No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 - California State University, Los
advertisement

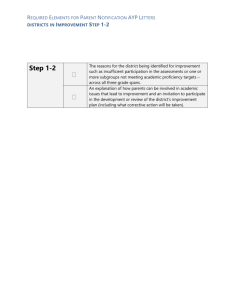
No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 Presented by: Karen Ryback Los Angeles County Office of Education Division for School Improvement Rejected Names for NCLB: Most Kids Doing Pretty Well Leave No Lawyers Behind Survivor NCLB: The Administrator’s Challenge Timelines and Benchmarks and Plans, Oh My! Goals 2005: Better than My Dad’s Elementary & Secondary Education Act (ESEA) Enacted in 1965 as cornerstone of President Johnson’s “War on Poverty” Reauthorized every 5-6 years No Child Left Behind Act Two years of negotiations Bi-partisan with political compromises Signed into law on January 8, 2002 Over 1,000 pages 14 Titles reorganized/consolidated into 10 Total Price Tag--$26.5 billion NCLB Themes Stronger accountability for results Greater flexibility Expanded options for parents Emphasis on scientifically-based research Implementation of NCLB SEA plans--describing how NCLB requirements will be met--must be approved by USDE (May 2003) LEA Plans are due June 1, 2003 to CDE for approval Five Goals 59 Assurances Overview of NCLB’s 10 Titles Title I: Improving Academic Achievement for the Disadvantaged Aid for pupils in highpoverty schools Reading programs for young children Education for migratory and neglected & delinquent children Comprehensive School Reform (CSR) grants Title II: Preparing, Training, and Recruiting High Quality Teachers and Principals Training & recruitment programs Math & science partnerships Teacher training on use of technology in the classroom Title III: Language Instruction for Limited English Proficient Language instruction to foster English fluency Successful academic achievement in core academic subjects Title IV: 21st Century Schools Safe & Drug Free Schools Drug & Violence Prevention Programs Student Code of Conduct Policy School Discipline Policies Crisis Management Plan Hate Crime Prevention Gun Possession After-school programs 21st Century Community Learning Centers Tobacco Prevention Title V: Promoting Informed Parental Choice & Innovative Programs Grants for Innovative Programs Public Charter Schools Magnet Schools Title VI:Flexibility & Accountability Grants to implement accountability mandates Transferability of funds Flexibility Demonstration Agreements Title VII: Indian, Native Hawaiian, and Alaska Education Special Programs for Native Americans Educational Opportunities Professional Development for Teachers/Education Professionals Fellowships Gifted & Talented Adult Education Family Literacy Title VIII: Impact Aide Aid for school districts affected by military bases, Indian reservations & other non-taxable federal land Title IX: General Provisions Definitions Highly Qualified Professional Development Scientifically Based Research School Prayer Military Recruiter Access Unsafe School Choice Option Title X: Repeals, Redesignations & Amendments Homeless Education Significant Changes in the Law Single Statewide Accountability System Goal: All students proficient or above in English Language Arts and Mathematics by 2013-14 All public schools, all students Economically disadvantaged Major racial/ethnic groups African American (not of Hispanic origin) American Indian or Alaska Native Asian Filipino Hispanic or Latino Pacific Islander White (not of Hispanic origin) Limited-English proficient Students with disabilities Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) Achievement of the statewide Annual Measurable Objectives (AMOs) in English Language Arts and Mathematics 95% participation rate Achievement on “other” indicator API for all schools Graduation rate for high schools AMOs Based on English-Language Arts (ELA) and Mathematics separately Grade 10 CAHSEE/CAPA ELA: Proficient or above = 387+ Math: Proficient or above = 373+ AMOs: English Language Arts Elementary and Middle Schools and Elementary Districts 100.0% 100% 89.2% 78.4% 67.6% 56.8% 46.0% 