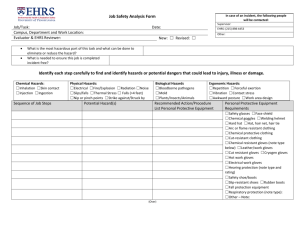
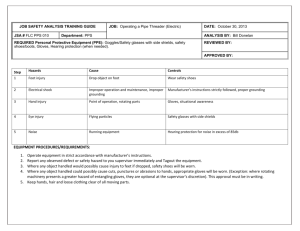
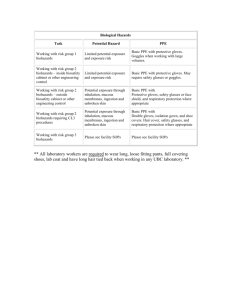
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)

Personal Protective Equipment
(PPE)
1
Purpose of PPE
To protect employees from hazards not eliminated from the workplace
2
Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment
–
–
–
–
Eyes
Face
Head
Extremities
Protective clothing
Respiratory devices
Protective shields and barriers
3
Design and Condition
Safe design and construction for work performed
Sanitary and reliable condition
–
–
–
Provided
Used
Maintained
Laundered
Repaired
Replaced
Defective and damaged equipment shall not be used
Must properly fit users
4
Purchase of PPE
The employer is normally responsible for the cost of personal protective equipment.
PPE used by trades may be an exception
5
Protect Against Hazards
–
–
–
Hazards
Physical
Chemical
Biological/Infectious
Capable of causing injury or impairment in the function of any part of the body through
(routes of entry)
–
–
–
–
Inhalation
Skin absorption
Ingestion
Contact with skin and/or eyes
6
Required Implementation
Engineering Control
–
–
–
–
Ventilation
Isolation
Selected Equipment
Redesign process or procedure
Administrative Control
–
–
–
–
–
Personal Hygiene
Maintenance
Hand washing
Scheduled breaks
Assignment schedules
7
Certified Hazard Assessment
Prepared by
–
–
Consultant
VA Personnel
Insert - date of written hazard assessment
Insert - how to obtain a copy of the written hazard assessment
Required by 29 CFR 1910.132d
8
Overview of Hazard
Assessment
Bloodborne pathogens
–
–
Latex gloves
Gown
–
–
Safety glasses
Hand washing
Handling trash
– Rubber gloves
– Safety shoes
Shops
–
–
–
Safety glasses
Safety shoes
Hearing protection
Facilities
–
–
–
Rubber gloves
Non-slip shoes
Safety glasses (when mixing detergents)
9
Reassessment of Hazards
Facility safety officer is responsible to reassess workplace hazards as necessary by:
–
–
–
Identifying and evaluating new equipment and processes
Reviewing accident records
Re-evaluating the suitability of previously selected PPE
10
Personal Protective Equipment
Program
Defined by insert appropriate facility policy
–
–
–
–
Ordering
Repair
Maintenance
Other requirements
11
Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (29 CFR 1910)
General Requirements --
Eye and Face Protection --
Respiratory Protection --
Head Protection --
Foot Protection --
135
Electrical Protection --
132
133
134
136
137
Hand Protection --
Hearing Protection --
138
95
Specialized Standards -- e.g., 1030
12
Eye and Face Protection
(29 CFR 1910.133)
13
Hazards to Eyes/Face
Physical
–
–
–
Flying Particles
Molten Metal
Potentially Injurious
Light Radiation
– Ultraviolet (UV) light
Chemical
– Gases or Vapors
–
–
Liquids
Acids or Caustics
Biological/Infectious
–
–
–
–
–
Blood
Saliva
Semen
Body Tissue
Wastes
–
–
Animal Tissue
Potentially Infectious
Materials
14
Safety Glasses
Can be used with side shields (Required if flying objects are present)
Plastic
–
–
Can fit over corrective lenses
Can be worn alone
Can accommodate most types of prescriptive lenses
15
Goggles
Should fit face snugly (sealing entire eye area)
Specially-coated lenses or ventilation holes may prevent fogging
Anti-fogging materials can be used
When removing goggles, tilt head down so that debris on top of goggles does not fall into eyes
16
Other Eye and Face Protection
Face Shields
–
–
–
Worn for extremely hazardous jobs
Worn with safety glasses or goggles
Do not completely protect face
Hoods
–
–
Protect entire head and face
Can be worn with respirators
Sunglasses
–
–
–
–
Provide protection against sun
Should filter 99 to 100 percent UV
Provide no protection against flying objects
Can reduce chances of cataracts
17
Inspection and Maintenance of
Eye and Face Protection
Must be kept clean
