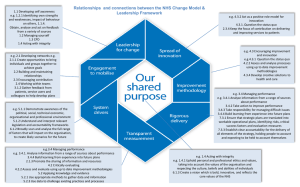
PPT_Develop_new_products_&_ser_refined
advertisement

DEVELOP NEW PRODUCTS AND SERVICES D1.HCS.CL6.07 Slide 1 Subject elements This unit comprises four elements: Analyse markets Evaluate market trends in food production and/or food and beverage service Create products or services based on market analysis and within budgetary constraints Monitor sales performance of products and services Slide 2 Assessment Assessment for this unit may include: Oral questions Written questions Work projects Workplace observation of practical skills Practical exercises Formal report from supervisor Slide 3 Element 1: Analyse markets Slide 4 Analyse markets Performance criteria for this element are: Target markets are identified in accordance with enterprise marketing and merchandising policies Analyse market competition Client requirements are monitored informally in order to evaluate market trends and client needs New products and services are identified Slide 5 Analyse markets Performance criteria for this element are: Opportunities to improve sales and services are identified Product and service range is monitored to identify the demand for individual items and seasonal variations Product and service range is planned Slide 6 Need for new products and services Need for new products and services It is normal practice for businesses, regardless of industry, to develop and introduce new products and services. This may include: Improvements to existing offerings Complete changes of direction Slide 7 Need for new products and services Need for new products and services New products and services will only be successful if: It is unique when compared with competitor’s offerings It provides value for money The customer views the product or service as valuable in their eyes Slide 8 Need for new products and services Examples of new products and services What have been successful new products and services that have entered: Generally The hospitality industry specifically? Slide 9 Change A rolling stone gathers no moss! Slide 10 Change What is change? Why is it important? What influences change Change is inevitable Slide 11 Continuous improvement What is it? Why is it important? Who is responsible for implementing it? Slide 12 Continuous improvement Regardless of their visit it is important that the customer receives a ‘quality offering’ A quality offering is being able to use a combination of products and services This combined offering, at a minimum, must meet the customer’s: Needs Expectations Slide 13 Continuous improvement Need for continuous improvement Continuous improvement and change focuses on improving: Products Services Slide 14 Continuous improvement Products and Services Which is more important – product or service? What do these include? Which aspects can be improved? Slide 15 The customer The customer is............ Slide 16 Market segments Identify market segments Any hospitality organisation, like in any business in any industry, cannot be everything to everyone. It must: Break down the potential audience into segments with similar characteristics Choose those segments they believe will be the focus of their efforts Slide 17 Market segments Generic market segments Age Social background Economic background Cultural background Special interests Physical and mental abilities Dietary needs Slide 18 Market segments Hospitality market segments Business Leisure Religious Sporting Slide 19 Market segments Tourism market segments Outbound Tourists Inbound Tourists Domestic Tourists International Tourists Slide 20 Target market segments Identify target market segments What are the key target segments for: Resorts City hotels Budget accommodation Stand alone restaurants Fine dining restaurant in a hotel Corner bar Coffee shop? Slide 21 Target market segments Benefits of establishing target market segments The analysis and collection of information in relation to different target market segments will guide: Products and services offered Prices charged Where advertisements are placed How advertisements are targeted Staff required Slide 22 Analyse market competition Importance of analysing the market? What do you want to analyse? What information do you seek? Where do you get this information? Slide 23 Analyse market competition What is market analysis? Market analysis provides us with the information necessary to understand what can cause changes in our operational environment A prime intent of this activity is to gain a more insightful and detailed view of the organisation and where it sits in the overall business and other settings Helps identify ‘current market situation’ Slide 24 Current market situation Market situation Total market characteristics – size, growth, trends Customer needs, perceptions and buying behaviour Products – service characteristics Prices Customer service and distribution Channels Communication Slide 25 Current market situation Competitive situation Industry structure The geographic market in which they compete Their current marketing performance Their competitive position Strengths and weaknesses, and vulnerabilities of each significant competitor Their objectives and competitive strategies Industry profitability Slide 26 Current market situation Product situation For each product/service that the organisation offers, sales, profits, contribution margins and growth should be displayed Product lifecycle and expected demand over the product’s life should be considered Growth of the product/service should be contrasted with total market growth Slide 27 Situation