Strategic Management - Tennessee Tech Blogs
advertisement

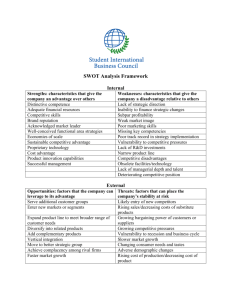
STRATEGIC THINKING Chapter 1 STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Definition The process through which organizations analyze and learn from their internal and external environments, establish strategic direction, create strategies that are intended to help achieve established goals, and execute those strategies, all in an effort to satisfy key organizational stakeholders External and Internal Environmental Analysis Strategic Direction Strategy Formulation Strategy Implementation and Control Strategic Restructuring The Broad Environment Sociocultural Forces The Task Environment Competitors Unions Suppliers Economic Forces Technological Forces Gov’t agencies Customers The Organization Owners & Directors Managers Employees Financial Intermediaries Local Communities Activist Groups Political/Legal Forces Internal Analysis External Analysis Strengths Opportunities Weaknesses Threats SWOT ANALYSIS Strengths Opportunities Weaknesses Threats APPROACHES TO STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Situation Analysis • Analyze the internal and external environments, develop a SWOT analysis, and derive mission, goals and strategy Environmental Determinism • Determine the best strategy that best fits environmental forces and work to carry it out Principle of Enactment • Create your own environment; do not wait for external forces to dictate your strategy Deliberate/Emergent Strategy • Strategies are intended courses of action but can also emerge from a stream of decisions Resource-based View • Acquire and manage resources to achieve sustainable competitive advantage Stakeholder Management • Develop mutually beneficial relationships and alliances with external stakeholders What does it take to have a successful company strategy? Situation Analysis Stakeholder Management Environmental Determinism Strategic Thinking Resourcebased View Principle of Enactment Deliberate / Emergent Strategy STRATEGIC THINKING: CHARACTERISTICS Intent Focused Long-Term Oriented Consideration of Past and Present Systems Perspective Ability to Seize Opportunities Scientific Approach