Rocks
advertisement

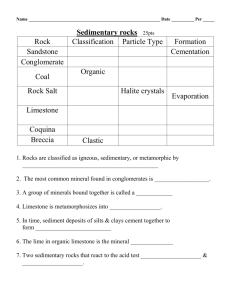
Rock Types and Uses Types of Rocks Igneous Rocks Metamorphic Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rocks How They are Made • Wind and water break down the earth • Bits of earth settle in lakes and rivers • Layers are formed and build up • Pressure and time turn the layers to rock Types of Sedimentary Rocks Sandstone Shale Limestone Conglomerate Metamorphic Rocks What are They? • Rocks that have changed • They were once igneous or sedimentary • Pressure and heat changed the rocks Types of Metamorphic Rocks Schist Gneiss Igneous Rocks What are They? • Fire Rocks • Formed underground by trapped, cooled magma • Formed above ground when volcanoes erupt and magma cools Types of Igneous Rocks Basalt Granite Pumice Rocks Have Been Used For Many Years and For Many Things Rocks Rock group Formed Examples and locations Uses When lava or magma Granite: Wicklow cooled and hardened Mountains in or on the crust Basalt: Giants Causeway, Co. Antrim Granite: worktops Basalt: in tarmac to surface roads etc Sedimentary The compressed bits of plants, animals or other rocks Limestone: central plain of Ireland Sandstone: Comeragh mtns, Waterford/Cork Limestone: front of buildings, cement Sandstone: cement blocks Metamorphic Other rocks changed by heat or pressure Marble: Co.Kilkenny Quartzite: Mt. Errigal, Donegal Marble: fireplaces and headstones Quartz: jewellery and road surfaces Igneous