Pneumonia - WordPress.com
advertisement
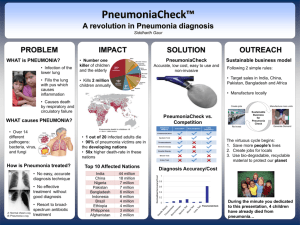
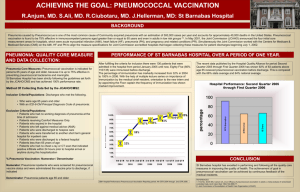
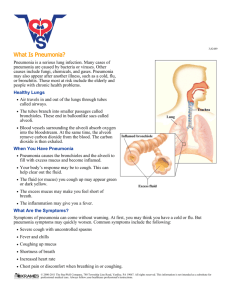
Visibility of Vaccination and How Do We Improve? What is Pneumonia? Pneumonia is an infection of the lower respiratory tract or alveoli Pneumonia is the most common infectious cause of death in children and adults. The most common causative agent in adult pneumonia is streptococcus pneumoniae How Much Does Pneumonia Cost? Mortality rate of 30-40% A study among Medicare patients showed healthcare costs the year after a pneumonia hospitalization to be $15,682 higher than control patients without pneumonia Total annual cost of hospital-treated pneumonia in elderly Medicare patients in 2010 was estimated at > 7 billion dollars What is the True cost? Time in the hospital Cost of medication (out-of-pocket) Burden on family Quality of life: Travel Freedom Health Family What is the Pneumonia Vaccine? The bacteria streptococcus pneumoniae accounts for up to 75% of cases of pneumonia in otherwise healthy adults Streptococcus pneumoniae has over 90 different serotypes Pneumovax covers 23 of these serotypes that cause the vast majority of infections Prevnar covers 13 of these serotypes and is designed to stimulate less developed immune systems. How does it work? The pneumonia vaccine, like other vaccines stimulates the body to develop antibodies to a specific microbe The pneumonia vaccines are targeted against the most common types of the most causative agent of pneumonia, streptococcus pneumoniae Neither Pneumovax nor Prevnar prevent against other causative agents of pneumonia such as viruses or fungi Risks of the Pneumococcal Vaccine Fortunately there are few adverse reactions with the pneumococcal vaccination such as: -Injection site pain, soreness, and tenderness (60% of patients) -Injection site swelling / induration (20.3%) -Headache (17.6%) -Injection-site erythema (16.4%) -Ashthenia & fatigue (13.2%) -Myalgia (11.9%) Confusion Over Pneumonia Vaccines Language from the CDC: The Guidelines Clarified Who else would benefit? Adults ages 19-64 with: Immunocompromising conditions or asplenia (anatomical or functional) Ceberobrospinal fluid leaks or cochlear implants Chronic heart disease Chronic lung disease Chronic liver disease Chronic renal failure Alcoholism Diabetes mellitus Smoke cigarettes Reside in nursing homes or long-term care facilities Where is the Vaccine Available? Physicians office Clinics Pharmacies!!! “Community pharmacies are uniquely positioned to increase immunization rates in the United States. In a 2009 survey, only 20% to 30% of internists and family physicians stocked all vaccines recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), with nearly 80% not planning to increase their offerings and 2% planning to stop carrying them altogether” Pharmacies…Lot’s of competition How Can a Pharmacy Stand Out? Signage Handouts Call lists Vaccination clinics Counseling and talking with patients “Pharmacists who talked with patients about their risk for pneumococcal disease were able to increase vaccination rates in their pharmacy greater than those in traditional care settings” So How Do We Make Vaccination More Visible “Drumming up business” Simply talking with patients has been proven by studies to increase vaccination the most Making Vaccination More Visible Talking with regular patients Talking with patients getting other vaccinations Automatically generated call lists of eligible patients for vaccines “Advertising” vaccinations and the pharmacy on store receipts Vaccination days with an immunizing pharmacist located in the front of the store Where We Give Vaccinations Chain Drug Stores and Clinics Vs. Our Vaccine Locations What This Means to Us Healthier patients Happier patients Developing a relationship with patients Developing trust for additional immunizations: -Travel immunizations -Zostavax -Yearly Influenza