Chapter 1: Creating Competitive Advantages
advertisement

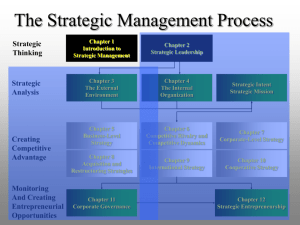
Chapter 1: Creating Competitive Advantages MNGT 4800 Dr. Shook Agenda Strategic management defined Strategic management process Schools of thought Corporate governance and stakeholder management Environmental forces creating change Hierarchy of strategic goals Two Perspectives of Leadership Strategic Choice Perspective (Romantic view) Leader is the key force in organization’s success Population Ecology (External control perspective) Focus is on external factors that affect an organization’s success Two Perspectives of Leadership Leaders can make a difference Must be aware of opportunities and threats faced in external environment Must have thorough understanding of the firm’s resources and capabilities Strategic Management Definition: Strategic management consists of the analysis, decisions, and actions an organization undertakes in order to create and sustain competitive advantages. Key attributes of strategic management Directs the organization toward overall goals and objectives. Includes multiple stakeholders in decision making Needs to incorporate short-term and long-term perspectives Recognizes trade-offs between efficiency and effectiveness Strategic Management Analysis (Chs. 1, 2, 3, and 4) Strategic decisions (Chs 5, 6, 7, and 8) Strategic goals (vision, mission, strategic objectives) Internal and external environment of the firm In which industry(ies) should we compete? How should we compete in those industries? Actions (Chs 9, and 10) Allocate necessary resources Design the organization to bring intended strategies to reality Strategic Management Strategic management is the study of why some firms outperform others How to compete in order to create competitive advantages in the marketplace How to create competitive advantages in the market place Unique and valuable Difficult for competitors to copy or substitute Strategic Intentions Intended Strategy Deliberate Strategy Unrealized Strategy Emergent Strategy Realized Strategy Two Foundational Schools of Thought 1 Industrial Organization Model 2 Resource-Based Model I/O Model of Superior Returns – Assumptions: The external environment imposes constraints that determine the strategies that can result in superior profitability. Competing firms control similar resources and pursue similar strategies Resources utilized by firms are highly mobile thus homogeneous I/O Model of Superior Returns The Industrial Organization Model suggests that above-average returns for any firm are largely determined by characteristics outside the firm. I/O Model of Superior Returns The Industrial Organization Model suggests that above-average returns for any firm are largely determined by characteristics outside the firm. The I/O model largely focuses on industry structure or attractiveness of the external environment rather than internal characteristics of the firm. Resource-Based Model of Superior Returns –Assumptions: Firms acquire different resources over time Resources heterogeneity within a particular industry Resources may not be highly mobile across firms Difference in resources and how they are used form the basis of competitive advantage Resource-Based Model of Superior Returns The Resource-Based Model suggests that above-average returns for any firm are largely determined by characteristics inside the firm. Resource-Based Model of Superior Returns The Resource-Based Model suggests that above-average returns for any firm are largely determined by characteristics inside the firm. The Resource-Based view focuses on developing or obtaining valuable resources and capabilities which are difficult or impossible for rivals to imitate. Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management Corporate governance: the relationship among various participants in determining the direction and performance of corporations Shareholders Management (led by the CEO) Board of directors Corporate Governance and Stakeholder Management Board of directors Elected representatives of the owners Ensure interests and motives of management are aligned with those of the owners Effective and engaged board of directors Shareholder activism Proper managerial rewards and incentives Exhibit 1.4 The Key Elements of Corporate Governance Stakeholder Management Two views of stakeholder management Zero sum Stakeholders compete for attention and resources of the organization Gain of one is a loss to the other Symbiosis Stakeholders are dependent upon each other Mutual benefits Social Responsibility Social responsibility: the expectation that businesses or individuals will strive to improve the overall welfare of society Managers must take active steps to make society better Socially responsible behavior changes over time Triple bottom line Four Additional Types of Capital In addition to financial capital Type of Capital Description Ecological Renewable resources generated by living systems, such as wood or animal by-products Nonrenewable or geological resources such as mineral ores and fossil fuels People’s knowledge, skills, health, nutrition, safety, security, and motivation Assets of civil society, such as social cohesion, trust, reciprocity, equity, and other values that provide mutual benefit Material Human Social Strategic Management Perspective Integrative view of the organization Assess how functional areas and activities “fit together” to achieve goals and objectives All managers and employees must take and integrative, strategic perspective of issues facing the organization Strategic Management Perspective Key driving forces increasing the need for strategic perspective and involvement Globalization Technology Intellectual capital These forces are Interrelated Accelerating the rate of change and uncertainty Coherence in Strategic Direction Company vision Massively inspiring Overarching Long-term Driven by and evokes passion Fundamental statement of the organization’s Values Aspiration Goals Company vision Hierarchy of Goals Coherence in Strategic Direction Mission statements Purpose of the company Basis of competition and competitive advantages More specific than vision Focused on the means by which the firm will compete Company vision Mission statements Hierarchy of Goals Coherence in Strategic Direction Strategic objectives Operationalize the mission statement Provide guidance on how the organization can fulfill or move toward the “higher goals” More specific Cover a more welldefined time frame Company vision Mission statements Strategic objectives Hierarchy of Goals Coherence in Strategic Direction Strategic objectives Measurable Specific Appropriate Realistic Timely Challenging Resolve conflicts that arise Yardstick for rewards and incentives Company vision Mission statements Strategic objectives Hierarchy of Goals