Minerals - LiveText
advertisement

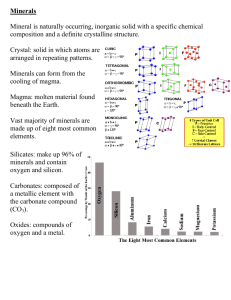
Minerals What is a mineral? • Naturally occurring, inorganic solid, with a specific chemical composition and a definite crystalline structure Mineral Characteristics • Earth’s crust is composed of 3,000 minerals. • Forming of rocks and shaping Earth’s surface. • Example: early humans began making tools from iron. • Minerals are formed by natural processes. • Can not be developed in labs – Exp: synthetic diamonds • They are not alive and never were alive. What’s a mineral and what’s not a mineral? • Salt is a mineral • Sugar is not, because its harvested from plants. • What about coal? What’s a mineral and what’s not a mineral? • Salt is a mineral • Sugar is not, because its harvested from plants. • What about coal? – No, millions of years ago it formed from organic materials. Crystalline structure • Crystal is a solid which atoms are arranged in repeating patterns • A mineral can form in an open space and grow into a large crystal Composition of solids • Each type of mineral has its own unique chemical composition. • Some might be specific – Copper, Silver, and Sulfur are single elements • others might be complex – Quartz (SiO2). Combination of 1 Silicon atom and 2 Oxygen atoms. Rock Forming Minerals • Of the 3,000 minerals occur in Earth’s crust, about only 30 are common. • 8 -10 are rock forming minerals • Composed of 8 common elements in Earth’s crust – Quartz – Feldspar – Mica – Pyroxene – Amphibole – Olivine – Garnet – Calcite Minerals from magma • Magma forms below Earth's surface, and rises toward the surface because its less dense. • Magma then cools and crystallizes • If magma cools slowly, atoms have time to arrange into large crystals • If magma reaches water or air and cools quickly, small crystals form Minerals from solutions • Most dissolve in water. – Such as salts dissolving in the ocean to make it salty • Minerals that form from the evaporation of liquid is called evaporites Identifying Minerals • Geologists use several tests to identify minerals – Crystal form – Luster – Hardness – Cleavage & Fracture – Streak – Color – Texture – Density & Specific gravity – Special properties