Leadership
advertisement

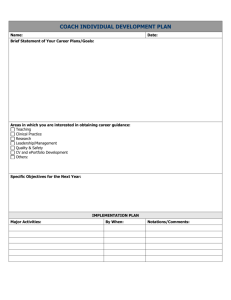
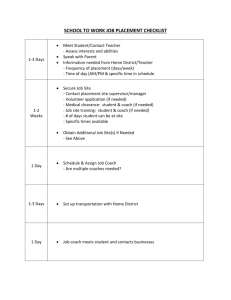
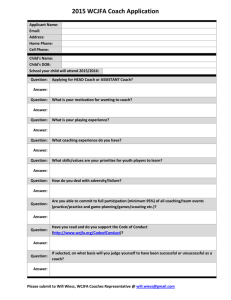
Leadership What do leaders do? Task leadership: – – Focus on group’s work & accomplishing goals To help group achieve its goals, initiate structure, define responsibilities, set standards & objectives, develop SOPs, give evaluative feedback, establish & use external communication networks Relational leadership – – Focus on interpersonal relationship within group To increase socio-emotional satisfaction & teamwork in group, boost morale, give support & encouragement, reduces conflict, establish rapport, show concern & consideration for group & members, provide a compelling vision of the future 2 What do leaders do? 4 Types of leadership behaviors Person focused – – – – Transformation: Sets vision through meaningful and creative exchange with subordinates Consideration: maintaining close social relationships and group cohesion Empowerment: development of followers’ self-management or self-leadership skills Motivation: Encouraging followers to exert effort Task focused – – – Transactional: Rewarding & punishing Initiating structure: Minimization of role ambiguity and conflict by letting people know what to do (directive) Boundary spanning: Getting information & resources by connecting outside the group 5 Classifying leadership behaviors Task Relationship Change 6 •Yukl, G., Gordon, A., & Taber, T. (2002). A hierarchical taxonomy of leadership behavior: Integrating a half century of behavior research. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 9(1), 15-32. Two types of leadership Transformational Charisma Transactional – – goes beyond self-interest – expresses confidence – talks of values – emphasizes the collective mission Intellectual Stimulation clarifies rewards – assists based on effort – rewards your achievement – recognizes your achievement – re-examines assumptions – seeks different views – suggests new ways – suggests different angles Individualized Consideration – individualizes attention – focuses on your strengths – teaches and coaches – rewards your achievement Contingent Reward MBA-Active – focuses on your mistakes – puts out fires – tracks your mistakes – concentrates on failures MBA-Passive/Avoidant – – – – – if not broke, don't fix reacts to problems, if chronic avoids involvement avoids deciding delays responding 7 Leadership styles & outcomes (I) Both Transformational Leadership & Contingent – strongly rewards associated with better affective outcomes – Moderately to weakly associated with group performance groups •Judge, T. A., & Piccolo, R. F. (2004). Transformational and transactional leadership: a metaanalytic test of their relative validity. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(5), 755. 8 Leadership styles & outcomes (II) Active Management by Exception moderately to weakly associated with better affective & group performance groups Passive MBE & Laissez-fare associated with worse affective & group performance groups Judge, T. A., & Piccolo, R. F. (2004). Transformational and transactional leadership: a metaanalytic test of their relative validity. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89(5), 755. 9 A more elaborate model Burke, et al . (2006). What type of leadership behaviors are functional in teams? A meta-analysis. The Leadership Quarterly, 17(3), 288-307. 10 Do these leadership behaviors work? Burke et all meta-analysis – Meta-analysis = quantitative literature review, estimating effect size of relationships or difference Relationship Task-oriented behaviors Task-focused leadership—perceived team effectiveness Task-focused leadership—team productivity/quantity Person-oriented behaviors Person-focused leadership—perceived team effectiveness Person-focused leadership—team productivity/quantity Person-focused leadership—team learning N effect N studies sizes N teams mean r 95% CI .333 .258–.404 19 25 1655 .203 .082–.317 5 6 271 .360 .284 .560 .301–.416 .233–.332 .338–.723 37 12 3 55 24 3 3139 1396 200 11 Coach P What kind of leader? Was it effective? 12 Does trust in team or leader influence team performance? 30 NCAA basketball teams. 375 surveys Trust in coach scale – – – – – – – – Most team members trust and respect the coach. (. 93) I can talk freely to the coach about difficulties I am having on the team and know that he will want to listen. (. 