Year 9 Scheme of Learning
advertisement
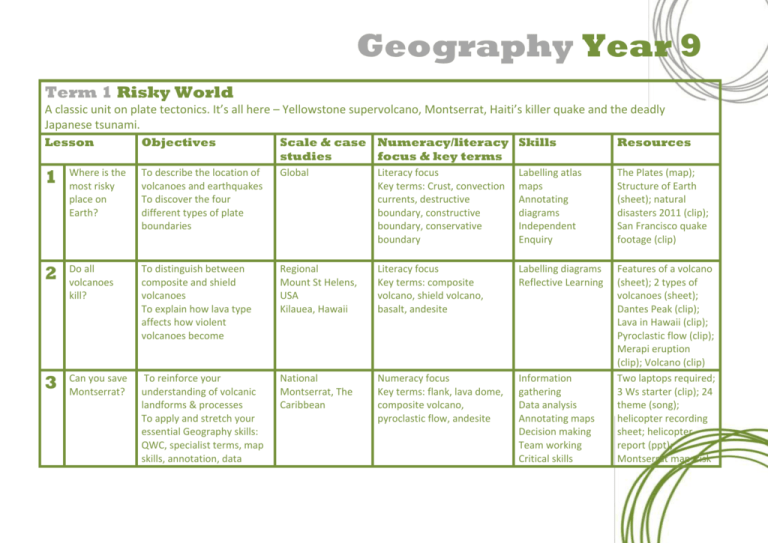
Geography Year 9 Term 1 Risky World A classic unit on plate tectonics. It’s all here – Yellowstone supervolcano, Montserrat, Haiti’s killer quake and the deadly Japanese tsunami. Lesson Objectives Scale & case Numeracy/literacy Skills studies focus & key terms Resources 1 Where is the most risky place on Earth? To describe the location of volcanoes and earthquakes To discover the four different types of plate boundaries Global Literacy focus Key terms: Crust, convection currents, destructive boundary, constructive boundary, conservative boundary Labelling atlas maps Annotating diagrams Independent Enquiry The Plates (map); Structure of Earth (sheet); natural disasters 2011 (clip); San Francisco quake footage (clip) 2 Do all volcanoes kill? To distinguish between composite and shield volcanoes To explain how lava type affects how violent volcanoes become Regional Mount St Helens, USA Kilauea, Hawaii Literacy focus Key terms: composite volcano, shield volcano, basalt, andesite Labelling diagrams Reflective Learning 3 Can you save Montserrat? To reinforce your understanding of volcanic landforms & processes To apply and stretch your essential Geography skills: QWC, specialist terms, map skills, annotation, data National Montserrat, The Caribbean Numeracy focus Key terms: flank, lava dome, composite volcano, pyroclastic flow, andesite Information gathering Data analysis Annotating maps Decision making Team working Critical skills Features of a volcano (sheet); 2 types of volcanoes (sheet); Dantes Peak (clip); Lava in Hawaii (clip); Pyroclastic flow (clip); Merapi eruption (clip); Volcano (clip) Two laptops required; 3 Ws starter (clip); 24 theme (song); helicopter recording sheet; helicopter report (ppt); Montserrat map; risk Geography Year 9 analysis & decision making 4 Supervolcano – the end of the world? To describe the features of supervolcanoes To explain how they form To understand their potential global effects Regional Yellowstone Caldera, USA Literacy focus Key terms: caldera, magma chamber, Yellowstone USA 5 How close did we come to a global nuclear meltdown? To explain how earthquakes are created To discover their impact and how people responded in Japan Global/National Japan earthquake Fukushima Literacy focus Key terms: Focus, epicentre, magnitude, Richter scale, nuclear meltdown 6 How do tsunamis form? To explain how tsunamis are created To discover their impact and how people respond National Japan tsunami Literacy focus Key terms: Tsunami, drawback, megathrust, train 7 Assessment To assess and level students’ progress Extracting information from sources Interpreting maps Drawing and labelling diagrams Extracting information from sources Drawing diagrams Sketching and labelling maps Extracting information from sources Independent enquiry Humanities Independent Project (HIP) accessed via blog ‘As an employee of USGS (United States Geological Survey) you have been asked to write a report on a hazard of your choice’. assessment (sheet); teacher notes 2012 eruption (clip); Mega Disasters (documentary); documentary sheet and notes; supervolcano sheet BBC This World 2012 Inside Fukushima (documentary); Fukushima sheet; raw footage (clips x2); Japan’s Tsunami Caught on Camera (documentary) How the Japan tsunami happened (video and sheet); Japan tsunami (sheet); clips x2 Geography Year 9 Term 2 Conflicted World A unit on population change and conflict. We start by looking at how the UK’s population has changed through time. We then look to conflict zones around the world to discover how war, drug trafficking and religion has affected populations. Lesson Objectives Scale & case studies Numeracy/literacy Skills focus & key terms Resources 1 How does a country’s population change through time? To discover how the UK’s population has changed through time To understand the factors that affect birth rate International/national UK Numeracy focus Key terms: Birth rate, death rate, natural increase, population density Choropleth map (sheet); population UK (clip, sheet & notes); birth and death rate clip, 7 billion clip 2 How do war, heroin and religion affect Afghanistan’s population? National Afghanistan Numeracy focus Key terms: Population structure, population pyramid, opium, Shariah Law 3 How did genocide affect Rwanda’s population? To