for example, interpersonal skills, teamwork skills, cultural awareness and understanding, self-education skills. Blended learning- the integration of online and traditional face to face approaches of learning. Cultural Competence- refers to a set of attitudes and skills that make it possible for organizations and staff not only to acknowledge cultural differences but incorporate these differences in working with people from various cultures. Personal barriers- refer to those individual factors that get in the way of our success. Social barriers- focus more on society, they refer to those factors that are external to the person and impede her or his success. Among these barriers are the perceptions, thoughts, and actions of others. BARRIER 1) Perceptions- refer to the way in which we receive and interpret information from any of our senses. Selective Perception- perceive what we want to perceive, focusing on those things that support our thinking and ignore information in neat, simple categories. BARRIER 2) Ethnocentrism- refers to the assumption that our way of thinking and acting is naturally superior to any other. BARRIER 3) Stereotypes- an unverified and oversimplified generalization about an entire group of people. BARRIER 4) Prejudice- an irrational and inflexible opinion formed on the basis of limited and insufficient knowledge. For example, xenophobiapeoples unreasonable fear of foreigners. (Prejudice affects you in becoming a source of distraction, resulting in resentment and in fear, impact one’s health) BARRIER 5) Prejudice plus power. Power- refers to the ability to influence others and bring about change. For example, institutional racism- that is built into the customs =, norms, and practices of social institutions. BARRIER 6) Discrimination- the denial of equal rights and opportunities to individuals and groups. Synergy- The concept that members of a team interacting cooperatively will accomplish much more than if they act alone. Developing teamwork skills: 1) Communication 2) Conflict management 3)Empathy 4) self-evaluation 5) Leadership. Also Make sure you understand your role and teams goals, respect ideas and feelings of others, Manage conflict effectively, Continue to build relations with other team members, think and act like a team, Decenter ad recenter, Avoid groupthink, be flexible, Periodically assess the teams performance. Digital natives- younger people born or raised during the age of digital technologies. Digital immigrants- people who were not born into the digital world but learned the language and the new technology later in life. Echo chamber- a situation in which like minded members of online communities echo our opinions and beliefs back to us. Microaggresions- daily insults or indignities that demean and stigmatize people who are perceieved as different, can migrate from real life to virtual life, and the affect of online microaggresions mirrors what takes place offline. OBSTACLES TO TEAMWORK: 1) Social Values 2) Sterotypes 3) Unequal distribution of power 3) Disagreement over the roles of team members or the teams mission 4) Disagreement over the roles o team members or the teams mission 5) Unequal treatment 6) Unequal treatment or perception of unequal treatment 7) Miscommuincation 8) Lack of trust Leadership- the process by which people inspire, influence, and empower others to achieve a common goal. Orpheus process- a process in which the sharing of leadership allows everybody to work together and maximize their expertise and creativity. Diversity- conscious leadership- the process by which people influence and empower others by recognizing, understanding, and adjusting to diversity in all its forms. MYTHS ABOUT A DIVERSITY CONSCIOUS LEADER: 1) THEIR “PEOPLE PERSONS” Reality is there is nothing natural about the ability to relate to others effectively. People develop and improve their competencies in this area. 2) TO BE THIS LEADER ITS AN EXTREME RARE ABILITY. Reality is everyone has the potential to be a diversity conscious leader. 3) THEY ARE INTELLECTUAL BRILLIANT. Reality is brilliance is not a precondition for diversity consiouness. People with “average” capacities can be this leader. 4) THESE LEADERS ARE CHARISMATIC EXTROVERTS. Reality is some are but many are not. 5) THIS LEADER MUST BE ABLE TO PERSUADE AND CONTROL PEOPLE IN SPITE OF THEIR DIFFERENCES. Reality is its not about the exercise of power as the empowerment of others. Instrumental leaders—tend to focus more on the task at hand ad less on how the group members get along. Expressive leaders- primary concern is the well being of group members and their ability to work as a unit. LEADERSHIP STYLES – REFER TO THE WAY WE INFLUENCE OTHERS. For example, authoritarian leaders- make all or most of the decisions and keep power to themselves. Democratic leaders- share power and encourage people discussion and decision making. Laissez faire leaders- minimally involve themselves in decision making and encourage group members to make their own decisions. Indiviualism – reinforces people’s reliance on self, and encourages a greater concern with one’s own interests. For example, AUSTRAILIA, NEITHERLANDS, US, GREAT BRITAIN. Collectivism- reinforces a greater reliance on the group and a greater concern for the welfare of all concerned. For example, SINGAPORE, JAPAN, PAKISTAN, COLOMBIA. Inclusion- refers to the process of promoting a sense of belonging and empowerment by involving everyone and valuing their unique talents and contributuions. Inclusive workplace- an environment that welcomes and utilizes diversity at all levels. Generation X born between 1965-1980 to be more open to interacial marriage, gay couples raising children, non traditional family agreements. Cohort effect- refers to the unique historical experiences that can shape and mold a generations thinking and behaviors. Millienials, the largest generation in the history of the US. Period effect- major, life altering events like wars, natural disaters, social movements, and techonological advancesthhat impact all generations but some more than others. Baby boomers born 1946-1964 Silent generation born 1928-1945 and greatest generation born prior to 1928. Life cycle effect- the transformation of an age cohorts behaviors and attitudes over time due to changes in the roles people play and their biological maturation.