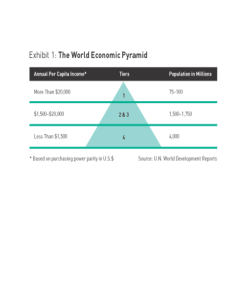
Bottom of Pyramid - University of Winnipeg
advertisement

Welcome to class of Bottom of the Pyramid by Dr. Satyendra Singh University of Winnipeg Canada Opportunity for growth • 7 b people • 2b can afford good products • 5b Bottom of Pyramid (BOP) o We need to cater BOP and develop market oriented products accordingly o Emerging markets o Developing countries o Moral responsibility to cater BOP! o Because they’re denied resources and opportunities 75 Marketing Strategies for EMs… • Need 2 strategies – Urban Global strategy is applicable • • • • • • • • • Consumers prefer global brands to local brand Global brand equates to quality and prestige Communicates sophistication and modernity Admire HIG lifestyle and the products that symbolize that Large cities have advanced distribution channels HIG customers are less price sensitive Serves as social distinction Firms do not need to be based in developed countries Concept of 3rd world countries multinationals – E.g. Nando’s fast food from Africa now in +30 countries • Over engineered brands unlikely to be successful in EM Marketing Strategies for EMs • Bottom of the pyramid strategy – LIG radically different • Low price/value focused segment Tata Nano – Less features, toothbrush with no angles (i.e new design is needed) • No need to focus western markets in the beginning • Satisfy needs of the mass markets – – – – Mahindra and Mahindra tractors, India Ranbaxy pharmaceuticals, India Orascom telecom, Egypt Embraer aerospece, Brazil • These firms have learned to make a profit at prices unheard of the developed countries due to mass marketing at low $ Firms from emerging markets • Acer • Bharti Airtel • Hailer • Lenovo • LG • QQ • Samsung • TATA move from OEM (1-5% margin) to leadership position (+40% margin) 76 Successful low-Cost providers to BOP 77 Sachet distribution in BOP markets 78 Not Free in BOP Yet But Will Be Soon 79 Multipoint Pricing for BOP -- Indonesia 80 Serve maximum # of segments – multi-point pricing 81 Demand for luxury products is very High in BOP Make it affordable by making it small Create aspiration value 82 How to add value? You must do something or have something new to say Commodity Goods Service Exp Then we do branding, positioning and communication 19 around it Patek Caliber $5m Most complicated watch X 2 Ferrari’s price! TATA Nano: $3,000 30 Sources of Growth Hermés Birkin named after Jane Birkin $9,000-$150,000 31 World’s slimmest watch 32 Hermés Cap Cod -Craftsmanship 33 Lamborghini ($445,000), 2013 model Ultra-light Lamborghini: $23,000 Where is the value coming from? 35 18 hours of single craftsmanship 36 British History – typical lines Gucci la pele Guccissima Shows mrf process Creating value online is even more important for transac Goal is to reduce abandoned carts with goods in it 87 IS BOP market suitable for your firm’s growth? 83 Source: Simanis (2012), HBR, June Strategy implementation in EMs • Leadership more involved – Socioeconomic • Low formal education and high unemployment – Culture • Highly embedded and hierarchical, risk avoidance • Organizational structure – More centralized and formalized is appropriate – Small team, and group reward, collective society • Intraorganizational relations – Social and relational identities • Rank, status, self esteem, well being > relations • Top managers available physically for guidance • Learning Five myths about EM! • EM are technology backwaters – I.e. Use outdated technologies; may not be true in case of cell phones • EM consumers won’t pay premium for brands – Brands affect preferences • EM cannot afford technology purchases – May not true in case of BRIC countries • Tech. from mature markets will succeed in EM – Develop new product with relevant feature – Nokia phone in India flashlight, individual call tracking for shared use of phones, multiple address book • EM consumers focus on products, not services Where are Emerging Markets? Emerging Markets Trading Blocks • Asia – Association of SouthEast Asian Nations (ASEAN) – Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) • Africa – Economic Council of West African States (ECOWAS) – Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) • South America – Mercosur (Mercosul) ASEAN: Asso. Southeast Asian Nations • Free Trade • 10 countries – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao, Malaysia, Mayamar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam • HO: Jakarta • ASEAN scholarship • ASEAN Univ.Network APEC: Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation • Eco. Growth & prosperity – Trade/invst Liberalization – Business Facilitation – Economic/tech cooperation • Important – 40% of world’s pop – 50% of world’s GDP – 40% of world’s trade • 21 countries – Australia, Brunei, Canada, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, NZ, Phil, Singapore, Thai, US, Taipei, HK, china, Mexico, PNG, Chile, Peru, USSR, Vietnam • HO: Singapore ECOWAS: Economic Council West African States • Economic integration – Mutual defense, court of justice – Ecowas rail, common currency 2015 – Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Nigeria, Sierra L • 15 countries – Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde Cote d’lvoire, Gambia, Ghana, GuineaBissau, Liberia, Mali, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Togo – Niger – suspended 2009– election problem – Guinea – suspended 2008 – coup attempt – Liberia wants to join Ecowas • HO: Abuja, Nigeria COMESA: Common Mkt for Eastern Southern Africa • Regional economic integration – Trade and investment • 19 countries – Burundi, Comoros, Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Eretria, Ethiopia, Kenya, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius Rwanda, Seychelles, Sudan, Swaziland Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe • HO: Lusaka, Zambia • Branding: Buy African, Build Africa • COMESA statistics MERCOSUR • Free trade and people movement • Full member – Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Urguay Venezuela (Paraguay to ratify) • Associate member – Bolivia, Chile, Columbia, Ecuador Peru • Observer – Mexico • HO: Sao Paula, Brazil