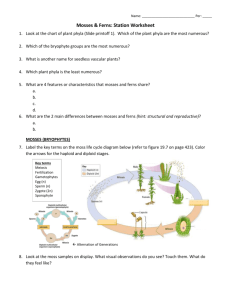
Moss / Fern
advertisement

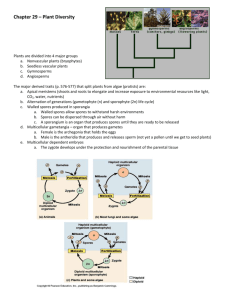
The Plant Kingdom • Origins 500- 475 MYA • 10 Phyla • 4 Basic lifecycles • Green algae that evolved onto land • Evolved becoming more terrestrial, independent from water • Then coevolved with pollinators, dispersal Tentative Phylogeny Fig 28.8 An overview of land plant evolution Land plants Vascular plants Figure 29.7 Angiosperms Origin of seed plants (about 360 mya) Origin of vascular plants (about 420 mya) Origin of land plants (about 475 mya) Ancestral green alga Seed plants Gymnosperms Pterophyte (ferns, horsetails, whisk fern) Seedless vascular plants Lycophytes (club mosses, spike mosses, quillworts) Mosses Hornworts Liverworts Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Lab • Chara Lifecycle • Moss Lifecycle – Liverworts • Fern Lifecycle – Lycophytes Charophyceans- plant’s green algae ancestor Chara - 30 Coleochaete- 31 Modern examples of charophyceans Chara sp. (green algae) Chara Slide #30 Oogonia Antheridia Chara sp. Oogonia Antheridia Alternation of Generations • Separate multicellular haploid and diploid phases – (2n) Sporophyte make spores by meiosis – (n) Gametophyte makes gametes by mitosis • Sperm and egg (moss & fern) • Pollen and Ovule (gymnosperm & angiosperm) • The sporophyte and gametophyte are very different in morphology – Vascular tissues only appear in sporophyte phase • Sporophyte becomes more dominant in new plant groups • Charophyceans lack sporophyte phase Characteristics that Plants share with the green algae group Charophyceans • Autotrophic Multicellular Eukaryote • Have cell walls made of cellulose – Made by rosette cellulose-synthesizing complexes – 20-26% of wall material, closest match in algae • Chloroplast similarities – have chlorophyll a & b, use β-carotene as accessory – Thylakoids stacked in grana – Chloroplast DNA comparisons Characteristics that Plants share with the green algae group Charophyceans • Peroxisome enzymes • Cell plate formation by phragmoplast • Nuclear membrane breaks down during mitosis • Sperm ultrastructure - biflagellate • Gene sequences – rRNA, Cytoskeleton proteins Switch to sporophyte dominance What’s new in Mosses? ( Derived Traits) • • • • • Spores / sporangia Sporophyte phase Upright growth on land Cuticle Multicellular gametangia The Bryophytes • Bryophytes are represented by three phyla: – Division Hepatophyta - liverworts – Division Anthocerophyta - hornworts – Division Bryophyta – mosses Liverworts and hornworts are believed to be more similar to what early plants were like. Bryophyte lifecycle: moss • Haploid dominant • No vascular tissues • Filamentous protonema stage • Swimming sperm • Disperse by spores • Dependent sporophyte • Dioecious gametophytes • No true leaves • Rhizoids, not roots Pteridophytes evolved over 400 MYA Seedless, Vascular plants (having Xylem & Phloem). Today represented by two phyla: Pterophyta: Ferns, Horsetails (Equisetum) Lycophyta: Club moss Cooksonia, an extinct plant over 400 million years old, is the earliest known vascular plant. Protonema Protonema - #32 Moss Antheridia Antheridia on stalk Moss Antheridia # 33 Moss Archegonia Moss Archegonia #34 Moss Archegonia #34 Moss Sporangia Moss Sporangia- 35 Moss Sporangia- # 35 An overview of land plant evolution Land plants Vascular plants Figure 29.7 Angiosperms Origin of seed plants (about 360 mya) Origin of vascular plants (about 420 mya) Origin of land plants (about 475 mya) Ancestral green alga Seed plants Gymnosperms Pterophyte (ferns, horsetails, whisk fern) Seedless vascular plants Lycophytes (club mosses, spike mosses, quillworts) Mosses Hornworts Liverworts Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) WALLED