Byzantine Empire - Walsingham Academy

History of the Ancient and
Medieval World
The Byzantine Empire
Walsingham Academy
Mrs. McArthur
Room 111
“Heirs” to Rome
What emerged from the Roman Empire?
1. Byzantine Empire (East Rome, Greeks)
2. Islam
3. Germanic Kingdoms
I. Plot 8 of 9 elements on map
• Bosporus
• Constantinople
• Asia Minor
• Jerusalem
• Dardanelles
• Aegean Sea
• Black Sea
• Balkan peninsula
• Rome
II. Identify and explain the importance of the heavy black line on map.
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe
Section 1: The Byzantine Empire
Witness History Audio: A Sovereign City
Constantine Creates a “New Rome”
Roman emperor Constantine rebuilt Byzantium, a trading port on the Bosporus strait, and named it Constantinople. It became the “New Rome” and its empire was the Byzantine Empire. This civilization blended ancient Greek, Roman, and
Christian influences with other Mediterranean traditions.
Color Transparency 52: Byzantine Art
Witness History Video: The Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe
Section 1: The Byzantine Empire
Byzantium Flourishes Under Justinian
Under emperor Justinian, the Byzantine empire reached its peak and included North Africa, Italy, and the southern Iberian peninsula.
Constantinople was rebuilt after a fire and became a grand city, with its jewel being the church of Hagia Sophia. Justinian also revised and organized the laws of ancient Rome into Justinian’s Code, which he used to unify the empire. Byzantium’s economy and military grew to be among the strongest in the world.
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe
Section 1: The Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Christianity
Byzantine Christians rejected the pope’s authority and clergy had the right to marry. Greek became the language of the Church and the main holy day was
Easter. In the 700s, a Byzantine emperor outlawed the worshiping of icons. That and other controversies caused a split between eastern and western Christianity.
Color Transparency 53: Byzantine Icon
Color Transparency 51: Major Religions, About 1300
Geography Interactive: Byzantine Empire to 1000
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe
Section 1: The Byzantine Empire
The Empire Suffers Crisis and Collapse
When local lords gained more power within the empire, its enemies saw weakness. Whole regions were conquered. The First Crusade was an effort to defeat the Seljuk Turks who had closed access to Jerusalem. Later Western crusades also turned on Constantinople. The Ottomans finally took the city and renamed it Istanbul.
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe
Section 1: The Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Heritage
For 1,000 years Byzantine culture had brought together Christian religious beliefs with Greek science, philosophy, arts, and literature. Byzantine art, such as the mosaics of biblical scenes, influenced later Western styles.
Color Transparency 54: Rise and Decline of the Byzantine
QuickTake Section Quiz
Progress Monitoring Transparency
Color Transparency 52: Byzantine Art
Note Taking Transparency 84
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe: Section 1
Color Transparency 53: Byzantine Icon
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe: Section 1
Color Transparency 51: Major Religions, About 1300
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe: Section 1
Color Transparency 54: Rise and Decline of the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe: Section 1
Progress Monitoring Transparency (1 of 2)
The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe: Section 1
Progress Monitoring Transparency (2 of 2)
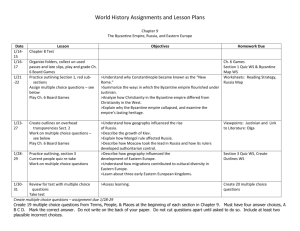
Assignment 1
(due 1/3)
1. Complete map
2. Read text, pp. 282, 283, 285.
3. Take notes following directions and sample, bottom of pp 282, Note Taking.
4. Identify terms: Constantinople, Justinian,
Theodora, Justinian’s Code, autocrat
Jan. 2-4: Check SCA on SPA and report any discrepancies: Last Chance before finalizing Term 2 grades!
Jan. 4-8: Homework Exam Study Period
Jan. 7-8: In-Class Review Time
Jan. 9: Semester Exam
Assignment 2
(due 1/4)
1. Read pp. 284, and sections: Byzantine
Christianity and The Empire Suffers Crisis and
Collapse , pp. 285-287 of your text.
2. Identify terms: patriarch, icon, Great Schism
3. Complete Note Taking Chart
4. Map Skills: pp 286
Jan. 2-4: Check SCA on SPA and report any discrepancies: : Last Chance before finalizing Term 2 grades!
Jan. 4-8: Homework Exam Study Period
Jan. 7-8: In-Class Review Time
Jan. 9: Semester Exam
In Summary:
Contemporary Testimony
Location, Location, Location: An asset becomes a liability
Read Sozeman’s account of “The City,” pp 283.
1.
From what you’ve learned what difference did location make?
2. How does he describe the city?
3. How could such a location become a liability in the later period?
Justinian Reforms Roman Law
Why is this one of Byzantium’s most important legacies?
1. How did the Byzantine Empire get its name?
2. How did Constantinople get its name?
3. What 5 things protected the city?
4. What was Greek Fire?
5. What church strengthened the empire and how?
6. Explain two factors that divided the Churches of
Rome and Constantinople
7. Name the title of the major leaders of each church.
8. Who was Justinian?
9. Explain why Justinian is remembered as the greatest
Byzantine emperor.
Question 1
Explain what is meant when the term byzantine is applied to politics ?
What is the historical origin of this meaning?
Question 2
In what ways did geography promote the success of Constantinople?
Question 3
Why is Justinian considered to be the
Byzantine Empire’s most important emperor? What were his short-term and long-term accomplishments?