The Laws of Chemistry
advertisement

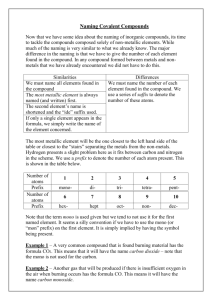
The Laws of Chemistry Dalton's Atomic Theory A. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of the same element are alike, and atoms of different elements are different B. The separation of atoms and the union of atoms occur in chemical reactions. In these reactions, no atom is created or distroyed, and no atom of one element is converted into an atom of another element C. A chemical compound is the result of the combination of atoms of two or more elements in a simple numerical ratio 1. Law of conservation of mass states that there is no detectable change in mass during the course of a chemical reaction e.g. AgNO3 + KI AgI + KNO3 170 g 166 g 235 g 336 g 101 g 336 g 2. Law of definite proportions states that a pure compound always contains the same elements in a fixed ratio e.g. Copper (II) oxide 1 g copper 0.252 g oxygen 3. Law of multiple proportions states that when two elements form more than one compound the amounts of one element that are combined with a fixed amount of the other element are in a small whole - number ratio Name oxygen g % Ratio nitrogen oxygen 1g nitrogen Dinitrogen oxide 63.7 36.3 0.57 1 Nitrogen oxide 46.7 53.3 1.14 2 Dinitrogen trioxide 36.8 63.2 1.71 3 Nitrogen dioxide 30.4 69.6 2.28 4 Dinitrogen pentoxide 25.9 74.1 2.85 5 4. Gay - Lussac's law of combining volums states that the volums of gases the are used or produced in a chemical reaction can be expressed in ratios of small whole numbers (const. temp. and p.) e.g. 1 volume hydrogen + 1 volume chlorine 2 volumes hydrogen chloride H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2HCl (g) The law is applicable only to gases! 5. Avogadro's principle (law) equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules








![Stabilization of highly polarized PbTiO[subscript 3]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012147479_1-fb25e6bbe22ad8dfb980a33940e3bbbe-300x300.png)