Must be free of scratches and other defects that may obstruct vision
Must be disinfected
–
–
Periodically, if used by same person
After each use, if shared
Headband should be replaced when slack, worn, or dirty
18
Eye Safety
Review Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) for chemicals used
–
–
Identify eye protection required
Become familiar with emergency response procedures
Contact Lenses
–
–
Do NOT provide protection
Should NOT be worn around chemicals or chemical vapors
19
Laser Eye Safety
Follow guidance of laser manufacturer
Wear safety glasses with filters that protect against the wavelength of light for the laser being used
Partial reflections from Class IV lasers can cause permanent eye damage
20
Head Protection
(29 CFR 1910.135)
21
Hazards to Head
Falling or flying objects
Electrical conductors
Contamination from bloodborne pathogens
Sunburn and sunstroke
Cold temperatures
22
Types and Classes of
Head Protection
Types of protective hats
–
–
Type 1, Helmets - full brim (at least 1.25”)
Type 2, Brimless helmets with peak extending forward from the crown
Classes of industrial head protection
–
–
Class A, General service - limited voltage protection
Class B, Utility service - high voltage protection
– Class C, Special service - no voltage protection
23
Hard Hats (Class A)
Hard exterior shell
Shock-absorbing lining
–
–
Headband
Crown straps
Protects against impact hazards
Used in construction
24
Electrical Bump Hats (Class B)
Protects against impact and penetration
AND against high-voltage shock or burn
Can be used where there is a possibility of bumping against a fixed object
Used by electrical workers
Sometimes used in construction
25
Other Head Protection
Safety Hat or Cap
(Class C)
–
–
–
Protects against impacts
Provides lightweight comfort
Provides no electrical protection
Hat or Cap
–
–
–
Protects against exposure to sun (4 inch brim)
Protects against exposure to cold (ear flaps)
Generally not considered PPE
26
Specialized Head Protection
Hairnets
–
–
Food service employees
Sanitation and cleanliness
Hoods
–
–
–
Can be used in extremely hazardous situations
Can be used with respirators
Can provide eye and face protection
Surgical Caps
–
–
Infection control and cleanliness
Worn during medical procedures that involve large amounts of blood
Autopsies
Orthopedic surgery
27
Inspection and Maintenance of
Head Protection
–
–
–
–
–
–
Damage
Dents
Cracks
Penetration
Abuse
Mutilation
Other damage that might reduce the degree of protection provided
Visually inspect daily
Clean periodically
May adversely affect protection provided
–
–
–
Paint
Sunlight
Extreme temperatures
28
Foot Protection
(29 CFR 1910.136)
29
Foot Hazards and Protection
Hazards to Feet
–
–
–
–
Falling or rolling objects
Objects that pierce the sole
Electrical exposures
Slipping
Foot Protection
–
–
–
–
–
Safety Shoes
Slip Resistant Soles
Shoe Covers
Rubber or Synthetic
Boots
Leather Work Boots
30
Safety Shoes
Steel-reinforced toe (protects foot from being pierced or crushed)
Puncture-resistant or heat-resistant soles
(optional)
Metal-free non-conductive materials
(working around exposed electrical conductors)
31
Other Foot Protection
Boots
–
–
Rubber/Synthetic
May be required when working around chemicals
Autopsies
Leather
Recommended for outdoor maintenance activities
Avoid wearing around chemicals
Shoe Covers
– May be required for some medical procedures
Slip-resistant Soles
–
–
OSHA recommends
Will reduce the number of injuries resulting from slips, trips, or falls
32
Electrical Protection
(29 CFR 1910.137)
33
Electrical Protective
Equipment (Insulated Rubber)
Required when exposed to electrical hazards
–
–
–
–
–
–
Blankets
Matting
Covers
Line hose
Gloves
Sleeves
Maintained in a safe and reliable condition
Cleaned as needed
Requires periodic electrical testing
34
Inspections
