Transliteracy
advertisement

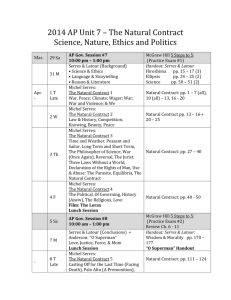
IVIG 2011, Prague, september 22 2011 « Nouveaux territoires pour la formation » Transliteracy : a trendy word or a real new perspective for information training ? Alexandre Serres URFIST de Rennes A. Serres, 2011 1 Presentation Professor and researcher ; Information Science ; University of Rennes 2 Co-manager of URFIST in Rennes : Regional Training Unit for Scientific and Technical Information 7 URFIST in France 3 missions : training, watching and research About information literacy, scientific information… 3 publics : Ph-D students, teachers and librarians A. Serres, 2011 2 Presentation 3 research topics : Evaluation of information on the internet Practical needs and expectations of PhD students about scientific information Information literacy, information cultures and transliteracy A. Serres, 2011 3 What is transliteracy ? A buzzword ? An interesting topic for libraries since June 2011 FORMIST meeting in France Workshop at ALA’s convention, in USA Different works, meetings and research in GB and USA A. Serres, 2011 4 What is transliteracy ? The linguistic origin From « transliteration » to « transliteracy » “The word ‘transliteracy’ is derived from the verb ‘to transliterate’, meaning to write or print a letter or word using the closest corresponding letters of a different alphabet or language” (Sue Thomas) A. Serres, 2011 5 What is transliteracy ? The canonical definition "Transliteracy is the ability to read, write and interact across a range of platforms, tools and media from signing and orality through handwriting, print, TV, radio and film, to digital social networks" (Sue Thomas and al.) A. Serres, 2011 6 What is transliteracy ? A large concept The whole set of interaction skills : A. Serres, 2011 7 What does transliteracy come from ? Two significant origins : The Anglo-Saxon world : USA, GB The academic research (not libraries’ culture) In USA : Works of Pr. Alan Liu Departement of English, at UCSB (University of California at Santa Barbara) Transliteracies Project, 2005 Research on online reading A. Serres, 2011 8 What does transliteracy come from ? In GB : Works of Pr Sue Thomas Faculty of Arts, Design and Humanities, De Monfort University, in Leicester 2006 : creation of the PART group (Production and Research in Transliteracy) Literary disciplines Impact of ICT on writing and literature Integration of PART into IOCT (Institute Of Creative Technologies) A. Serres, 2011 9 What does transliteracy come from ? Transliteracy idea : a set of research projects on broad topics effects of digital revolution on : A notion quite far from libraries and information literacy (at the beginning) Reading, writing, literature, arts and sciences Educational dimension generally absent Recently, interest of the libraries Many websites, blogs, articles… A. Serres, 2011 10 The « digital melting-pot » Multiple and literacies on digital networks The « digital melting-pot » and the blurring of borders Three levels of blurring : Documents Tools Practices A. Serres, 2011 11 The « digital melting-pot » : the documents Change of the definition of a document Phenomena of the « re-documentarization of the world » Permanent and unlimited mixing of digital traces Example of photos Limits of documents are blowing up Implications on different literacies : Information, media & computer literacies are intermigled A. Serres, 2011 12 The « digital melting-pot » : the hybridization of tools Information tools as « Swiss army knives » Tools are used : Ex. of Diigo : to look for information, to identify, to select, to write comments, to integrate into a personal database… Example : the platforms for sharing bookmarks A. Serres, 2011 13 The « digital melting-pot » : the confusion of practices search communicate orientate talk google organize print share Tagging/ indexing orkut earth API’s A. Serres, 2011 (d’après O. Ertzscheid) 14 Global or analytical approach of literacies ? How to encompass the interweaving of the literacies ? 2 types of answers : Analytical approach Holistic approach The traditionnal approach is analytical To identify, define and distinguish all the literacies A. Serres, 2011 15 Analytical approach of literacies ? To recognize the specificity of each literacy To define the relations between them Links between computer, information and media literacies ? A. Serres, 2011 16 Global approach of literacies ? Transliteracy And also « digital literacy » : "Digital literacy is the set of attitudes, understanding and skills to handle and communicate information and knowledge effectively, in a variety of media and formats“ (Paul Gilster) Proximity of the definitions A. Serres, 2011 17 What is the relationship between transliteracy and specific literacies ? "transliteracy does not replace, but rather « A unifying ecology » contains, "media literacy" and also "digital literacy“” (S. Thomas) Reference to the media convergence (Jenkins) or the media ecology (McLuhan) Transliteracy as the “mother of all literacies” A. Serres, 2011 18 Information evaluation as a leading figure of transliteracy ? Evaluation of information on the internet : a complex process To filter the results to understand the nature of a website to identify the author to judge the credibility to measure the authority of the author to assess the reliability and the quality of information to appreciate the relevance of the resource A good example of transliteracy Many intermingled skills and cultures at stake A. Serres, 2011 19 Information evaluation as a leading figure of transliteracy ? 5 types of cultures involved in the process of evaluating information : The « general culture », with historical, scientific knowledge ; All disciplinary cultures : a set of basic knowledge to understand the world varying levels of proficiency Information and documentary culture : Advanced use of tools, research methods… Understanding information key-notions : source, document… A. Serres, 2011 20 Information evaluation as a leading figure of transliteracy ? 5 types of cultures : Computer or digital literacy : Media culture (media literacy) : Knowledge, understanding and practical use of basic principles about computers, networks, Internet... « digital natives » : often into a « digital ignorance » about computer literacy Knowledge of mediation, media sources… Fundamental culture to evaluate information Mix of these 5 cultures in the evaluation of information A. Serres, 2011 21 Conclusion : what is the interest of transliteracy for the librarians ? Information literacy as a centerpiece of transliteracy Transliteracy as a possibility of a shared perspective For research and education To build a better link between different literacies Invitation to develop teamwork, to build together new knowledge about information, communication and media in the XXI century. A. Serres, 2011 22 Thank you for your attention ! Over to you for discussion ! Contact : alexandre.serres@uhb.fr Website of URFIST of Rennes : http://www.sites.univ-rennes2.fr/urfist/ A. Serres, 2011 23