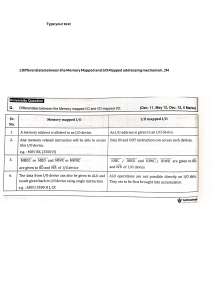
CPU PowerPoint
advertisement
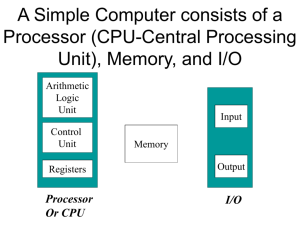
IT Chapter 2 Part B CPU CPU • The CPU is contained on a single integrated circuit called the microprocessor. • Often referred to as the brains of a computer • The CPU contains two basic components: – Control unit – Instructs the rest of the computer system on how to follow a program's instructions. It directs the movement of data to and from processor memory – Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU) – The ALU performs both arithmetic and logical operations • The processor handles most of the operations that are required of the computer by processing instructions and sending signals out, checking for connectivity, and ensuring that operations and hardware are functioning properly CPU cont. • The microprocessor is connected to the rest of the computer system through three buses, including the data bus, address bus, and control bus • Many different companies that produce CPUs, including Intel, Advanced Micro-Devices (AMD)TM, and Cyrix • Socket X (X being any numerical number) is a descriptive term for the way certain processors plug into a computer motherboard so that it makes contact with the motherboard's built-in circuitry or data bus • Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) socket. A ZIF socket is designed to make it easy to replace and upgrade the microprocessor. A typical ZIF socket contains a lever that opens and closes, securing the microprocessor in place Pentium Processors • Current family of the Intel Pentium microprocessors includes the Pentium II, III, IV, and Pentium D’s , Dual Core • Pentium class is the current standard for processor chips • The combined chips cover less than 2 square inches (6 cm2) and comprise over a million transistors AMD Processors • Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) processors are the Athlon, Thunderbird, Duron series, A Series, FX Processors, Phenom II and APU’s • AMD is first to break the historic 1GHz (one billion clock cycles per second) with the AMD Athlon™ processor. Processor Speed Rating • CPU descriptions as Pentium 133, Pentium 166, or Pentium 200 are well known • These numbers are specifications that indicate the maximum (reliable) operating speed at which the CPU can execute instructions. • The CPU speed is not controlled by the microprocessor itself, but by an external clock located on the motherboard • It is typically expressed in megahertz (MHz), and the higher the number, the faster the processor • Generally, three factors determine how much information can be processed at any given time. These include: – The size of the internal bus – The size of the address bus – The processor's speed ratings