compare the population structure of the UK with Afghanistan To discover the impact of war, heroin and religion on population structure To discover the dark history behind Rwanda’s genocide To explain the affect the genocide had the population structure of Rwanda To understand what is meant by forced migration National Rwanda Numeracy focus Key terms: Genocide, Hutu, Tutsi, forced migration Choropleth mapping Extracting information from sources Independent enquiry Drawing and labelling sketch maps Interpreting population pyramids Extracting information from sources Interpreting line graphs and population pyramids Population structure (sheet); Afghan farmers and traffickers (clips x2) Rwanda (sheet & clip) Geography Year 9 4 Who are asylum seekers? 5 Who’s taken all the jobs? 6 Assessment To explain why people are forced to seek asylum To understand the effects asylum seeking has on the UK To discover why people move from Poland to the UK To understand the benefits and the drawbacks National Iraq Literacy focus Key terms: Immigration, asylum seeking, country of origin, destination country International/regional EU Poland UK Peterborough Numeracy focus Key terms: Economic migration, migrant worker, EU, standard of living Decision making Extracting information from sources Reflective learning Interpreting choropleth maps Communicate information clearly Form opinions, debating Asylum seeking pros and cons (sheet); Iraq (clip) Polish People in the UK (clips x3); Polish migration (sheet) To assess and level students’ progress Humanities Independent Project (HIP) accessed via blog ‘You work for the United Nations (UN). You have been asked to create a report on the affect of conflict on a country’s population. This could be a report on Afghanistan, Rwanda, Iraq or any other conflict zone’. Geography Year 9 Term 3 Urbanised World An introduction to the global growth of urban areas. The unit covers the phenomenon of rural to urban migration, the growth of squatter settlements and their problems and ends with a look at sustainable cities. Lesson Objectives Scale & case studies Numeracy/literacy Skills focus & key terms Resources 1 What is meant by an urbanised world? Global Miami, USA Numeracy focus Key terms: Urban , rural, urbanisation, rural to urban migration, bright light syndrome Extracting information from sources Interpreting atlas maps, comparative line, pie charts and bar graphs Two faces of Miami (video); Internal migration (sheet); maps of an urbanising world (sheet); The True Miami (sheet) 2 What is a megacity? To explain what is meant by urbanisation To discover the reasons why so many people are moving from rural areas to the city To understand what is meant by bright light syndrome To locate the world’s megacities To describe the features of a megacity To discover what life is like in the world’s biggest cities National Shanghai, China Mexico City, Mexico Tokyo, Japan London, UK Dhaka, Bangladesh Literacy focus Key terms: Megacity, rural, urban, migration Interpreting atlas maps Extracting information from sources 3 What is life like in squatter settlements? To explain how rapid urbanisation leads to squatter settlements To discover what life is like there Regional Rocinha, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Literacy focus Key terms: Squatter settlement, slum, rapid urbanisation Interpreting photographs Creative thinking Team work Andrew Marr’s Megacities: Living in the Megacity (video, sheet and notes); World map (pdf); Megacities (sheet and table) Reflection (sheet); Rocinha (sheet); sensogram (sheet); starter (sheet) Geography Year 9 4 What are the problems of living in squatter settlements? To discover how people living in a squatter settlement in Bhopal, India were suffocated as they slept. Regional Bhopal, India Literacy focus Key terms: Transnational corporation, Union Carbide, Methyl Isocynate, asphyxiation 5 Can cities be made to be more sustainable? To discover how some cities are being built with the environment in mind To understand how Bristol and Curitiba are sustainable cities Regional/local London Bristol Masdar, Abu Dhabi Literacy focus Key terms: Hydrogen, public transport, sustainable, zero emissions 6 Assessment To assess and level students’ progress Extracting information from sources Drawing and labelling sketch maps Extracting information from sources Creative