Bacterial Pneumonia
advertisement

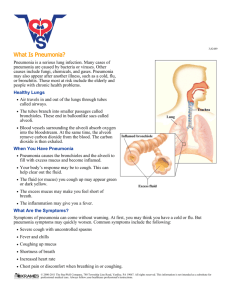
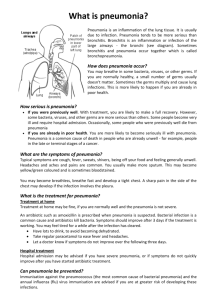
Pneumonia is a breathing (respiratory) condition in which there is an infection of the lung o Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)- pneumonia in people who have not been in a hospital setting or in a hospital o Hospital Acquired Pneumonia (HAP)- infection of the lungs that occurs during a hospital stay • at least 48-72 hours after being admitted • Can be very severe because patients in hospital are often very sick and cannot fight germs • Types of germs in hospital are often more dangerous • Often seen on those on respirator machine Can be caused by Bacteria, Viruses, or Fungi o If caused by bacteria, it tends to be more severe o Most common cause of bacterial pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae • Normal inhabitant of the human upper respiratory tract • Gram + • Lancet shaped cocci o Most common viral causes (especially in infants and young children) are influenza and parainfluenza viruses Certain people are more likely to become ill with pneumonia o This includes adults 65 years of age or older and children younger than 5 years of age o People up through 64 years of age who have underlying medical conditions (like diabetes or HIV/AIDS) and people 19 through 64 who smoke cigarettes or have asthma are also at increased risk for getting pneumonia In 2009, 1.1 million people in the United States were hospitalized with pneumonia and more than 50,000 people died from the disease. Bacteria and viruses living in your nose, sinuses, or mouth may spread to your lungs You may breathe some of these germs directly into your lungs You can catch the bacteria or viruses from people who are infected with them, whether they are sick or not You breathe in (inhale) food, liquids, vomit, or fluids from the mouth into your lungs (aspiration pneumonia) The most common symptoms of pneumonia are: o Cough (with some pneumonias you may cough up greenish or yellow mucus, or even bloody mucous) o Fever, which may be mild or high o Shaking chills o Shortness of breath(may only occur when you climb stairs) The health care provider will likely order a chest x-ray if pneumonia is suspected Your doctor must first decide whether you need to be in the hospital. If you are treated in the hospital, you will receive: o Fluids and antibiotics in your veins o Oxygen therapy o Breathing treatments (possibly) It is very important that you are started on antibiotics very soon after you are admitted (unless you have viral pneumonia) With treatment, most patients will improve within 2 weeks. Elderly or very sick patients may need longer treatment. Vaccines may help prevent some types of pneumonia o They are even more important for the elderly and people with diabetes, asthma, emphysema, HIV, cancer, or other long-term condition • Flu vaccine prevents pneumonia and other problems caused by the influenza virus. It must be given each year to protect against new virus strains • Pneumococcal Vaccine (Pneumovax, Prevnar) lowers your chances of getting pneumonia from Streptococcus pneumoniae Washing hands often