Analysis Analyse the environments It is vital to understand what can cause changes in our operational environment. It is important that managers analyse what is happening both: Outside the business (external environment) Inside the business (internal environment) Slide 28 Analyse the environments SWOT analysis Strengths – what the business does well Weaknesses – what the business can improve upon Opportunities – where the business can improve or take advantage Threats – where the business may become disadvantaged, weakened or susceptible Slide 29 Analyse the environments Analysis of external environment Competitors Economic climate Customer preferences E-business Slide 30 Analyse the environments Analysis of external environment Environment Technology Political issues Legal issues What other external influences exist? Slide 31 Analyse the environments Analysis of internal environment Environment Organisational structure Products Services Equipment Marketing Slide 32 Customer focus Before we can tailor our products and services to provide an offering that the customer wants, we first need to find out what they actually want Many businesses make the mistake of providing an offering they THINK the guest wants, but what is offered doesn’t meet their needs Slide 33 Customer focus Who are your customers? What are the needs of your customers? How do you identify their needs? Slide 34 Customer needs Generic needs Value for money ‘Offering’ reflecting what was advertised Expectations met/exceeded To feel respected To feel welcomed To be served by friendly staff Slide 35 Customer needs Generic needs To be dealt with in a prompt and courteous manner To receive assistance when necessary To be in comfortable, clean surroundings To feel remembered and recognised To be heard and understood Slide 36 Customer needs Specific needs What are the specific needs of your markets? Business Women Family Leisure Elderly Others Slide 37 Expectations Expectations come from: The company’s image or reputation in the market Past visits Advertisements and promotional messages Competing hotels Industry standards Comments from family, friends and colleagues Price charged for the offering Slide 38 Identify new products and services As mentioned, an ongoing process for a hotel to stay ‘fresh, unique and in demand’ is to identify new products and services to attract and maintain customers. In hospitality the product/service offering is combined to meet customer needs and consists of the following elements: A tangible product or products Environment Services Slide 39 Identify new products and services Products What is classified as a product? What are examples of products in the hospitality environment? Slide 40 Identify new products and services Services What is classified as a service? Who provides the service? What are examples of services in the hospitality environment? Slide 41 Identify new products and services Characteristics of services Pure services are activities or benefits characterised by: Intangibility Inseparability Perishability Variability Slide 42 Opportunities to improve sales and services Need to identify improvement opportunities The need to identify opportunities for improvement is especially important when new products and services are introduced as new opportunities may become apparent as they are implemented into the marketplace: How can you do this? Slide 43 Opportunities to improve sales and services Ways to identify improvement opportunities Observing what occurs in the workplace Develop and use a checklist to guide what you observe Involve workers in your observations Analysing documentation Slide 44 Opportunities to improve sales and services Ways to identify improvement opportunities Being advised by management/owners Monitoring the external business environment Making ‘improvement/continuous improvement (CI)’ a standing topic in every staff meeting Involving staff Slide 45 Generate ideas Generating ideas How would you generate ideas? Why is it important to involve staff in the process? Slide 46 Generate ideas Common techniques to generate ideas include: Talking to colleagues and supervisors Looking at what happens in other venues Contacting industry peak bodies Reading industry literature Conduct internet research Using creative thinking techniques Slide 47 Generate ideas Creative thinking techniques Brainstorming Visualising Making associations Lateral thinking Six thinking hats Slide 48 Generate ideas Use relevant knowledge In addition to creative thinking ideas, there is always the need to apply relevant knowledge to a situation where workplace improvements are being considered: Technical knowledge Service-based knowledge Information from different work areas Information from colleagues Slide 49 Review ideas Review ideas for relevance and practicality When you have captured ideas and information relating to them your next step is to review and evaluate these ideas. Slide 50 Review ideas Review ideas for relevance and practicality This allows you to: Make legitimate and rational decisions about the options which were generated. Evaluating the alternatives to determine: Which ones remain as viable alternatives Which ones should be discarded as inappropriate Slide 51 Review ideas Practicality considerations Impact on other existing house protocols, policies and procedures Impact on layout Staff ability Expected revenue Cost Impact on service delivery Slide 52 Monitor and identify demand for products and services Once new products and services have been identified it is important to identify the demand for