Separating Mixtures
advertisement

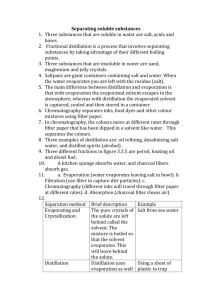
1st Year Science – Chemistry Separating Mixtures – Introduction Mixtures: ‘A mixture is made up of 2 or more substances mingled together but not chemically combined’ e.g. Air – oxygen, carbon dioxide, Nitrogen e.g. Cup of Coffee – coffee granules, milk, water, sugar e.g. Sea Water– water, salt, chlorine and many more Ways of Separating Mixtures • Decanting: Very Basic method • Filtration & Evaporation: Separating solids from liquids • Distillation: Uses evaporation to separate 2 liquids • Chromatography: Separating Different Dyes in inks Filtration Evaporation Distillation Chromatography Separating Solids from liquids The type of separation depends on whether the solid is Soluble or Insoluble in the liquid Soluble: Solids that dissolve in liquids to form a solution e.g. Sugar in tea or coffee, Salt in sea water Evaporation can be used to separate soluble solids and Liquids Insoluble: Solids that don’t dissolve. Instead they sink to the bottom of the liquid e.g. Sand & soil in water Filtration can be used to separate insoluble solids and Liquids Filtration Experiment Title: ‘Separation of Soil and Water’ Apparatus: Beaker, Stirring rod, Retort stand, Funnel, Filter paper, Soil/water mixture Filter paper Filtrate Evaporation Experiment Title: ‘Separation of Salt and Water through Evaporation’ Apparatus: Bunsen Burner, Tripod, Evaporating Dish, Salt water solution, Beaker of Water (optional) Evaporating Dish Salt water Solution Tripod Bunsen Burner Separating Solids from liquids Another basic method of filtration is Decanting Water Water Sand Solids are allowed to settle at the bottom of the liquid and then water is gently drained off. Distillation • The problem with evaporation is that the liquid is lost. • Distillation is a method of separation that saves the liquid(s) Distillation is used to separate... 1. Two miscible liquids (liquids that mix) e.g. Water and alcohol 2. Soluble solids from liquids e.g. Salt and water Two types of Distillation... 1. Simple distillation 2. Fractional Distillation Immiscible means substances that do not mix together e.g. Water & oil Distillation Simple Distillation: e.g. Separation of two miscible liquids – Water and alcohol • Both liquids have two different boiling points... Round Bottom Flask Water = 100⁰C Alcohol = 78⁰C • Some water evaporates with the Thermometer Water Out Liebig Condenser alcohol, therefore it is not a perfect method of separation Solution • Cooling water condenses steam back into water droplets (distillate) Water In • Can also be used to separate liquids and solids (salt & water) Wire Gauze Tripod Bunsen Burner Distillate Simple Distillation Distillation Fractional Distillation: • Greater quality of separation • Fractionating column is heated to the Fractionating Column Thermometer boiling point of alcohol (78⁰C) Round Bottom Flask • The water cools down over the long Liebig Condenser Water Out distance and condenses back into droplets. Water In • The pure alcohol continues on Distillate through the Liebig condenser and Solution condenses at the other end as Wire Gauze distillate. Tripod Bunsen Burner Fractional Distillation Distillation – Separating Salt and Water Chromatography • Chromatography is a method used to separate complex mixtures e.g. Hospitals: Analysing blood samples e.g. Forensics: Analysing samples from crime scenes How Chromatography is carried out: • A coloured dot is placed at one end of the chromatography paper • The strip is placed in a beaker/cylinder that contains a solvent (water) • The strip is placed in the solvent with the ink dots above solvent (water) level. • The solvent (water) is absorbed upwards through the paper and carries the different dyes with it • Some dyes only go up to a certain point therefore separating them out. Chromatography How Chromatography is carried out: Container Separated Dyes After 10-15 minutes Chromatography Paper Solvent (water) Ink Spots Direction of Absorbed Solvent