Before each day’s use
Following any incident that caused damage
Insulating properties cannot be degraded
Insulating equipment failing to pass inspections or electrical tests may not be used unless specific requirements are met
Cannot use equipment with:
–
–
–
–
Hole, tear, puncture, or cut
Ozone cutting or ozone checking
Embedded foreign objects
Swelling, softening, hardening, stickiness, or inelasticity
35
Storage
Location and manner of storage must protect from:
–
–
–
–
–
Light
Temperature extremes
Excessive humidity
Ozone
Other injurious substances and conditions
36
Hand Protection
(29 CFR 1910.138)
37
Hand Protection
–
–
–
–
–
Provided to protect against
– Absorption of harmful substances
Severe cuts or lacerations
Severe abrasions
Punctures
Chemical or thermal burns
Harmful temperature extremes
–
–
–
–
Types of hand protection
–
Machine guards
Electric eyes
Push sticks
Controls requiring two hands
Gloves
38
Glove Selection Criteria
Selection based on evaluation of performance characteristics
–
–
–
–
Task(s) to be performed
Conditions present
Duration of use
Hazards and potential hazards identified
Selection based on individual characteristics
–
–
–
–
–
Grip
Dexterity
Flexibility
Hand size
Glove length
Too tight - may rip
Too loose - affects grip and comfort
39
General Purpose Gloves
Cotton
–
–
–
Can be specially coated
Allows handling of delicate components
Absorbs oil
Leather
–
–
–
Rough surfaces
Heat
Sparks
Protect against
–
–
–
–
–
Abrasion
Cuts
Punctures
Snags
Temperature extremes
40
Cut-resistant Gloves
Designed for use with sharp knives and blades
May contain
–
–
–
Cut-resistant yarns
Composite materials
Metal mesh (Required of most meatcutting and de-boning operations)
Protect against
–
–
Cuts
Abrasion
Some may protect against punctures
41
Special Purpose Gloves
Surgical
Examination
Firefighters
Smelters
Welders
Clean rooms
Protect against specific hazards
–
–
HIV/Hepatitis
Heat and burns
– Patient protection
42
Latex Gloves
Natural
–
–
–
–
Required for surgery
Can be used for examinations
Label NOT required
Hypoallergenic gloves
NOT tested for natural rubber proteins
(source of latex allergies)
Synthetic
–
–
–
Cannot be used for surgery
Can be used for examinations
Label NOT required
43
Chemical-resistant Gloves
Must be selected for the specific chemical used
(Consult manufacturer’s guidance)
Non-porous
Selection based on
–
–
–
Potential toxic effects of chemicals used
Likely routes of entry
Degree of hazard
Protect against
–
–
–
Dermatitis
Chemical burns
Cancer
Resist
–
–
–
Penetration
Permeation
Degradation
44
Penetration
Natural rubber
–
–
Protects against liquids that mix with water
Provides no protection against petroleum or oil-based solvents
Synthetic rubber resists
–
–
Oils
Greases
–
–
–
Acids
Caustics
Many petroleum products
45
Permeation
Must consult manufacturer’s technical data for specific chemical used
No protective barrier provides permeation protection for all chemicals
Often coated with
–
–
–
–
Polyvinyl chloride
(PVC)
Nitrile
Neoprene
Latex
46
Degradation
Signs of degradation
–
–
–
–
Stiffer
More brittle
Softer
Weaker
Major indication that gloves should be replaced
Inspect before each use
–
–
Rips
Holes
–
–
Weak seams
Imperfections
47
Hand Safety
Do NOT wear gloves that are damaged
Clean off contaminants before you remove gloves
Remove gloves safely
Properly decontaminate and store gloves
Monitor the condition of your gloves as you work
Follow manufacturer’s guidance for maintenance and storage
Dispose of gloves properly
48
Skin Protection
49
Hazards to Skin
Hazards
–
–
–
–
–
Sunburn
Skin Cancer
Dermatitis
Poison ivy, oak, sumac
Insect and animal bites
Protections available
–
–
–
–
–
Protective clothing
Sunscreen
Insect repellent
Scheduling of work
Ointments
50
Prevention of Sun Damage
Avoid the sun’s strongest rays
(10 a.m. - 4 p.m.)