specific items and any seasonal variations that may affect it How can you do this? Slide 53 Monitor and identify demand for products and services Product and service lifecycles When deciding on the introduction of products and services it is important to understand how long they will have a positive and profitable impact. Most products and services will have some lifecycle. This lifecycle is divided into four stages: Market introduction Market growth Market maturity Sales decline Slide 54 Monitor and identify demand for products and services Identifying demand for individual products and services Observation Conduct a trial run Place an advertisement Suppliers Industry associations Journals and articles Other hotels in the chain Competitors Feasibility study Slide 55 Monitor and identify demand for products and services Understand seasonal demand Ways to identify seasonal demand include: Analyse historical data Review sales figures The level of demand for specific products and services at different times Identify expected peak times Identify expected low demand times Slide 56 Planning product and service range Once ideas for products and services have been identified as a concept, further thought must be given as to how it is to be introduced into the market: What are product considerations? What are service considerations? Slide 57 Planning product and service range Product considerations Product line decisions Packaging Warranties Branding Brand rejection Slide 58 Planning product and service range Service considerations Intangibility Inseparability Perishability Variability Slide 59 Element 2: Evaluate market trends in food production and/or food and beverage service Slide 60 Evaluate market trends in food production and/or food and beverage service Performance Criteria for this Element are: Identify and access information sources on market trends in food production and/or food and beverage service Evaluate market trends for relevance to the enterprise current and potential markets Identify and access relevant information to assist development of new products or services Slide 61 Understanding trends Identify and access information sources on market trends Understanding trends of the industry is vital in ensuring that what you are seeking to provide to the market is not only fresh and relevant but is in demand: How can you gather information on industry trends? Slide 62 Understanding trends Types of information sources Colleagues, supervisors and managers Representatives Developing your own industry network Conferences and seminars Product launches Trade magazines Slide 63 Understanding trends Types of information sources Hotel school publications Newsletters Brochures Advertisements Government bodies Slide 64 Understanding trends Types of industry statistics and trends Industry Statistics General industry trends Tourism patterns Technology Leisure time Slide 65 Understanding trends Types of industry statistics and trends Environmental issues Discount operators Customer demands Quality demands Slide 66 New product and service development Every hospitality business conducts product and service development, whether it's done intentionally or unintentionally This section will explore some of the steps associated with product and service development Slide 67 New product and service development Risks in new product and service development Developing a new product or service first and hoping it will sell Financial risks Duplication from competitors The time taken to develop new products or services, particularly in fast moving industries Slide 68 Steps in product and service development New product or service development process steps Idea generation Screening Idea evaluation Development - technical and commercial Commercialisation Slide 69 Element 3: Create products or services based on market analysis and within budgetary constraints Slide 70 Create products or services based on market analysis and within budgetary constraints Performance criteria for this element are: Incorporate relevant market trends into food service and menu planning Develop products and services to take account of market trends Develop products and services to take account of enterprise operational constraints or limitations Construct products and services to meet profitability targets Slide 71 Incorporate trends into menu planning Types of menus Table d’hôte À la carte Banquet Conferences Slide 72 Incorporate trends into menu planning Types of services Breakfast: Continental English breakfast American Eastern Morning tea Brunch Slide 73 Incorporate trends into menu planning Types of services Lunch Afternoon tea High tea Dinner Supper Slide 74 Menu constraints Menu length Cost to maintain each dish on the menu Ready availability of ingredients Time available to prepare ingredients Slide 75 Menu layout trends Entrée 6 or 8 offerings Mains One or two of each of the main foods: Beef, lamb, chicken, fish, seafood, vegetarian options Slide 76 Menu layout trends Side orders Potato dish (hot) Green vegetable (hot) Salad (cold) Desserts Chocolate flavoured Citrus flavoured Hot dessert Cold dessert (ice cream) Slide 77 Menu layout trends Cheese plate Cheddar, brie, blue cheese Coffee and tea selection Local styles are popular Italian style coffee Wide variety of tea Slide 78 Menu balance Balance in terms of: Prices Ingredients Cooking styles Complexity and simplicity Traditional dishes New experiences Taste Slide 79 Final menu considerations Considerations Personal likes and preferences of the owner/manager Equipment available in the kitchen