thinking Team work Humanities Independent Project (HIP) accessed via blog ‘Bristol City Council have asked you to create a plan to make their city more sustainable’. Bhopal Gas Tragedy (video); Bhopal report; Bhopal disaster (clip starter) Bristol Green Capital (sheet); Cycling city (x3 clips); London’s Hydrogen buses (sheet & clip); Top Gear hydrogen car (clip); Masdar (sheet) Geography Year 9 Term 4 Flooded World A wet and watery tour of global flooding. We start by looking at the flood hydrograph and the factors affecting river discharge. We revisit Boscastle and Pakistan and end by taking a look at the world’s largest dam – The Three Gorges in China. Lesson Objectives Scale & case studies Numeracy/literacy Skills focus & key terms Resources 1 What is a flood hydrograph? National Toowoomba, Australia Numeracy focus Key terms: Flash flood, hydrograph, discharge, lag time, peak discharge, peak rainfall Interpreting hydrographs Annotating maps Student hydrograph sheet (ppt slide); Toowoomba clips x2; Toowoomba mapping the causes (ppt); train vs flood (clip) 2 What are the causes of flooding? To explain what is meant by the term flash flood To label the features of and be able to read a hydrograph To explain how different factors affect river discharge To model flood events To understand what conditions cause flooding Regional/National Taroko Gorge, Taiwan Indonesia Literacy focus Key terms: Surface runoff, deforestation, v shaped valleys, impermeable Cress, tables, water bottles, scissors, plates Taroko flood (clip); Indonesia flood (clip) 3 Why was Boscastle washed out? To explain the causes of a flash flood To describe the impacts and responses to the floods in Boscastle Regional Boscastle Numeracy focus Key terms: saturated, interception, steep slopes, impermeable, confluence Modelling Extracting information from sources Team work Creative thinking Interpreting photographs Interpreting OS maps Six and four figure grid references Boscastle (video, sheet and notes); Boscastle Flash Floods (sheet); footage (clips x2); Boscastle map (ppt slide) Geography Year 9 4 Why did Angelina Jolie visit refugees in Pakistan? 5 Why did China flood 13 cities, 140 towns and over 1000 villages? Assessment 6 To discover how the monsoon lead to flooding in Pakistan To understand why it took so long to save people and why so many died To know why the Three Gorges Dam was built To discover the impact that the dam has had Pakistan Afghanistan Kashmir Literacy focus Key terms: monsoon, aid, cholera, refugees Annotating maps Extracting information from sources Pakistan map; Pakistan Press Report (sheet); Flooding clips (x2) Three Gorges Dam, China Literacy focus Key terms: relocation, environmental, social, reservoir Extracting information from sources Three Gorges Dam (sheet x2); dams in films (sheet); Goldeneye (clip); Ungorgeous China (video); news clip To assess and level students’ progress Humanities Independent Project (HIP) accessed via blog ‘The MET Office has asked you to create a report of a flood of your choice’. Geography Year 9 Term 5 Warming World An introduction to global warming and the impact on our coastal zones. We take a look at the disappearing island of Tuvalu and the storm surges that threaten New Orleans. We end by studying the Thames Barrier and the defence it gives to London. Lesson Objectives Scale & case studies Numeracy/literacy Skills focus & key terms Resources 1 What is global warming? To distinguish between climate change and global warming To explain the factors are causing global warming Global Numeracy focus Key terms: Greenhouse gases, atmosphere, climate change, global warming Ranking Interpreting line graphs Drawing and labelling diagrams Extreme weather cards (laminated); Global warming (sheet); Global warming clips x3; climate change (video) 2 Why are our oceans and seas rising? To know by how much our seas are expected to rise To explain the phenomena of thermal expansion, glacier melting and postglacial rebound Global The Maldives, Indian Ocean Literacy focus Key terms: Sea level rise, thermal expansion, glacier melt Extracting information from sources 3 Why are people fleeing Tuvalu? To discover why Tuvalu is at the forefront of sea level rise To outline the impacts of Regional Tuvalu, Polynesia Literacy focus Key terms: Salt water intrusion, coral bleaching, forced migration Team working