35.2% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 24.4% 13.6% 2001- 2002- 2003- 2004- 2005- 2006- 2007- 2008- 2009- 2010- 2011- 2012- 20132002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 AMOs: Mathematics Elementary and Middle Schools and Elementary Districts 100.0% 100% 89.5% 79.0% 68.5% 58.0% 47.5% 37.0% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 26.5% 16.0% 2001- 2002- 2003- 2004- 2005- 2006- 2007- 2008- 2009- 2010- 2011- 2012- 20132002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 20 01 -2 20 00 02 2 -2 20 00 03 3 -2 20 00 04 4 -2 20 00 05 5 -2 20 00 06 6 -2 20 00 07 7 -2 20 00 08 8 -2 20 00 09 9 -2 20 01 10 0 -2 20 01 11 1 -2 20 01 12 2 -2 20 01 13 3 -2 01 4 AMOs: English Language Arts High Schools and High School Districts 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 11.2% 100.0% 88.9% 77.8% 66.7% 55.6% 44.5% 33.4% 22.3% 20 01 -2 20 00 2 02 -2 20 00 3 03 -2 20 00 4 04 -2 20 00 5 05 -2 20 00 6 06 -2 20 00 7 07 -2 20 00 8 08 -2 20 00 9 09 -2 20 01 0 10 -2 20 01 1 11 -2 20 01 2 12 -2 20 01 3 13 -2 01 4 AMOs: Math High Schools and High School Districts 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 9.6% 100.0% 88.7% 77.4% 66.1% 54.8% 43.5% 32.2% 20.9% AMOs: English Language Arts Unified Districts and High School Districts with Grades 7/8 100.0% 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 89.0% 78.0% 67.0% 56.0% 45.0% 34.0% 23.0% 12.0% 2001- 2002- 2003- 2004- 2005- 2006- 2007- 2008- 2009- 2010- 2011- 2012- 20132002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 AMOs: Math Unified Districts and High School Districts with Grades 7/8 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 100.0% 89.1% 78.2% 67.3% 56.4% 45.5% 34.6% 23.7% 12.8% 2001- 2002- 2003- 2004- 2005- 2006- 2007- 2008- 2009- 2010- 2011- 2012- 20132002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 The API “Status Bar’ Defining Progress on the API as the "Other" Indicator of AYP 800 800 770 750 740 710 API Score 700 680 650 650 620 600 560 590 550 500 2001- 2002- 2003- 2004- 2005- 2006- 2007- 2008- 2009- 2010- 2011- 2012- 201302 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 2011 2012 2013 2014 Graduation Rate High schools must show progress Increase of one tenth of one per cent per year until the school reaches 100% Based on the National Center for Educational Statistics (NCES) four year completion rate NCLB Student Mobility Rules Student was enrolled since CBEDS date Yes Count in school accountability report No Student was enrolled in more than one school in the same district since CBEDS date No Yes Count in district accountability report Count in state accountability report Subgroup Size Schools will be held accountable for groups that have: 100 students, OR 50 students that comprise 15% of the student population Reporting will occur for groups with at least 11 students Program Improvement YE AR: 1 Does Not Adequate Year ly Progre ss 2 Does Not Adequate Year ly Progre ss 3 4 Progra m Improve ment Impl ement Plan 10% Pro f. Dev. Technical Assistance (LEA ) Choice School is identified as PI and develops a 2-year plan 5 Corr ective Action 6 Restructuring Impl ement Plan 10% Pro f. Dev. Technical Assistance (LEA ) Choice 10% Pro f. Dev. Technical Assistance (LEA ) Choice Supplemental Services 10% Pro f. Dev. Technical Assistance (LEA ) Choice Supplemental Services Supplemental Services Corr ective Action (LEA) Plan for Alternative Governance Replace Staff New Curriculum Dec rease Manage ment Authority Outside Exper t Extend Yr/Day Charter or Replace Staff or Private Mgmt. or State Control or Other Funda mental Reform Restructure Does Not AYP Does Not AYP Does Not AYP Does Not AYP 7 Impl ement Alternative Governance Plan “OF COURSE, IF THEY’’RE ALL LEFT BEHIND, THEN, RELATIVELY SPEAKING, NONE ARE LEFT BEHIND” …FOR WHAT IT’S WOR From the comic strip: Pett Peeves by Joel Pett Proposed Regulations NCLB Compliant Teachers “New” to the profession Hired on or after July 1, 2002 “Not new” to the profession Hired prior to July 1, 2002 Timelines