Staff skills Historic records Market research Slide 80 Final menu considerations Considerations Seasonal offering Staff numbers Contractual requirements Demographic considerations Local produce Slide 81 Develop products and services in line with market trends Food and beverage trends What are different food and beverage trends around the world? Refer to Manual on pages 77 – 83 for examples Slide 82 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Organisational requirements Access and equity principles and practices Maintaining ethical standards Meeting goals, objectives, plans, systems and processes Legislated obligations Slide 83 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Organisational requirements Management and accountability channels Manufacturer’s and operational specifications OHS policies, procedures and programs Quality assurance and continuous improvement processes and standards Slide 84 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Involve stakeholders Quantities of items to be obtained or prepared Timelines that apply Restrictions that apply – such as preferred supplier arrangements, budget, compatibility, space issues, compliance requirements Compliance issues that need to be addressed Slide 85 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Involve stakeholders The needs of those who will be using the product Customer needs, wants and preferences Introduction and commissioning requirements Training required Financing arrangements Slide 86 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Types of resources Resources can encompass: Physical resources Human resources Financial resources Intellectual property Slide 87 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Common resources Location/premises Occupational health and safety (OHS) resources Plant/machinery Raw materials – used to produce the products or service Refurbishment requirements Staff amenities Slide 88 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Common resources Stock and supplies Storage space Technical equipment and software Staffing Training Training materials Slide 89 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Notification of new products and services It is essential that an organisation which chooses to introduce a new product or service to the market lets all relevant stakeholders know about it: Customers Managers Finance Human resources Sales and marketing Staff Slide 90 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Communicate information about new products and services This product and service knowledge can therefore include: Details about physical products Information about the services that are available Information on prices, specials, deals and packages Details about the operation of the business Slide 91 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Develop organisational policy, procedures and standards Organisational service culture and values Strategic goals of the organisation Service policies, guidelines and processes Ethical standards established by the organisation Legislation, codes and practice Technical standards Slide 92 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Effective communication of expectations Communicating customer service standards can come in many different ways including: SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) Job descriptions Task sheets Orientation programs Slide 93 Consider organisational constraints and limitations Effective communication of expectations Formal meetings Staff briefings at the start and end of shifts Training sessions Observation and mentoring Informal communication during a shift Slide 94 Consider profitability targets Naturally the introduction of new products and services normally is an expensive exercise from a financial point of view When deciding on new products and services they must be done in a way that is financially feasible in the long term No business aims to introduce any new concept unless there is some financial benefit to it Slide 95 Consider profitability targets Initial costs Closure of revenue generation outlets or rooms Refurbishment costs Purchase of furniture, fixtures and equipment Removal of old equipment Project management planning and implementing costs Slide 96 Consider profitability targets Initial costs Purchase of new supplies including food, beverages, furnishings or amenities Employment of staff Training of staff Promotional materials and activities to make customers aware of new offerings Loss of productivity until people come ‘up to speed’ Slide 97 Consider profitability targets Budgets What is a budget? Why is it important to have one when planning new products and services? What is contained in a budget? Who prepares a budget? Slide 98 Deciding prices Deciding on prices for new products or services Determining a fair and accurate price for any new product or service can be hard as no existing benchmarks may have been set: How do you set prices? What needs to be considered? Slide 99 Deciding prices Pricing questions How do my customers perceive my product or service, in terms of price and value? How do my prices compare with my competitors? What values and benefits do my customers get from my product or service? Are my prices consistent with those benefits and values? Slide 100 Deciding prices Pricing questions What is the current supply and demand relationship of my product or service? Am I in an industry where the demand for my product or service has a short life cycle, and thus I need to cash in quickly? Do I have a product with a