File - Ms. De Buono
advertisement

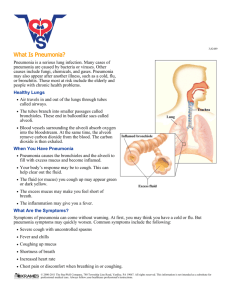
PNEUMONIA By: Larissa and Kyla What is Pneumonia? • Inflammation of the lung; an infectious disease - caused by bacteria or a virus Pneumonia can target: • an area of a lung • The bronchioles and pulmonary alveoli • It can be prevented with simple interventions and treated with low-cost, low-tech medications and care Statistics • Threatens children, the elderly, and chronically ill of any respiratory condition and people suffering from a viral infection are at a higher risk of contracting pneumonia - 200,000 to 300,000 Canadians develop pneumonia each year - more than 900,000 children worldwide in 2013 dies from pneumonia - the mortality rate is high as 30% in Canada - mortality rate worldwide: 15% under 5 worldwide and 2% newborns - children in poor and rural communities are most affected Causes of pneumonia • When germs reach the lungs, the alveoli become inflamed and fill up with fluid • Caused by 30 different factors: • Bacteria • Viruses • Infections (e.g Fungi) • There are 3 forms of pneumonia: • Bacterial • Viral • Mycoplasmas Bacterial Pneumonia • It can affect all people of all ages. • The most vulnerable are alcoholics, weakened individuals, people after operation, and people with respiratory diseases and viral infections. • Types of bacterial pneumonia: • Streptococcus pneumonia, Pneumococcus Bacterium • The bacteria multiplies and invades the lungs and causes the alveoli to become inflamed. • Liquids begins to build up in the tissues of the lobe section. The infection then spreads through the body by the bloodstream Symptoms of Bacterial Pneumonia • Fever, chills, chattering teeth • Body’s temp. may rise to 40.5 C • Acute chest pains and coughing that produces greenish/ rust mucus • Sweating, accelerated respiration and pulse • Lips and nail beds may turn to a bluish color due to the lack of oxygen • Confusion or even delirium Viral Pneumonia • Half of all pneumonia cases are due to viruses • Viral pneumonia caused by the influenza virus • There are no physical signs of lung tissues filled with fluid. • Cause respiratory infections that mainly affect the upper respiratory tract • Victims of this form of pneumonia are mostly pregnant woman or individuals with cardiovascular conditions and diseases • Symptoms: • Fever, dry coughs, headaches • Muscle pains and weakness Mycoplasma Pneumonia • Also known as “Primary Stypical Pneumonia” • Caused by mircoorganisms that are smaller than the bacteria and viruses discovered and identified in WW2 • This mild and widespread form of pneumonia occurs in older children and adolescents • Symptoms: • Severe cough attacks • Chills and fever that could lead to nausea and vomiting • Reduced heart rate Technologies/ methods to diagnose • Patient’s medical history • Chest X-Ray • Blood test • Physical examination Treatments available • Non- Medical • It can be treated at home with remedies • Pleurisy Root • Garlic • Altering your diet Medical • Antibiotics (treated for bacterial) • Medicines that ease chest pain and relieve violent coughing • Antiviral drugs to treat viral pneumonia • Types of antibiotics: • Penicillin and macrolide Treatments available (Continued) o Side effects of treatments: o Can have an allergic reactions from antibiotics o Infection, stomach problems, and/or vaginal infections o Person does not have to go to hospital unless : o Older than 65 o Health problems o Chest pain o Not able to eat or keep food down, so you need to take fluids o Infants younger than 2 months Is pneumonia curable? o Yes, it can be cured. It is an infection that can be treated with antibiotics and medications. o In most cases, it can be treated at home Outcome after treatment o Person recovering from mycoplasma pneumonia may be weak for a period of time o For middle-aged people, may be weeks before they regain their usual strength o Viral Pneumonia improves in 1-3 weeks Lifestyle Changes • Stop smoking. it is also known as a lung irritant. It will be difficult to get oxygen in system • Limit alcohol intake. It can lower you immune resistance and it will be difficult to recover. • Take daily dose of prescriptions. If stopped early, lungs may continue to harbor bacteria and causes pneumonia to reoccur Risk Factors • Cigarette smoking • Infection • Difficulty swallowing • Chronic lung disease such as Cystic Fibrosis • Other serious illness such as heart disease and diabetes • Recent surgery/ Trauma • Weak immune system Sleeping in Dentures doubles the Risk of Pneumonia in Elderly • Poor oral health and hygiene are recognized as a major risk factors for pneumonia among the elderly • 524 seniors were randomly selected. Amon the 453 denture wearers, 186 who wore dentures were at a higher risk of pneumonia • Wearing dentures at night leads to swallowing difficulties and a higher risk of the incidence of pneumonia which was comparable to cognitive impairment, history of stroke and respiratory disease • They were also likely to have tongue and denture plague and gum inflammation Refrences • 11 Home Remedies for Pneumonia - www.naturalalternativeremedy.com Managed WordPress Site. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.naturalalternativeremedy.com/11-homeremedies-for-pneumonia/ • Lifestyle Changes to Manage Pneumonia | Lifescript.com. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.lifescript.com/health/centers/heart_health/articles/lifestyle_changes_to_manage _pneumonia.aspx • Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment - American Lung Association. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.lung.org/lung-disease/pneumonia/symptoms-diagnosis-and.html • Understanding Pneumonia - American Lung Association. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.lung.org/lung-disease/pneumonia/understanding-pneumonia.html • WebMD - Better information. Better health. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.webmd.com/default.htm •