for Compliance New teachers teaching a core academic subject in a Title I SWP school or funded with Title I funds in a TAS school, must have been NCLB compliant when hired. All other public school teachers teaching a core academic subject, must be compliant by the last day of the 2005-06 school year. Core Academic Subjects English Reading/language arts Mathematics Science History Geography Civics/government Economics Foreign languages Arts 3 Requirements for Core Subject Teachers Bachelor’s degree State credential or Intern certificate/credential (for no more than three years Demonstrated core academic subject-matter competence Core Academic Subject Matter Competence Elementary Must pass the California Subject Examination for Teachers (CSET) Middle/High School CCTC approved subject matter exam or program A major A major equivalent Graduate degree “New” Teachers Core Academic Subject Matter Competence “Not New” Teachers Elementary: Pass any past/current CCTC approved subject matter exam OR complete the HOUSSE Middle/High School: For each core subject taught: CCTC approved subject matter program OR A major OR A major equivalent OR A graduate degree OR National Board Certification (NBC) Complete the HOUSSE HOUSSE “High Objective Uniform State Standard of Evaluation” 100 points required to be satisfied through Part I and/or Part II HOUSSE: Part I Summation of: Years of experience in grade span/subject (Max. 50 pts.) Core academic coursework in grade span/subject In-depth standards aligned professional development Service to the profession in relevant core academic content HOUSSE: Part 2 Completion of successful observations Required documentation: lesson plan, analysis of student performance, and observer notes (Each observation = 20 pts) Completion of portfolio assessment 4 entries required: 5 sequenced lesson plans, student assignments, analysis of student performance, reviewer notes (100 pts--no partial credit) Paraprofessionals All instruction paraprofessionals Must have a high school diploma/equivalency May only be assigned to work under the direct supervision of a HQ teacher Must be assigned only permissible duties as listed in the law Heightened Requirements Must meet one of the following: Associate’s degree Two years of study at an institution of higher education (48 semester units) Local rigorous academic assessment Knowledge of reading, writing, & mathematics (or readiness) Ability to assist in instructing in reading, writing, & mathematics (or readiness) Timelines for Paraprofessionals Affected Paraprofessionals All newly hired Title I-funded paraprofessionals and all newly hired paraprofessionals in a Title I Schoolwide Program school Date of Implementation January 8, 2002 All previously hired Title I-funded January 8, 2006 paraprofessionals and all previously hired paraprofessionals in a Title I Schoolwide Program school Cap on Funding The district may not fund any additional paraprofessionals with Title I, Part A funds, if after 3 years, the district does not make progress toward meeting its HQ teacher objectives and AYP. Parent Notifications Parents Right-to-Know (Title I Schools) May request the qualifications of their child’s teacher/paraprofessional 4-Week Notice (Title I Schools) When child has been taught for 4 or more consecutive weeks by a core subject teacher who does not meet the NCLB Unsafe School Choice Option Option to transfer to a safe school must be given if child is: • in a school identified as “persistently dangerous” • the victim of a violent crime on school property Military Recruiter Access to Students LEAs are required to provide secondary students’ names, addresses, and telephone listings, when requested (unless a parent “opts out”) LEAs must provide the same access to military recruiters to secondary school students as given to postsecondary institutions or prospective employers Questions Karen Ryback Title I/NCLB Consultant Los Angeles County Office of Education Division for School Improvement (562) 922-6752 Ryback_Karen@lacoe.edu