MobileAware W3C Presentation
advertisement

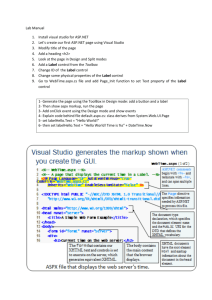
MobileAware XHTML will unify multi-device authoring Visual Authoring Tools will evolve to become the main interface for multi-device content creation Co Authors: Dr. Rotan Hanrahan Eamonn Howe MobileAware http://ww.mobileaware.com Contents Markup Evolution HTML WML Convergence Industry Need Author once – delivery to multiple end-devices Case Study – Operator MobileAware Approach Extending XHTML to support multi-channel – Web, Wap,PDA Example – structure, navigation Example – pagination, hierarchical, sequential Lessons learned Requirements on W3C Enable the vision The authoring challenge Conclusion © MobileAware 2003 Slide 2 Markup Evolution HTML – Web Browser Markup – An Evolution HTML Evolution Simplicity Standards capture best-practices Evolve but support legacy Authoring tools evolve at same pace However Time HTML markup evolved with incremental enhancements that enabled new features while still supporting the existing authoring community and existing browsers. © MobileAware 2003 Orignal HTML structure compromised with addition of in-line style Not such a bad idea in a world dominated by the PC Browser Supported by authoring tools that continue to encourage authors to add specific adaptation information to HTML mark-up Slide 4 WML - Mobile markup - A revolution Markup languages for mobile devices are revolutionary offerings TTML – HDML -WML Imode Web Clipping Often new features exclude legacy New WML features appeared without concern for legacy content, legacy devices or legacy content creation tools/skills Even Worse Proprietary “enhancements” became common • Example - Openwave ‘localsrc’ attribute • Ericssson R380 suppoort for HTML ‘table’ tag Mobile authoring tools & emulators stuggle keep up Mobile content creators are still in the dark ages of markup generation, despite often being constrained by the necessity of well-formedness as required by XML Often vendor specific markup tools offer the best supportfor their device offerings Image: Nokia Time Mobile markup has advanced in revolutionary steps, adding and altering features without much concern for the existing authoring or user community © MobileAware 2003 Slide 5 Convergence – web and mobile world XHTML is adopted for fixed and mobile XHTML is an evolution of HTML Building on years of mark-up experience Roots in PC world Return to mark-up as structure XHTML 2 CSS 3 Abstract TODAY WML was a revolutionary approach HTML 1 New form factor = new mark-up With OMA adoption of XHTML Mobile Profile we are seeing a convergence back to XHTML XHTML MP CSS 2 HTML 2-3 WML 1.1 In a multi-channel world Content creator still has duplicate authoring tools on desktop Example (Dreamweaver, Nokia Mobile Internet Toolkit) HTML 4 Style WML 2.X XHTML 1 The XML Revolution Concrete Ill-Formed Well-Formed None XHTML 2.x WAP 2.0 is a step in the right direction Content Maintanance WML 1.x Content Skills Maintenance But you still cannot create content in XHTML 1.1 that can be rendered to a WAP device Without excluding unsupported constructs Without including device specific structure, navigation If one version of XHTML could be used (in conjunction with style) for web and mobile, the cost saving would be huge Duplication © MobileAware 2003 XHTML 1. CSS 2 Slide 6 Industry Need – more mobile content services Mobile Internet Growth Mobile will outstrip the PC Mobile handsets are coming prepackaged with mobile browsers The majority now support XHTML Mobile Profile This is the biggest driver of XHTML adoption 1200 1000 800 Mobile Internet Users (millions) NTT DoCoMo Mobile Portal 307 million page hits per day (Aug. 2002) Thousands of signed up content providers Its not m-banking, m-stocks but consumer applications All are written specifically for the Imode paradigm Not auto-transferabble to other mobile portals © MobileAware 2003 600 400 200 1996 1998 2000 Year Mobile Subscribers Worldwide Web Enabled Handsets PC’s with Web Browser Slide 8 2002 2004 The content creation requirement Content providers need to be able to created device and context independent content Content provders will want to supply content to many mobile portals Focus is on creativity and fast service creation Operator Portal Needs to be simple to create Needs to be created once Needs to be device indepenent Needs to be end-use context independent Delivery Context A News Animation Images Video Games Device Independent Content Media/Content Company Operator Portal Content needs to be mapped to a mark-up rich enough to be interpreted by device/channel/context specific scenarios © MobileAware 2003 Delivery Context B Slide 9 Mobile Browsing – Latent demand is there Phase 1 of mobile Internet B/W handsets Proprietary WML content Poor content optimisation Poor access times Walled garden portals the norm GPRS usage No. of optimised web sites Phase 2 – now Colour handsets Open XHTML Mobile Porfile content GPRS access Phase 3 – future No. of colour devices Access to any web site supporting multi-device XHTML Context specific CSS to provide base device adaptation Case study European operator moved from walled garden to open garden portal Initial launch succeeded multiplying GRPS revenue by 10+ times Key characteristics of service • Simple 2 step navigation to service • Attractive colour device • GPRS • Optimised web sites © MobileAware 2003 Slide 10 MobileAware Approach (to multi-device mark-up) Extending XHTML to support multi-channel – ‘Author once’ Key issues to address – MobileAware experience Structure Make structure explicit Enables application of navigation • Hierarchical for mobile devices • Sequential for PDAs Enables condition/explicit content inclusion/exclusion Pagination of content/forms Automatic pagination Author controlled