SPORES PRODUCED IN SPORANGIA Spores Sporangium Longitudinal section of Sphagnum sporangium (LM) Sporophyte Gametophyte Sporophyte and sporangium of Sphagnum (a moss) MULTICELLULAR GAMETANGIA Female gametophyte Archegonium with egg Antheridium with sperm Archegonia and antheridia of Marchantia (a liverwort) Male gametophyte MULTICELLULAR, DEPENDENT EMBRYOS Embryo Maternal tissue 2 µm Embryo and placental transfer cell of Marchantia 10 µm Wall ingrowths Placental transfer cell Liverwort Gametophyte Female Gametophyte Liverwort Antheridia • Antheridia are on the upper surface of the “umbrellas” Liverwort Antheridia Liverwort Archegonia • Archegonia are on the undersides of the “umbrellas” Liverwort Archegonia Liverwort Archegonia - egg Liverwort Sporangia • On undersides- develop from archegonia Gemmae & cups Gemmae & cup An overview of land plant evolution Land plants Vascular plants Figure 29.7 Angiosperms Origin of seed plants (about 360 mya) Origin of vascular plants (about 420 mya) Origin of land plants (about 475 mya) Ancestral green alga Seed plants Gymnosperms Pterophyte (ferns, horsetails, whisk fern) Seedless vascular plants Lycophytes (club mosses, spike mosses, quillworts) Mosses Hornworts Liverworts Charophyceans Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) Vascular tissue • Allows plants to grow taller • More support by lignified xylem tracheids • Can pull water up from soil – Can tolerate soil that is drier on the surface • Form parts of true leaves and roots. • Only found in diploid tissue – Lead to sporophyte dominance? Fern Lifecycle • Diploid dominate • Gametophyte still independent, short lived, – monoecious in fern (Pteridophyta) – dioecious in club “moss” (Lycophyta) • Spores disperse plant • Sporophyte perennial Pteridophytes evolved over 400 MYA Seedless, Vascular plants (having Xylem & Phloem). Today represented by two divisions: Pterophyta: Ferns, Horsetails (Equisetum) Lycophyta: Club moss Cooksonia, an extinct plant over 400 million years old, is the earliest known vascular plant. LYCOPHYTES (PHYLUM LYCOPHYTA) Strobili (clusters of sporophylls) Isoetes gunnii, a quillwort Selaginella apoda, a spike moss Diphasiastrum tristachyum, a club moss Psilotum nudum, a whisk fern PTEROPHYTES (PHYLUM PTEROPHYTA) Equisetum arvense, field horsetail Vegetative stem Athyrium filix-femina, lady fern Strobilus on fertile stem WHISK FERNS AND RELATIVES HORSETAILS FERNS Carboniferous forest based on fossil evidence Fern Gametophyte # 37 Fern Gametophyte # 37 Young Sporophyte #38 Vascular tissues in young frond Fern Antheridia Fern Arcghegonia Fern Sporangia - Sori Annulus Sporangium # 40 Indusium Whisk Ferns (formerly separate phylum: Psilophyta) Figure 29.13 Hypotheses for the evolution of leaves Vascular tissue (a) Microphylls, such as those of lycophytes, may have originated as small stem outgrowths supported by single, unbranched strands of vascular tissue. (b) Megaphylls, which have branched vascular systems, may have evolved by the fusion of branched stems. Horsetails – Equisetum sp. (formerly separate phylum: Sphenophyta) LYCOPHYTES (PHYLUM LYCOPHYTA) Strobili (clusters of sporophylls) Isoetes gunnii, a quillwort Selaginella apoda, a spike moss Diphasiastrum tristachyum, a club moss Psilotum nudum, a whisk fern PTEROPHYTES (PHYLUM PTEROPHYTA) Equisetum arvense, field horsetail Vegetative stem Athyrium filix-femina, lady fern Strobilus on fertile stem WHISK FERNS AND RELATIVES HORSETAILS FERNS Lycophyta Club “Moss” Strobilus • Not a moss !!! ( a common name) • Heterosporous – Meagsporania & Microsporangium – Form Strobili (cones) Selaginella – strobilus Microsporangium #41 Megasporangium 4 megaspores Many microspores Megaspore gametophyte Switch to sporophyte dominance