Communication Research Methods
advertisement

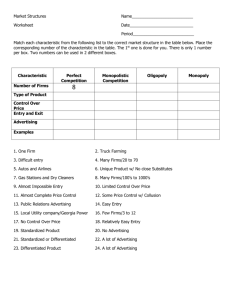
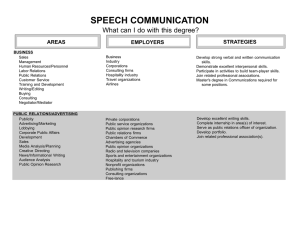
Journalism 658: Communication Research Methods Prof. Dhavan Shah Purpose 1. Basic grounding in research methodology for Undergrads: Journalism and Strategic Communication Investigative, analytic, and evaluative Graduate students: Foundation for thesis and dissertation research Introduction to range of research methods 2. Evaluating and critiquing research 3. Hands-on research experience Group project - analysis of existing data Readings Babbie, E. (2007). The Practice of Social Research. 11th ed. Reserve Readings: Journalism Reading Room and PDFs Notes available from class website: http://www.journalism.wisc.edu/~dshah/teaching.htm Look under the “class link” for 658 Exams 2 In-class exams: Midterm (40 points) Final (40 points) Take-home final Receive in class and due at final (20 points) Assignments Ungraded assignments Brief assignments provided in class Most will not be graded, but I may spot check Definitions, scenarios, and discussion points Class Research Project Existing survey data 2006 DDB Life Style Study Relationships between media use and relevant outcomes Linkage of message to attitudes and behaviors Sample of adults collected from across the nation Will meet with groups next week to discuss interests Cluster you into groups based on common themes Class Project Assignments Concept Explication Assignment 20 points, due week 6 Research Question/Hypotheses Assignment 20 point, due week 12 Statistical Analysis Assignment 20 points, due week 14 Group Presentations 20 minute presentations: Framework and results of class project 40 points toward final grade Peer evaluation Each group members evaluates each other member Consider all aspects of project work 25 points toward final grade Class Participation Small Class requires full participation 25 points - OR Ten percent of your overall grade Should be speaking up in class, engaging in small group activities, offering your perspective or opinion, asking questions Also means being a respectful listener to other Posting relevant materials to the class listserv also counts Good way for those who are shy about speaking out in class to engage Academic Misconduct Harsh penalties (course failure referral to Dean of Students): Cheating Plagiarism Falsification of data Grading 250 points Collective Grading (curve adjustments) Basic curve: 93-100% 88-92% 83-88% 78-83% 73-78% 68-73% below 68% A AB B BC C D F Why Research Methods? 1. Testing claims, observations, explanations, arguments, 2. Solving practical problems 3. Increasing knowledge and understanding 4. Honing precision of knowledge 5. Inherently interesting 6. Research ubiquity 7. Growing permeation in communication careers Contexts of Communication Research • A. Advertising • B. Public Relations • C. Marketing • D. Public Opinion • E. Political Campaigns • F. Health Communication • G. Research Consulting • H. Interest Group Research • I. Academic Research A. Advertising Research Consumer research Establishing target market Demographic, Geographic, Psychographic analyses Media research Diagnostic research Campaign evaluation Media Research Firms A. Advertising Research Consumer research Media research Diagnostic research Campaign evaluation Advertising Research Large agencies have their own research departments Independent advertising research firms Advertising research databases Advertising Agencies Advertising Research Firms and Data Centers B. Public Relations Research Image assessment Public opinion assessment Media image assessment – content analysis Campaign assessment Public Relations Firms C. Marketing Research Product research Product feasibility, performance testing, market testing Pricing analysis Distribution efficiency Promotion analysis (Ad/PR research) Marketing Research Firms and Associations D. Public Opinion Research Describing public opinion (opinion polls) Predicting election outcomes Understanding public opinion dynamics/processes Public Opinion Research Firms and Media Polls Gallup Poll – Presidential Approval E. Political Campaign Research Candidate viability/image assessment Strategy/opinion assessment Ad campaign analyses Fund raising Political Campaign Research Consulting Firms F. Health Communication Research Community-based campaigns E.g., heart health, cancer, anti-smoking, anti-drugs, safe sex Implementation and evaluation research G. Consulting Research Research consulting in a variety of communication fields H. Interest Group Research Watchdog groups, public service groups Non-profit organizations Advocacy groups, interest groups Interest Group Research Examples I. Academic Research Social science disciplines engaging in communication research: Mass communication, psychology, sociology, political science, linguistics/rhetoric, etc. Research tools: Experiments, surveys, content analysis, focus groups, participant observation, field studies, textual analysis Becoming a competent researcher… Mastering basic concepts and principles Following systematic procedures Striving for objectivity Having good research questions Using the right tool to answer the question Testing underlying explanations