84) If I shared my problems with the coach, I know he would respond constructively and caringly. (.90) I have a sharing relationship with the coach. I can freely share my ideas, feelings, and hopes with him. (. 86) I would feel a sense of loss if the coach left to take a job elsewhere. (. 96) The coach approaches his job with professionalism and dedication. (. 87) Given the coach's past performance, I see no reason to doubt his competence. (. 87) … Dirks, K. T. (2000). Trust in leadership and team performance: Evidence from NCAA basketball. Journal of applied psychology, 85(6), 1004. 13 Good leaders make a difference .44 reduced .44 to .20 Prior team performance .61 Trust in coach Player talent Trust in players .44 Future team performance .41 -.07 14 Much of leadership is influence Gathering information Making decisions Allocating resources Convincing others to carry out the decisions 15 Leadership as influence 16 Forsyth, D. (2010). Group dynamics (5th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Pub Co. Leadership as role vs behavior Saw behavior patterns that leaders/managers do Correlational evidence that both taskoriented & personal-oriented behaviors improve group functioning Can think of leadership as the behaviors that are typical of leaders. They don’t have to be done by a formal leader! 17 Vertical vs Shared Leadership If leadership is influence, then it can be exercised by more than a single, formal leader in a group – – Many groups (e.g., self-managed teams) don’t have a formal leader Even in groups with formal leaders, much of the leadership is shared Shared leadership = dynamic, interactive influence process among individuals in groups to lead one another to the achievement of group or organizational goals Pearce, C. L., & Conger, J. A. (2003). Shared leadership: Reframing the hows and whys of leadership: Sage Publications, Inc. 18 Shared Leadership in WikiProjects WikiProject: A group of editors who collaborate on managing & writing a collection of pages on a topic (e.g., military history, medicine, US states) – – – Defined membership Production tasks Variation in how they are run 19 Types of leadership behaviors Transactional Leadership Providing Positive Feedback Aversive Leadership Providing Negative Feedback Directive Leadership Directing Person-based Leadership Socializing Burke et al 2006, Pearce et al 2002, Yukl 1998 •20 20 Example leadership behavior in Wikipedia Providing positive feedback I am so impressed. This is a very fine article! 21 •21 Example leadership behavior in Wikipedia Providing negative feedback “…there is a concern that the rationale you have provided for using this image under "fair use" may be invalid. ... If it is determined that the image does not qualify under fair use, it will be deleted within a couple of days… 22 •22 Example leadership behavior in Wikipedia Directing Hey, one of these days do you think you could take some pictures at Mission Mill? I’d like to spruce up the article but it really needs some photos. Thanks! 23 •23 Example leadership behavior in Wikipedia Socializing Drop me a line on my talk page sometime, we’ll get a coffee over at Hot Rize or the new King Kocoa… 24 •24 Results •Weekly change in number of edits •% •% •Not receive any message •Non- •Positive •Negative Leadership Feedback Feedback •Direction •Social Exchange •25 25 •% •Weekly change in number of edits Results •Non- •Positive •Negative Leadership Feedback Feedback •Direction •Social Exchange •26 26 Weekly change in number of edits Results % 19 % ** NonPositive Negative Leadership Feedback Feedback Social Direction Exchange 27 27 Results •Weekly change in number of edits •% 14 % ** •Non- •Positive •Negative Leadership Feedback Feedback •Direction •Social Exchange •28 28 Results change in number of edits •% •Weekly 9 % ** •Non- •Positive •Negative Leadership Feedback Feedback •Direction •Social Exchange •29 29 Results change in number of edits •% •Weekly 23% ** •Non- •Positive •Negative Leadership Feedback Feedback •Direction •Social Exchange •30 30 Experimental replication: Effects of shared leadership Send relevant message to Wikipedians creating new articles Random assignment to: – – – – Neutral Positive feedback Negative feedback Friendly social Compare newcomers and established members’ response to leadership messages. •VS 31 •31 Strong Effects on Newcomers •Newcomers’ Total Number of Edits •* •* * •* * 32 •32 No Effects on Established Members •Established Editors’ Total Number of Edits •Positive •Negative •Directive •Social Feedback Feedback Message Message 33 •33