Minerals
advertisement

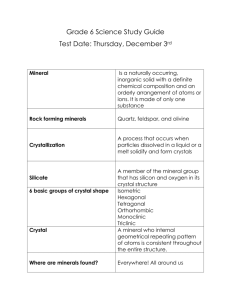
Chapter 2: Earth Materials Elements and Compounds • Element – Most fundamental substance into which matter can be separated by chemical means • Atom – Smallest single particle that keeps element’s distinct chemical properties – Protons (+) – Neutrons (neutral) – Electrons (-) – Net atom charge • Protons (+) + electrons (-) Elements and Compounds • Atomic number – # of protons • Atomic mass – # of protons + # of neutrons • Isotopes – Atoms with same atomic # but different mass # Elements & Compounds • Electron (-) – Electron “shells” – Ion – Cation (+) – Anion (-) Compounds, molecules and bonding • Compound – Combo of atoms from 1 or more elements in specific ratio • Molecule – Smallest unit with all properties of a specific compound • Bond – Force that holds together atoms in molecules &/or compounds Compounds, molecules & bonding • Ionic Bonding – 1 atom transfers electron to another • Gain or lose electrons – I.e. = Table salt (sodium chloride or NaCl) Compounds, molecules and bonding • Covalent Bond – Electrons from different atoms “pair up” & create bond • Share electrons – Strongest of chemical bonds Compounds, molecules and bonding • Metallic Bond – Electrons shared among several atoms • Outer electrons drift between atoms – Good conductors of heat & electricity Compounds, molecules and bonding • Van der Waals Bond – Attraction between electrically neutral molecules with asymmetrical charge • Dipolar molecules • Weak bonds • I.e. Water What Is a Mineral? • Mineral – – – – – Naturally formed Solid Inorganic Specific crystal structure Specific chemical composition Composition of minerals • Atomic substitution – Elements with similar size & charge can substitute for each other • Crystal structure – Atoms/molecules arranged into regular patterns – Mineraloid • Polymorphs – Same chemical composition but different crystal structure Telling minerals apart • Luster – Quality & intensity of light reflection • Metallic • Non-metallic – Vitreous – Resinous – Pearly Telling minerals apart • Crystal form – Any flat or planar surface that forms during mineral growth • Habit – Particular mineral’s distinctive shape Mineral Telling minerals apart • Hardness – Mineral’s resistance to scratching – Mohs scale (1-10) Hardness Talc 1 Gypsum 2 Image Common Objects Reference Fingernail (2.5) Calcite 3 Copper Penny (3.5) Fluorite 4 Wire Nail (4.5) Apatite 5 Glass (5.5) Feldspar 6 Streak Plate (6.5) Quartz 7 Topaz 8 Corundum 9 Diamond 10 Telling minerals apart • Cleavage – Mineral breaks in a regular pattern – Relates to crystal structure within mineral Telling minerals apart • Color – Least reliable • Light absorbed by mineral • Streak – Powdered trace of mineral made by rubbing specimen across unglazed porcelain piece Telling minerals apart • Density – Mass / volume – Compactness of atoms • Other mineral properties – Birefringent • Double images – Effervescence • Fizzes in acid – Magnetic • Attracted to magnet – Luminescence or fluorescence • UV “glow” Mineral families & their uses • Minerals of Earth’s crust – Silicate minerals • Minerals contain both silicon & oxygen – Silicon-oxygen tetrahedron • 1 Si atom bonded to 4 O atoms Mineral families & resources • Other minerals of Earth’s crust – Oxides – Carbonates • Ore deposits – Localized concentration that can be extracted profitably Rocks: A First Look • Rock Biotite Feldspar – Naturally formed aggregate of minerals & possibly other nonmineral matter – Record history of Earth processes Granite Quartz Rocks: A First Look • Igneous – Form by cooling & solidification of molten rock • Magma • Sedimentary – Form under conditions of low pressure & low temperature near the surface • Metamorphic – Altered by exposure to high temperature, high pressure or both