Reflective learning Extracting information from Which cities will flood? (infographic); Greenland melt (clip); Day After Tomorrow (clip); Maldives cabinet (clip); thermal expansion (clip); Simon Reeve Maldives (full episode) Twelve Tuvalu Questions (sheet and notes); how to get rescued from an Geography Year 9 sea level rise on the island sources 4 Was Katrina created by global warming? To discover how Hurricane Katrina flooded New Orleans To explain the link between hurricanes, storm surges and global warming Regional New Orleans Numeracy focus Key terms: Storm surge, hurricane, low pressure 5 Is London threatened by rising sea levels? Regional London Literacy focus Key terms: Storm surge, Thames barrier, floodplain 6 Assessment To discover how the Thames Barrier operates and protects the capital To comprehend the cost of coastal flooding and the costs of defending against it To assess and level students’ progress Tracking the path of a storm Longitude and latitude Grid references Sorting information Interpreting maps Extracting information from sources island (starter clip); Tuvalu clips (x2) Hurricane Katrina (tracking sheet); Atlantic Chart (pdf); Katrina introduction sheet; card sort (sheet) Flood (clip); BBC Five Disasters Waiting to Happen (video, sheet and notes); 1953 newsreel (clip) Humanities Independent Project (HIP) accessed via blog ‘You work for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). You have been asked to create a report on the impacts of rising sea levels on different parts of the world’. Geography Year 9 Term 6 Extreme World An overview of adventure tourism. We start by looking at extreme environments and adventure activities. We head to Blue Canyon Utah, Antarctica and Kenya. Two major heroes make an appearance too – Aaron Ralston and Ed Stafford. Legends. Lesson Objectives Scale & case studies Numeracy/literacy Skills focus & key terms Resources Extreme environments (sheet); Extreme Top Ten (sheet & clip); Bear Grylls (x2 clips); Anaconda hunter (clip) 127 Hours (trailer); 127 Hours (full film); Aron Ralston (clip); Aron Ralston story (sheet) Antarctica extreme environments (sheet); MS Explorer clips (x2); Bird Island (clip); Frozen Planet Maroon 5 (clip); Frozen Planet (full episode) Kenya Tourism Exposed full 1 What is an To understand what makes extreme an extreme environment environment? To know what is meant by adventure tourism To understand why it as a sector is growing National Venezuela, South America Sahara, South Africa Iceland Numeracy focus Key terms: Extreme environment, adventure tourism, DINK Interpreting bar and line graphs Extracting information from sources 2 Why did Aron Ralston cut his arm off? Regional Blue John Canyon Utah, USA Literacy focus Key terms: Niche market, DINK, canyon, adventure tourism Extracting information from sources 3 How is Antarctica being affected by tourism? To describe the profile of an adventure tourist To retrace the events of a very fateful adventure holiday To discover what Antarctica is like To describe its attractions To understand the impacts of tourism on its ecosystems National Antarctica Literacy focus Key terms: IAATO, SSSI, management, MS Explorer Interpreting pie charts Extracting information from sources 4 What are the problems of To discover the problems that mass tourism can National Mombasa Literacy focus Key terms: mass tourism, Annotating maps Extracting Geography Year 9 mass tourism in Kenya? 5 6 bring To explain the impacts of tourism on Kenya What is To discover how safaris are ecotourism? going to change in Kenya And why is Ed To understand what is an eco-head? meant by ecotourism by taking a look at Ed Stafford Assessment To assess and level students’ progress Masai Mara National Park, Kenya International/national Kigio Conservancy, Kenya The Amazon safari, honeypot sites, Mombasa, Masai Mara Game Park Literacy focus Key terms: ecotourism, sustainable tourism information from sources documentary (video, sheet and notes) Report writing Extracting information from sources You are a wimp compared to Ed Stafford (sheet); Ed Stafford website Humanities Independent Project (HIP) accessed via blog ‘You work for BBC Three. Write an article exposing the darker side of mass tourism in Kenya, East Africa to go alongside Stacey Dooley’s documentary. Outline the specific problems of tourism and suggest a way forward’.