Nervous System Health Concerns
advertisement

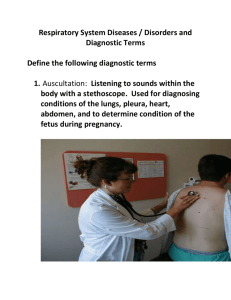
Nervous System Health Concerns Health Occ Concussion Etiology • Injury to the brain caused by an impact with an object S/S • Headache, noise and light sensitivity, dizziness, nystagmus Treatment • No activity until symptom free for 24 hours • Stress test and re-evaluation by Health care professional Spina Bifida Etiology • A defect in the spinal cord in which the cord and/or its covering protrude outside the vertebrae • congenital S/S • Protrusion outside the skin • Varying degrees of paralysis, lack of feeling and movement below protrusion Treatment • surgery Etiology Hydrocephalus • An overproduction of CSF in the brain • Congenital, or result of infection or tumor S/S • Headache, swelling Treatment • Drain the fluid through the use of a shunt Cerebral Palsy Etiology • Cerebral damage during gestation or birth S/S • Lack of motor coordination, and other neurological deficiencies Treatment • No cure Alzheimer’s Disease Etiology • Progressive degeneration of neurons in brain S/S • Deterioration in mental capacity • Loss of memory, inability to use familiar objects, and understand outside stimuli Treatment • No cure • Keep brain active to help prevent it Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Lou Gehrig’s Disease Etiology • Degenerative disease of the motor neurons S/S • Loss of muscle control • Death Treatment • Medications to relieve symptoms and complications, maintain muscle functions and movement, and delay paralysis and disability for as long as possible. Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Etiology • Destruction of the myelin sheath S/S • Muscle weakness, unsteady walking, paraesthesia (tingling), extreme fatigue, paralysis Treatment • No cure • Medication to help slow and reduce symptoms Myasthenia Gravis Etiology • Overproduction of antibodies keeps neurotransmitters from sending proper nerve impulses to skeletal muscles S/S • Muscle weakness, easily fatigued Treatment • No cure • Medication can help, lifestyle changes Parkinson’s Disease Etiology • Degeneration of nerves in the brain S/S • Tremors, weakness of muscles, difficulty walking Treatment • Drugs that increase levels of dopamine to help relieve symptoms • No cure Epilepsy Etiology • Abnormal conditions in the brain cause sudden excessive electrical activity S/S • Chronic, recurrent seizure activity • Petit Mal = momentary disorientation • Grand Mal = convulsions, twitching of limbs, loss of consciousness Treatment • Anti-seizure medication Tourette’s Syndrome Etiology • Neurological dysfunction S/S • Uncontrollable sounds and twitches Treatment • Drugs to control symptoms Meningitis Etiology • Inflammation of the meninges • Bacterial, or viral S/S • Fever, headache, stiff neck Treatment • Antibiotics • Medications for symptoms Encephalitis Etiology • Inflammation of the brain from a viral infection, or spread of infection to brain • Infection from measles, mumps, or chickenpox, herpes (type 1) S/S • Fever, headache, seizures, weakness, visual disturbances, vomiting, stiff neck and back, disorientation Treatment • Antiviral medications to prevent death Hemiplegia Etiology • Paralysis on one side of the body • Usually due to a stroke S/S • Unable to move one side or feel heat, cold, pressure, pain • Drooping eyelid or side of face Treatment • No cure Paraplegia Etiology • Paralysis from the waist down caused by accident/injury S/S • Inability to move or feel distal to the injury sight • Inability to control urine and bowel functions Treatment • No cure Quadriplegia Etiology • Paralysis from the neck down • Injury to the 4th cervical vertebrae S/S • Inability to move or feel distal to the injury • Prone to respiratory and urinary tract infections Treatment • No cure