recognizable name that allows me the luxury of overpricing? Slide 101 Deciding prices Pricing considerations Price indicates ‘value’ Understand customer perception of ‘value’ Consider fixed and variable costs Consider the competition Consider different price points Slide 102 Element 4: Monitor sales performance of products and services Slide 103 Monitor sales performance of products and services Performance criteria for this element are: Evaluate new products and/or services in consultation with stakeholders Analyse products and services in terms of business objectives Adjust products and services based on feedback and profitability Slide 104 Evaluate new products and services Need for evaluation After new products and services have been implemented, a formal evaluation needs to analyse and assess the above information to determine operational effectiveness: Why is this important? How do you do it? Slide 105 Evaluate new products and services Evaluation questions Did it work? What aspects worked and what didn’t? Did it represent value for money? Were sufficient contacts or sales made? Did it come in on budget? Slide 106 Evaluate new products and services Evaluation questions Did the campaign/idea achieve the stated objectives? To what extent? What feedback was received from customers and agencies? What implications does this have for future undertakings? What wouldn’t we do the same next time, and why? Slide 107 Evaluate new products and services Areas to evaluate The procedures or systems The workflow – that is the order in which things are done Whether or not there are gaps or overlaps in service provision The workload of staff The time it takes to do a task or job Job design Slide 108 Evaluate new products and services Areas to evaluate Level of customer satisfaction with the service or product provided Cost Level of interest created Demand patterns Ease of implementation Increase in sales or leads Return on investment Slide 109 Evaluate new products and services Getting feedback from stakeholders Owners of the business Site/property managers Supervisors Staff, teams and workgroups Customers Government agencies Slide 110 Methods to gather feedback Getting feedback from internal management and staff Encouraging staff to feedback all relevant comments from customers Not shooting the messenger Setting agenda items for staff meetings Developing appropriate documentation Slide 111 Methods to gather feedback Getting feedback from internal management and staff Conduct regular meetings Conduct specific feedback sessions Get staff to provide scheduled feedback when problems occur Gather thoughts during debriefing sessions at the conclusion of shifts Slide 112 Methods to gather feedback Getting feedback from customers From guest comment cards Use an online option Observing customers Direct communication from customer/guest to staff Management meeting customers on departure Requiring frontline customer/guest contact staff to inquire about the customer experience Staff should also be required to feedback any comments they have overheard Slide 113 Analyse products and services against business objectives Importance of business objectives The basic requirement when analysing the success of new products and services is its ability to reach its desired objectives of performance standards: What types of business objectives exist in relation to new products and services? How can you measure success against these objectives? Slide 114 Analyse products and services against business objectives Types of business objectives The basic requirement when analysing the success of new products and services is its ability to reach its desired objectives of performance standards. Business objectives may be related to: Quantity Quality Time Sales figures Profitability Customer satisfaction Service standards Slide 115 Analyse products and services against business objectives Monitoring and evaluating implementation success of new products and services Work out what needs to be monitored Decide on methods or measures to use (see next slide) Compare what is happening with what should be happening Take appropriate action Slide 116 Analyse products and services against business objectives Methods of analysis Reports Obtaining customer feedback Using a pretend customer Observation Use of checklists Brainstorming sessions Staff input and review Slide 117 Adjust products and services Possible changes to products and services As a result of input from all stakeholders and a comprehensive analysis of the performance of new products or services the following actions may need to be taken to improve the successful implementation of products or services: Remove the product or service if it is not successful Reduce or expand the product or service range Amend product or service inclusions Slide 118 Adjust products and services Possible changes to products and services Change or enhance the promotional message Establishing additional or revised pre-programmed decisions to address shortcomings or problems Providing training to staff to improve service provision Revising the allocation of duties to staff Buying new equipment, or more equipment or different equipment Making changes to establishment policies and standard operating procedures (SOPs) Slide 119 Adjust products and services Possible changes to products and services Increasing staff numbers Changing operating/trading times Changing layout of the premises/department Organise more information for customers Change prices to meet customer demands whilst still meeting financial expectations Slide 120