Money and Banking
advertisement

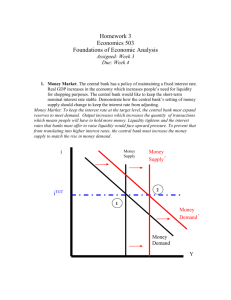
The Money Market and the Loanable Funds Market 1 The Demand for Money People are face with the decision to hold their wealth as money OR as interest bearing assets. Opportunity Cost of holding money? Forgone interest! 3 types of money demand (motives for holding money): 1. Transactions: To make purchases of goods and services 2. Precautionary: To serve as protection against an unexpected need 3. Speculative: To serve as a store of wealth (money for investment purposes) The Demand for money shows an inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money demanded 1. What happens to the quantity demanded of money when interest rates increase? Quantity demanded falls because individuals would prefer to have interest earning assets instead 2. What happens to the quantity demanded when interest rates decrease? Quantity demanded increases. There is no incentive to convert cash into interest earning assets 2 The Demand for Money Inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money demanded Nominal Interest Rate 20% 5% 2% DMoney 0 Quantity of Money (billions of dollars) 3 The Demand for Money What happens if price level increase? Money Demand Shifters 1. Changes in price level Nominal & real GDP Interest Rate 2. Changes in income 20% 3. Changes in taxation that affects investment 5% 2% 0 DMoney1 DMoney Quantity of Money (billions of dollars) 4 The Supply for Money The U.S. Money Supply is set by the Federal Reserve System (FED) Interest Rate (ir) 20% The FED is a nonpartisan government office that sets and adjusts the money supply to adjust the economy 5% This is called Monetary Policy. 2% SMoney DMoney 200 Quantity of Money (billions of dollars) 5 Increasing the Money Supply Interest Rate (ir) SM SM1 10% 5% If the FED increases the money supply, a temporary surplus of money will occur at 5% interest. The surplus will cause the interest rate to fall to 2% 2% DM 200 Increase money supply 250 How does this affect AD? Quantity of Money (billions of dollars) Decreases interest rate6 Increases investment Increases AD Decreasing the Money Supply Interest Rate (ir) SM1 SM 10% 5% 2% If the FED decreases the money supply, a temporary shortage of money will occur at 5% interest. The shortage will cause the interest rate to rise to 10% How does this affect AD? D M 150 Decrease money supply 200 Quantity of Money (billions of dollars) Increase interest rate Decrease Decrease AD investment 7 Loanable Funds Market Q: Is an interest rate of 50% good or bad? A: Bad for borrowers but good for lenders The loanable funds market brings together those who demand funds to borrow (Dlf) with those who want to lend by supplying funds (Slf) 4 Groups Demand and Supply Loanable Funds: 1. Consumers 2. Government 3. Foreigners 4. Businesses Demand- Inverse relationship between real interest rate and quantity loans demanded (negative slope)- more loans demanded at lower interest rates. Supply- Direct relationship between real interest rate and quantity loans supplied (positive slope) 9 Loanable Funds Market At the equilibrium real interest rate the amount borrowers want to borrow equals the amount lenders want to lend. Real Interest Rate SLenders re DBorrowers QLoans Quantity of Loans 10 Loanable Funds Market Demand Shifters 1. Confident businesses 2. Changes in government borrowing/spending 3. Consumer concerns about future 4. Rising incomes Supply Shifters 1. Government reduces interest tax rate on interest income 2. Other actions by the FED… 11