Wear protective clothing
–
–
Broad-brimmed hats
Long pants
– Long-sleeved shirts
Wear sunglasses
(99 - 100% UV ray protection)
Always wear a sunscreeen with SPF of 15 or more
Avoid sunlamps, tanning beds, and tanning parlors
51
Torso Protection
52
Hazards to Torso
Hazards
–
–
–
–
–
–
Heat
Splashes from hot metals and liquids
Impacts
Cuts
Acids
Radiation
53
Types of Protection
Options
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Vests
Jackets
Aprons
Coveralls
Full body suits
Lead lined coverings
Gowns
Materials
–
–
–
–
–
Fire retardant wool
Specially treated cotton
Leather
Rubberized fabrics
Disposable suits
54
Lifting or Back Belts
Must follow manufacturer’s guidance
Back belts can be obtained by contacting
55
Appropriate PPE for Exposure to Bloodborne Pathogens
Does NOT permit blood or other potentially infectious materials to pass through to
–
Employee’s work
– clothes
Employee’s street clothes
– Undergarments
Under normal conditions of use
Does NOT permit blood or other potentially infectious materials to reach
–
–
Skin
Eyes
–
–
Mouth
Other mucous membranes
For the duration of time to be used
56
PPE for Bloodborne Pathogens
Gloves
Gowns or aprons
Laboratory coats
Face shields or masks and eye protection
Goggles or glasses with side shields
Mouthpieces
Surgical caps or hoods
Shoe covers or boots
Clinic jackets
Resuscitation bags
Pocket masks
Other ventilation devices
57
Gloves Required for Exposure to Bloodborne Pathogens
When reasonably anticipated that employee may have hand contact with
– Blood
–
–
–
Other potentially infectious materials
Mucous membranes
Non-intact skin
When performing vascular access procedures
When handling or touching contaminated items or surfaces
58
Hearing Protection
(29 CFR 1910.95)
59
Hearing Protectors
If exposed to 85 dB or greater for eight-hour
TWA:
–
–
Hearing protection must be available
Hearing protection must be worn if
No baseline audiogram has been established
Hearing threshold has changed an average of 10 dB or more at 2000,
3000, or 4000 hertz in either ear
Must be worn if:
Duration Sound Level
(hours per day) (dBA)
4
3
2
8
6
90
92
95
97
100
1.5
1
0.5
0.25 or less
102
105
110
115
60
Locations Requiring
Noise Protection
Building #
–
–
–
Room ###
Mechanical room
Penthouse
Building #
–
–
Room ###
Shop area
Building #
– Insert appropriate locations
Building #
– Insert appropriate locations
61
Types of Hearing Protectors
Earplugs
–
–
–
–
–
Lightweight
Comfortable for long periods of time
Made of soft fibers or foam
(self-forming)
Disposable or reusable
Performed, pre-molded, or custom molded
Earmuffs
–
–
–
–
Easily put on or removed
Require entire ear to fit inside cup (seal)
May interfere with glasses or goggles
Can be designed for use with hard hats
62
General Considerations
Proper initial fit required
Must be used correctly
Must receive training in the use and care of hearing protectors provided
Must be allowed to select hearing protectors from a variety of suitable hearing protectors provided by employer
Must be replaced as necessary
63
Hearing Safety
If you have to shout to talk to someone within 2 or 3 feet - Wear hearing protection
Off-the-job activities (woodworking, shooting, etc.) can hurt your hearing - Hearing protection is recommended
Never remove hearing protection in high noise areas
Do NOT share hearing protection with others
64
Respiratory Protection
(29 CFR 1910.134)
65
Hazards Requiring Respirators
Protect against breathing air contaminated with harmful:
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Dusts
Fogs
Fumes
Mists
Gases
Smokes
Sprays
Vapors
– Infectious biological agents
Healthcare-related exposures that may require respirators:
–
–
–
–
Tuberculosis
Ethylene oxide
Some chemicals used for disinfection or preservation
(morgues)
Animal fecal matter
Other related exposures
–
–
Asbestos
Paint fumes
66
Respirators
–
–
–
Types of Facepieces
Half-face
Full-face
Hoods
Types of Respirators
–
–
Air Purifying
N95 (Tuberculosis)
Dust, fume, mist
Powered air purifying
Air Supplied
Self-contained breathing apparatus
Air Line
67
General Considerations
Written program required
Medical examination in accordance with ANSI
Z88.6
Annual follow-up
Certification by NIOSH
Selection in accordance with ANSI Z88.2
Fit testing required in accordance with ANSI
Z88.10
Cleaning and disinfection
Proper storage
68
Emergency Response
(29 CFR 1910.120)
Facility Emergency
Response Plan addresses
PPE if:
–
–
An industrial facility intends to use the medical center, if there is an emergency
Medical center provides support during responses to natural phenomenon
Level A - Encapsulating chemical protective suit
Level B - Respiratory protection
69
Summary
–
–
–
PPE must
Protect against the hazard
Protect the route of entry
Be maintained in a safe and sanitary condition
– Be used properly
PPE is available by contacting
–
–
Your supervisor
Facility safety office personnel
If you have questions concerning PPE provided contact
–
–
Your supervisor
Facility safety personnel
If you have questions concerning the health effects associated with
PPE contact employee health personnel
70