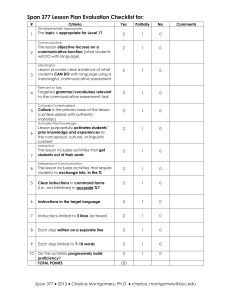
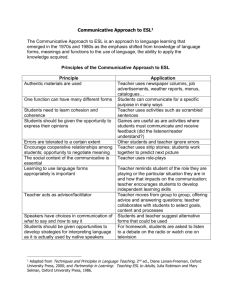
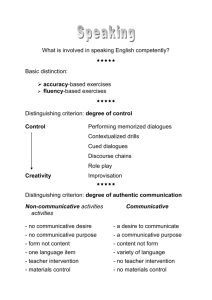
PowerPoint Presentation - Research in Communicative Disorders

Research Design & Measurement
Considerations (chap 3)
Group Research Design
Single Subject Design
External Validity Issues
Factors Affecting the Measurement
Process
Research in Communicative Disorders 1
Group Research Design
•
•
•
Between Subjects Design
Within Subjects Design
Mixed Subjects Design
Research in Communicative Disorders 2
Between Subjects Design
•
•
Examines differences between groups of subjects
Control and experimental groups
– Groups are identical except for variable under question
– Randomization and counter-balancing
Research in Communicative Disorders 3
Within Subjects Design
•
•
•
One group of subjects are examined under two or more conditions.
Used often with longitudinal research
Problems
– Order or learning effect
– Carry-over
Research in Communicative Disorders 4
Mixed Subjects Design
•
•
Combination of Between and Within
Subject Design.
Comparing two or more different variables.
Research in Communicative Disorders 5
Single Subject Design
•
•
•
Purpose and application
Types of Designs
– The ABCs
Evaluation of Single Subject Design
– YOU CAN NOT USE SUMMARY OR
INFERENTIAL STATISTICS ON SINGLE SUBJECT
DESIGN
!
Research in Communicative Disorders 6
Single Subject Design Example
Research in Communicative Disorders 7
External Validity Issues
•
•
External validity refers to the ability to generalize from a sample to a population.
Can be improved by random sampling techniques and by replication.
Research in Communicative Disorders 8
Factors Which Affect the
Measurement Process (chap 4)
•
•
•
•
Test environment
Instrument calibration
Instructions to subjects
Observer bias
Research in Communicative Disorders 9
Test environment
•
•
Ambient noise reduced or eliminated
Avoid Distractions
– Lighting
– Temperature
– Visual distractions
Research in Communicative Disorders 10
Instrument calibration
•
•
Audiometric equipment (ANSI S3.6-1989)
Recording equipment
Research in Communicative Disorders 11
Instructions to subjects
•
•
•
Clear, concise, and appropriate
Use appropriate language
Often use a script to insure inter-subject validity and reliability
Research in Communicative Disorders 12
• Rosenthal Effect
– Interactional
– Non-interactional
Observer Bias
Research in Communicative Disorders 13
Measurement Reliability
•
•
What is reliability?
How is it evaluated
– Stability (test-retest reliability)
– Equivalence
– Internal Consistency
Research in Communicative Disorders 14
•
•
•
Content Validity
Criterion Validity
Construct Validity
Measurement Validity
Research in Communicative Disorders 15
Content Validity
•
•
•
This is somewhat subjective.
Involves making sure that the content of your procedures are appropriate.
No specific tests for content validity … often use peer review for evaluation.
Research in Communicative Disorders 16
Criterion Validity
•
•
Concurrent validity
– Ability to correlate to a test of known validity
Predictive validity
– Attempt to predict performance based on a given test.
Research in Communicative Disorders 17
Construct Validity
•
•
How well a test relates to a theoretical construct. Assumes theory is correct.
Specific statistical measurements can be used to evaluate construct validity.
Research in Communicative Disorders 18
Efficacy of Treatment Research (chap 5)
•
•
•
Factors Affecting Internal Validity
Factors Affecting External Validity
Protection of Subjects
Research in Communicative Disorders 19
Factors Affecting Internal Validity
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
• History
Maturation
Testing Effects
Instrumentation
Statistical Regression
Differential selection of subjects
Mortality
Hawthorne Effect
Interaction of Factors
Research in Communicative Disorders 20
•
•
•
Involves repeated measures.
A change in the subject between the measurements.
Longitudinal studies most susceptible.
History
Research in Communicative Disorders 21
Maturation
•
•
Different than “history” since it deals specifically with age.
Use control group to factor out maturation effects.
Research in Communicative Disorders 22
Testing & Practice Effects
•
•
•
The more times you perform a task the better you will become.
Can minimize by …
– Counterbalancing presentation
– Train stubjects
Reactive and non-reactive measurements
Research in Communicative Disorders 23
Instrumentation
•
•
•
•
Calibration of instrumentation
Use of non-standardized tests
Observer bias (Rosenthal effect)
Test environment
Research in Communicative Disorders 24
Statistical Regression
• Occurs when you create subject groups based on their test scores.
Research in Communicative Disorders 25
Differential selection of subjects
•
•
•
Can occur with comparative and descriptive research
Can use counter balanced groups or random sample.
Problems can occur if there is an overlap of a variable.
Research in Communicative Disorders 26
Mortality
•
•
•
Refers to subjects who drop out of study.
Drop outs might be different than remaining subjects.
Big problem with surveys and questionaires.
Research in Communicative Disorders 27
Hawthorne Effect
•
•
Subjects change behavior simply because that person knows that they are a subject in a research subject.
Can use blind study and double blind study.
Research in Communicative Disorders 28
Interaction of Factors
Research in Communicative Disorders 29
Factors Affecting External Validity
•
•
•
•
Subject Selection
Reactive or Interactive Effects of Pretesting
Reactive Arrangements
Multiple Treatment Interference
Research in Communicative Disorders 30
Subject Selection
•
•
Generalizing results of the test sample to another another group from a different population.
Not only done in research, but done clinically all the time. This is a common problem in the educational setting.
Research in Communicative Disorders 31
Reactive or Interactive Effects of
Pretesting
• The administration of a pretest can affect the attitudes by sensitizing the subject.
Research in Communicative Disorders 32
Reactive Arrangements
• Degree to which the setting of the research is reactive or interacts with the independent variable in determing the subject’s performance on the dependent variable.
Research in Communicative Disorders 33
Multiple Treatment Interference
Research in Communicative Disorders 34
Protection of Subjects
•
•
•
Human Research
Animal Research
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
Research in Communicative Disorders 35
Last Slide
Research in Communicative Disorders 36