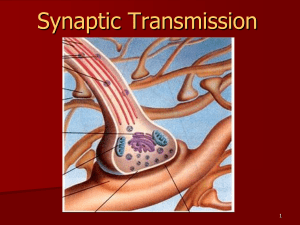
Neurotransmitters
advertisement

Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitter Criteria 1. Identity Substance must be found in neurons Neurotransmitter Criteria 1. Identity 2. Synthesis Cell has precursors and enzymes necessary for synthesis Neurotransmitter Criteria 1. Identity 2. Synthesis 3. Release Must be released from terminals; (collect substance from cleft after nerve stimulation) Neurotransmitter Criteria 1. 2. 3. 4. Identity Synthesis Release Receptors Cross desensitization between substance and suspected n.t. Blockade of n.t. action by receptor antagonists Applicaton of suspected n.t. mimics action of nerve stimulation Neurotransmitter Criteria 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identity Synthesis Release Receptors Inactivation Inactivation mechanism enzymatic degradation reuptake Neurotransmitter Criteria 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Identity Synthesis Release Receptors Inactivation Pharmacology Same effect on ion channels; p.s.p.’s have same reversal potentials Same effect on membrane resistance and potential Applied substances must be effective in physiological concentrations Inhibition of degrading enzyme prolongs action of both Neurotransmitter Criteria 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Identity Synthesis Release Receptors Inactivation Pharmacology Acetylcholine Synthesis Choline Acetyltransferase (ChAT) Acetyl CoA + Choline Acetylcholine + CoA + CoA Degradation Acetylcholine Esterase (AchE) Acetylcholine Choline + Acetate Chemicals that Act on ACh Systems black widow spider venom stimulates release of ACh botulinum toxin blocks release of ACh curare blocks ACh nicotinic receptors insecticides AChE inhibitors atropine as antidote blocks muscarinic receptors Clinical Aspects of ACh Systems Alzheimer’s disease loss of ACh neurons in the basal nucleus of Meynert Aricept—ACh agonist Monoamines single amine (NH2) group Catecholamines (CAs) dopamine (DA) norepinephrine (NE, noradrenaline) epinephrine (EPI, adrenaline) Indoleamines serotonin (5-hydroxy tryptamine, 5-HT) Catecholamine synthesis Serotonin synthesis Dopamine Systems Norepinephrine Systems SystemsSerotonin Characteristics of Monoaminergic Systems Diffuse distribution of targets Fine, unmyelinated axons Metabotropic synapses Functions of Monaminergic Systems “State” phenomena sleep and arousal hunger mood Amino Acid Transmitters Excitatory Amino Acid Glutamic Acid, or Glutamate Inhibitory Amino Acids Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase (GAD) Glutamic Acid Glycine GABA Glutamate Receptor Subtypes NMDA receptor binding sites http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/anisamples/neurobiology/receptors.htm Glutamate non-NMDA receptors Na+ channels open removes blockade depolarization NMDA receptors Ca2+ channels open (Mg2+ blockade) Ca2+ enters when Mg2+ is removed postsynaptic effects (learning) Ca2+dependent K+ channels open reinstates blockade repolarization a. Non-NMDA Na+ channels open, Na+ enters and depolarizes membrane b. Mg2+ blockade of NMDA Ca2+ channels removed by membrane depolarization; Ca2+ enters c. Ca2+ dependent K+ channels open; membrane repolarized d. Mg2+ blockade reinstated a b c d GABA receptor binding sites Peptide Neurotransmitters (Often serve hormonal functions as well) Substance P (P for “Peptide”) Principal somatosensory transmitter First peptide transmitter discovered Gut hormones e.g. angiotensin neuropeptide Y cholecystokinin Releasing factors for hormones e.g. tryrotropin releasing hormone somatotrophin, somatostatin corticotropin Opiates Enkephalins, Endorphins Diffusible Gases Nitric Oxide (NO) Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) Arginine NO + Citrulline Carbon Monoxide (CO) Heme Oxygenase Heme CO + biliverdin Functions of Diffusible Gas Neurotransmitters regulate blood flow cerebral peripheral (e.g. penis) retrograde messenger Hebb’s postulate of learning Summary of Neurotransmitters Small Molecule Neurotransmitter Substances Acetylcholine (ACh) Serotonin (5-HT) Dopamine (DA) Histamine Norepinephrine (NE) Epinephrine Amino Acids Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) Glycine Glutamate Aspartate Neuroactive Peptides - partial list bradykinin cholecystokinin gastrin secretin oxytocin beta-endorphin enkephalin substance P somatostatin prolactin bombesin dynorphin neurotensin motilin thyrotropin sleep peptides galanin neuropeptide Y gonadotropningrowth hormonereleasing hormone releasing hormone luteinizing hormone calcitonin insulin glucagon vasopressin angiotensin II thyrotropinreleasing hormone vasoactive intestinal peptide Soluble Gases Nitric Oxide (NO) Carbon Monoxide