psychopharmacology
advertisement

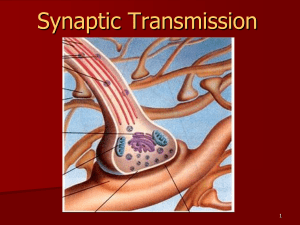
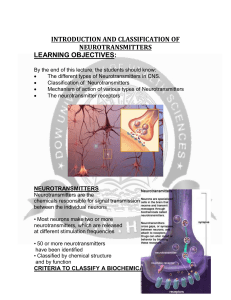
Drugs of abuse Psychopharmacology Chemical Signals Target tissue can respond to chemical signal Target cells (within target tissue) must have sensors (RECEPTORS) to be able to respond Types of chemical signals: Hormone – goes through blood Neurotransmitter – from neuron directly on cell Paracrine – in area of tissue Neuron Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters Some Neurotransmitters At muscle and brain Acetylcholine (ACh) Main inhibitory neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) Monoamines Serotonin (5HT) Dopamine (DA) Purines Adenosine Peptides Endorphins Reward system Most drugs of addiction influence the action of the neurotransmitter dopamine (DA) in the nucleus accumbens Directly- alter DA neurotransmission Indirectly – alter another neurotransmitter which controls DA neurons http://www.drugabuse.gov/pubs/teaching/ 2 Ways to alter DA neuron activity in the nucleus accumbens Directly- alter DA neurotransmission Indirectly – alter another neurotransmitter which controls DA neurons Neurotransmitter Receptors Bind neurotransmitter Receptor causes effect in postsynaptic cell Channel for ions or Second messenger effects Acetylcholine (ACh) as Neurotransmitter Cholinergic neurons: Use ACh as NT. ACh is both an excitatory and inhibitory NT. Different effects due to type of receptors present on postsynaptic cell Acetylcholine (ACh) as Neurotransmitter Receptors classified by binding pharmacology Nicotinic: binds nicotine Muscarinic: bind muscarine from poisonous mushrooms Both bind ACh Acetylcholinesterase AChE: Enzyme that inactivates ACh. Prevents continued stimulation. Sarin blocks GABA as inhibitory neurotransmitter Two receptors GABAA – ion channel GABAB – second messenger Stimulating the GABAA receptor Inhibits cell activity Decreases anxiety Muscle-relaxant Sedative Hypnotic Amnestic Stimulating the GABAA receptor Drugs Barbiturates Alcohol Benzodiazepines Valium Dictyostelium Report -- Dicty has GABAA receptor! Monoamines Monoamine neurotransmitters: Epinephrine (adrenaline) Norepinephrine (NE)(noradrenaline) Serotonin (5HT) Dopamine (DA) Release of Monoamines Released by exocytosis from presynaptic vesicles. Diffuse across the synaptic cleft. Interact with specific receptors in postsynaptic membrane. Inactivation of monoamines Reuptake of monoamines into presynaptic membrane. Enzymatic degradation in presynaptic membrane by enzymes. Monoamine receptor effects Monoamine NT do not directly open ion channels. Act through second messenger, cAMP. Adenylate cyclase, converting ATP to cAMP. cAMP causes effect throughout cell cAMP inactivated by phosphodiesterase Inactivation of second messenger cAMP Inactivated by phosphodiesterase Caffeine and theobromine resemble cAMP inhibit phosphodiesterase Dicty uses cAMP for extracellular signal Cocaine action http://www.cerebromente.org.br/n08/doencas/drugs/animrecap_i.htm Serotonin as NT Regulation of mood, behavior, appetite, and cerebral circulation. SSRIs: Used as an antidepressant. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Inhibit reuptake and destruction of serotonin, prolonging the action of NT. MDMA Action MDMA Action