pagination Tables Table row/column re-shaping for different screen sizes Content inclusion/formatting Media object inclusion Media object selection/adaptation © MobileAware 2003 Slide 12 Adopted approach Extend XHTML 1.1 Define a range of new tags and tag attributes to address multi-channel requirement Author uses XHTML to create content and applies additional tags to make content multi-channel capable Provide a server side adaptation solution that translates XHTML+ to end-device format ‘Author once ‘ paradigm is satisfied HTML Adaptation Server WML Re-purpose content (channel, device) MobileAware has extended a widely used authoring tool Dreamweaver MX - by providing drop-down windows to XHTML+ documents, that speeds mobilisation and reduces author errors Result - Author can create multi-channel content in a familiar web environment iMode XHTML+ VoXML XHTML Mobile Profile Authoring Delivery Context © MobileAware 2003 Slide 13 Structure – enabling content navigation Approach relies on the use of additional mmXHTML tags – ‘group’ and ‘structure’ Applying an explicit structure enables server-side adaptation agent to apply different device navigational structures Hierarchical menu structure for WAP devices Sequenctial structure for PDAs By using an environment like Dreamweaver these tags can be autogenerated by the author The process involves the author selecting content for inclusion on a mobile device This gets wrapped in a group tag The group tags are marshalled by the structure tag which has a configurable suite of parameters Adaptation Process XHTML (with structure tags) WML Authoring Environment (Select content for display on Mobile Device) Result XHTML ….. <group id = a> <p>Paragraph One</p> </group> <group id = b> <p>Paragraph Two</p> </group> <stucture> <group id = a disply=all> <group id = b disply=heading> </structure> …… End-user Device Resolve structure tags © MobileAware 2003 Slide 14 Pagination for small devices For devices with small screen sizes pagination of display content makes sense How is this best achieved with XHTML? Automatic Pagination Based on heurisitics in server-side adaptation • Avoid splitting words • Avoid splitting elements No authoring mark-up input Author Controlled Pagination Explicit break - Page-break avoid Implicit or suggested break • A combination of XHTML (in this case using ‘style’ attribute) combined with a heuristic set of rules for XHTML processing generates the desired result • Use of ‘suggestion’ moves in the direction of abstraction enabling the definition of content in a device independent way Pagination Heuristics Page breaks to be avoided inside elements such as tables, paragraphs Authoring Environment (Grab paragraph – add suggested pagebreak) Result XHTML ….. Adaptation Process WML XHTML (with pagination hints) <p style=“page-break-before: suggested”> Paragraph One </p> <p style=“page-breakinside:avoid”> Paragraph is long…. </p> …… End-user Device Resolve pagination rules, XHTML content, device screen size © MobileAware 2003 Slide 15 Content Inclusion Combining an explicit include/exclude tag with a conditional ‘where’ attribute <include where “DeviceClass=PDA”> <p>Paragraph a….</p> </include> Include/exclude is acted upon by server-side adaptation engine by evaluation of ‘where’ Boolean – true/false Typically the condition evaluates the state of a number of known parameters of the device such as: Device name Device classification Screen size Media-object tag to enable conditional selection of the correct media type: Image, video etc., depending on the device type <media-object where “DeviceClass=PDA”> src=“image.gif”, “image.jpeg”, “image.mpeg” </media-object> © MobileAware 2003 Slide 16 Lessons Learned Explicit addition of new tags and tag attributes to XHTML works well in enabling content for web, mobile and PDA The solution is viable and cost effiective Author-once paradigm is achieved The learning curve is low for existing HTML/XHTML developers Explicit targeting of content for device classes or individual devices is possible Well-formed nature of XHTML makes it easy to enhance author tools to support extensions Limitations Not an industry standard approach Requires use of MobileAware adaptation engine Does not provide full abstraction of source from delivery context Use of ‘where’ attribute puts onus on author to define content inclusion based on known end-user device types General Issues Mark-up vs Style – where should multi-channel structure lie? Content authors in general will want to maximise differentiation by leveraging latest browser capabilities and technologies – flash, javascript, wmlscript etc Their effective combination with mark-up in rich media sites is a growing trend © MobileAware 2003 Slide 17 Standards approach using XHTML Structure/Navigation XHTML 2.0 (and related standards) provide a range of possibiites for substituting this functionality • Use of ‘nl’ element to create a navigation structure • Extend role of CSS and CSS media queries to alter device naviagation Pagination A more abstracted concept required in XHTML Possibly working in combination with delivery context heuristics Explicit include/exclude ‘Object’ element in XHTML 2.0 could form basis of solution for conditional media selection Combined with use of ‘embedding’ attribute collection within elements • For example its use within an <img> element to generate the user-agent accept header is a viable abstraction approach – switches onus to adaptation engine Possible use of ‘class’ selection attribute in conjunction with CSS for determining if to include content on client device Possible new elements like ‘strong’ to indicate a components importance for inclusion © MobileAware 2003 Slide 18 Requirements on W3C Enable the vision Creativity Author Once Syndication/Aggregation/ Delivery/Adaptation Create Device Independent Content Generate Device Independent Mark-up Delivery Context User Context Application Context Aggregate Application Server supporting MVC F/W Context Aware Device Independent Mark-up Intermediate server or device Process Media Server Content Aware Device Specific Content End-user Device © MobileAware 2003 Slide 20 Author abstraction and decoupling Mark-up Animation Video Image Display Sequence Client Script Audio Author Possible Roles Creates Media Assets Author GUI Environment Content Style Template Image Picture GUI Application (Acrobat/Word) Defines relationship between media assets (structure, layout etc) Create Preview Creative Process GUI Application enbles multimedia document creation Enables preview on different form-factors Enables rule setting for behaviour on different form factors Target Content (Device Independent) Emulate Software Process XHTML/ SMIL Maps target content to concrete display form Server Process Logic UaProf Target Device HTML/ WML Client Process Logic PostScript macros Captures presentation rules PostScript Processor PostScript Processor Printer Display Client Web authoring will evolve as document authoring has Document editors today enable the author to focus on document content and author structure intent – hiding the underlying macro language This is the result of 2 decades of evolution In the same manner web authoring will evolve to enable the author focus on content creativity and structural intent In addition some web authors will want to combine many different media types in rich media offerings that combine content, Flash, Audio and Video all in the one display. To the author using a GUI environment these may become seamless to integrate together. An early example of this is the availability of MMS creation tools. Underling markup must be rich enough to capture all this author intent generated from a GUI front-end and abstracted enough so that the content can be created once but be rendered to a concrete end-user display, either by the device itself or by an intermediate process. © MobileAware 2003 Slide 21 Focus now XHTML is the enabler It has momentum with the adoption of XHTML Mobile Profile by the mobile community XHTML 2.0 is a step in the right direction Further evoluton towards full device independence is key DIWG has identified a number of deficiencies in proposed XHTML 2.0 elements Addition of missing features is also key • Pagination support • Softkey support • Other Potentials • Importance: do we need to display all content on all devices • Proximity: should certain pieces of content be diplayed together on the same page There are likely to be in the near term Content authors used to HTML that will continue to work with markup A new breed of content developers creating rich-media content who may rely more on GUI environments to generate underlying mark-up Increased modularisation of XHTML with focus on structure will move them in the directon of consolidating media from disparate sources, e.g. generic e-commerce forms, product flash demos However they will be supported by Authoring environment developers ASP/JSP programmers Portal framework builders For these intimate knowledge of XHTML will be a requirement Standards experts XHTML does not yet deliver for multi-channel But it is moving in the right direction Focussing on structure, enabling abstraction Do not be afraid to add complexity to achieve the vision If you work with mark-up some additional complexity is cheaper than costs associated with duplication of content source If you work with graphical authoring tools additional complexity will be hidden from the content creator © MobileAware 2003 Slide 22 Role of Authoring Tool – growing in importance There will be a gradual shift of focus towards the authoring tool as the primary means of expressing content Enable author expression The tool captures what the author creates. This includes the “text” and it’s structure and the relationships within the content This should be mapped to actual mark-up Seamless Integration Creation, selection and addition of other media objects should be seamless Flash animation, images, XForms Media sequencing will be as important as site navigation Identify context sensitive constraints The tool should recognise certain properties of the authored content and detect when these may be affected by delivery constraints. For example, a long unbroken block of text may require pagination guides, which could (upon request) be provided by the author, or could be implied by an author’s profile (known by the authoring tool). Capture author decisions and preferences Configure authors profile within authoring tool Provide feedback An authoring tool should be able to assess the content being authored, so that it can (for example) indicate the accessibility of the content or identify specific problems that might be encountered by target devices © MobileAware 2003 Slide 23 Conclusion Mobile Internet is poised for real growth Mobile content will be delivered using XHTML in conjunction with other media formats This is a real apportunity to speed broader XHTML adoption An increase in the amount of abstraction within XHTML content will enable multi-device delivery Fast content creation will be key Content will not just be about markup – authoring tool will enable creation of full multi-media content – Video, Audio, Flash, XHTML, Xform Authoring tool will play a role as previewer and delivery context simulator A whole new generation of content creators will rely on the authoring tool and not the underlying mark-up The W3C and all who support the Web must address this audience Finally - Get involved in shaping Device Independence! http://lists.w3.org/Archives/Public/ © MobileAware 2003 Slide 24