Identifying Minerals
advertisement

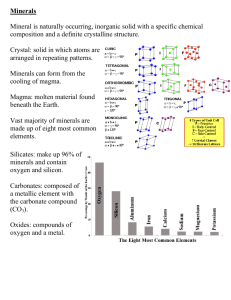
Essential Questions • How are minerals defined? • How do minerals form? • How are minerals classified? Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Vocabulary Review New • • • • • • • • • element Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education mineral crystal luster hardness cleavage fracture streak specific gravity What is a mineral? Mineral Characteristics • Earth’s crust is composed of about 3000 different minerals that play important roles in forming rocks and in shaping Earth’s surface. • A mineral is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid, with a specific chemical composition and a definite crystalline structure. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Mineral Characteristics Naturally occurring and inorganic • Minerals are naturally occurring, meaning that they are formed by natural processes. • All minerals are inorganic: they are not made from living organisms. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Mineral Characteristics Definite crystalline structure • The atoms in minerals are arranged in regular, repeated, geometric patterns that result in the formation of a crystal. • A crystal is a solid in which the atoms are arranged in repeating patterns. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Mineral Characteristics Solids with specific compositions • Minerals are solids and therefore have definite shapes and volumes. • Each type of mineral has a chemical composition unique to that mineral. • A few minerals are composed of single elements; however, the majority are made from compounds. • In some minerals, such as varieties of feldspar, chemical composition can vary within a certain range, depending on the temperature at which the mineral crystallizes. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Rock-Forming Minerals • Eight to ten of the 30 most common minerals are referred to as rock-forming minerals because they make up most of the rocks in Earth’s crust. • Rock-forming minerals are primarily composed of the eight most common elements in Earth’s crust. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Rock-Forming Minerals Minerals from magma • Molten material that forms and accumulates below Earth’s surface is called magma. • Magma is less dense than the surrounding solid rock, so it can rise upward into the cooler layers of Earth’s interior, where it cools and crystallizes. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Rock-Forming Minerals Minerals from magma • The type and number of elements in the magma determine which minerals will form. • The rate at which the magma cools determines the size of the mineral crystals. Small crystals form from rapidly cooling magma, and large crystals form from slowly cooling magma. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Rock-Forming Minerals Minerals from solutions • A liquid is saturated when it becomes full of a dissolved substance and can dissolve no more of that substance. • If more of the substance is added to a saturated solution, it is called supersaturated, and mineral crystals form into solids from the solution. • Minerals that form from the evaporation of the liquid in which they were dissolved are called evaporites. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals • Geologists identify minerals using tests based on a mineral’s physical and chemical properties: crystal form, luster, hardness, cleavage, fracture, streak, color, specific gravity, texture, density, and special properties. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Crystal form • Some minerals form such distinct crystal shapes that they are immediately recognizable. • However, perfect crystals are not always formed, so identification based only on crystal form is rare. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Luster • The way that a mineral reflects light from its surface is called luster. • There are two types of luster—metallic luster and nonmetallic luster. • Luster should usually be used in combination with other physical characteristics to identify a mineral. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Hardness • Hardness is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. • German geologist Friedrich Mohs developed a scale by which an unknown mineral’s hardness can be compared to the known hardness of ten easily recognized minerals that, with the exception of diamond, are readily found in nature. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Cleavage and fracture • A mineral that splits relatively easily and evenly along one or more planes of weak atomic bonds is said to have cleavage. • To identify a mineral based on its cleavage, geologists count the number of cleaved planes and study the angle or angles between them. • Minerals that break with rough, arclike, or jagged edges because of their tightly bonded atoms are said to have fracture. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Streak • Streak is the color of a mineral when it is broken up and powdered. • The streak test, which typically involves rubbing the mineral against an unglazed porcelain plate, is most useful in identifying metallic minerals. It can be used only on minerals that are softer than the porcelain plate. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Color • Color is one of the most noticeable characteristics of a mineral. • It is also one of the least reliable clues of a mineral’s identity. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Special properties • Several special properties of minerals can also be used for identification purposes. Some of these properties are magnetism, iridescence, double refraction, effervescence with hydrochloric acid, and fluorescence. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Texture • Texture describes how a mineral feels to the touch, and, like luster, it is subjective. It is often used in combination with other tests to identify a mineral. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Density and specific gravity • Two minerals of the same size may have different weights due to a difference in density. • Density reflects the atomic mass and structure of a mineral. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Density and specific gravity • 𝑀 Density is expressed as D = 𝑉 where D = density, M = mass, and V = volume. • Because density is not dependent on the size or shape of a mineral, it is a useful identification tool. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Identifying Minerals Density and specific gravity • The most common measure of density used by geologists is specific gravity, the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of an equal volume of water at 4°C. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What is a mineral? Review Essential Questions • How are minerals defined? • How do minerals form? • How are minerals classified? Vocabulary • mineral • crystal • luster Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education • hardness • cleavage • fracture • streak • specific gravity What is a mineral?