Name: SIMPLE CARBOHYDRATES REVIEW STUDY GUIDE The
advertisement

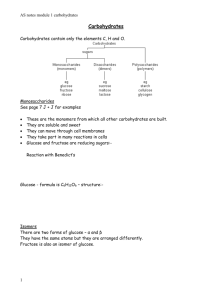
Name:_________________________________ SIMPLE CARBOHYDRATES REVIEW STUDY GUIDE 1. The process that produces carbohydrates is called _photosynthesis______. It converts _radiant____ energy from the sun into _chemical_____ energy. There are 4 items that must be present for this to occur. Name all four: Sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, and water 1. Light shining down from the sun is absorbed by the plant’s cells. 2. Inside these cells is a special ingredient, chlorophyll. This is the compound that traps the sun’s light to start the process of photosynthesis. 3. The hydrogen atoms are stripped from the water, leaving only oxygen. 4. Oxygen left is released into the air 5. Hydrogen atoms are mixed with carbon dioxide to make sugar the plant uses as food. 6. The sugar created is sent to the rest of the plant for food. 2. All carbohydrates are originally produced into _glucose_____________. 3. Carbohydrates are composed of what elements? Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen 4. One oxygen atoms and one hydrogen atom bonded together creates a _hydroxyl group______. What is its symbol? -OH 5. _monosaccharide_____ are sugars containing one basic molecule. Name all three and provide food sources for each. Which is the sweetest? 1. Glucose – grapes & corn 2. Fructose – fruits & honey; sweetest 3. Galactose - animals & humans 6. _disaccharides___ are pairs of monosaccharide’s. Name all three, provide the formula to create each disaccharide and provide a food source for each. 1. Sucrose – glucose + fructose; table sugar 2. Maltose – glucose + glucose; malted grains 3. Lactose – glucose + galactose; milk 7. _condensation__________ creates a disaccharide. What is the byproduct? 8. _hydrolysis_____________ breaks down a disaccharide. What 3 things can trigger this process? How does the suffix change? 1. Presence of an enzyme 2. Addition of an acid 3. Addition of heat 9. List the sugars in order from sweetest to least sweet. Fructose, sucrose, glucose, galactose, maltose, and lactose 10. Explain how carbohydrates are used as a preservative. The water is drawn first to the bacteria and will evaporate. Without water, bacteria can’t grow. 11. _tenderizing_______ effect of sugar in food preparation will increase the pourability of a batter. 12. _supersaturated___ is any solution that has been heated to dissolve more solute than the water would normally hold. 13. List the 6 interfering agents that affect crystal formation. Corn syrup, butter, cream, egg whites, cream of tartar, and vinegar 14. _caramelization__ is the process of subjecting sugar to high or prolonged heat, which changes into a brown liquid. Explain how this process occurs. Hydroxyl groups combine with hydrogen atoms from other molecules and combine to form water and evaporate at high heat 15. When digested, sugar is converted to _glucose____ in the _liver_____ and stored as _glycogen____ in either the _muscles___ or _liver____. 16. What is the main function of carbohydrates for the body? To provide energy 17. List and describe other health concerns related to the consumption of carbohydrates. Diabetes – body’s inability to move glucose Weight gain – excess calories will be stored as fat 18. Name for type of complex carbohydrates. Starches, cellulose, gums, and pectins 19. Identify the different structures of starches and explain the difference between the two. Amylose – chain (gels) Amylopectin – branched (thickens) 20. How is cellulose used in the body and what are examples of food sources? Provides bulk (fiber); Sources: fruits, vegetables, whole grains 21. Compare/contrast carbohydrate gums and pectin. Both: stabilize and thicken mixtures Gums- trap color and flavor Pectins – derived from sugar, called sugar acids, found naturally in plant cells. 22. What are the functions of complex carbohydrates in food preparation? Provide examples. Provide structure (flour in baked goods); bind products together (keeps skin on fruits, holds batter to vegetable/meat for deep frying; thickens product (roux) Name:_________________________________ 23. _retrogradation_ is firming of a gel during cooling and standing. If that gel leaks water, the liquid is called _syneresis_. 24. Describe how to complete a viscosity line spread. What does it mean, in terms of viscosity, if there is reading is a low number? Add up the number at each of the four points, then divide by four. Low number = high viscosity (did not spread as much) 25. What is the difference between opacity and translucency? Opacity means to block light whereas translucency means the amount of light that passes through an object 26. Name the functions of complex carbohydrates in the body. Provides bulk (helps you feel full); lowers cholesterol levels in the blood, promotes use of fat