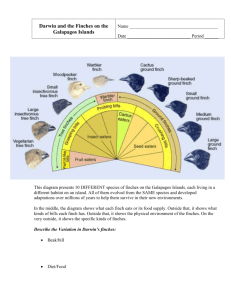
survival of the fittest
advertisement

TOPIC: Evolution AIM: Explain the theory of Natural Selection. Do Now: Root Word Organizer: Homozygous and Heterozygous Take out the Genetic Engineering ISN HW: Selective Breeding ISN Punnett Square Lab due tomorrow CL Genetics due Monday Human gene for insulin Bacterial DNA Bacterial that produce insulin Mitosis 1. According to this evolutionary tree, which species is the common ancestor? Protists 2. Which 2 species are most closely related? a. Flatworms and Sponges b. Mollusks and Annelids c. Annelids and Arthropods d. Rotifers and Cnidarians 3. Which species is more complex? a. Protists b. Rotifers c. Echinoderms d. Mollusks Lamarck • First person to propose a theory of evolution. –Inheritance of acquired traits. –Theory of use and disuse. (because of a need) Weismann • Acquired characteristics are NOT passed on to offspring • Cut off the tails of mice for 22 generations – Offspring born with tails Charles Darwin • 1830’s • Studies on Galapagos Islands Darwin’s Model of Evolution Darwin observed a 13 species of finches that were all similar except for differences in body size, beak shape and eating habits. • Adaptation: A variation (inherited trait) that makes an organism better suited to its environment • Ex: Camouflage Leaf-tailed gecko Ducks are birds that have waterproof feathers. They live on a pond and on land. Kangaroos Habitat: Dry inland Australia, including deserts and grasslands Adaptations: •They are able to go with out drinking as long as green grass is available and it adapts well to drought. •They can hop as fast as 40 mph (64 km). They use this as their first line of defense. •The tail serves as a balance when the animal leaps and as a prop when it stands. 1. The 5 points to Darwin’s Theory of natural Selection. Write the name of each point in the spaces provided. 1. One of the prime motives for all species is to reproduce and survive, passing on the genetic information of the species from generation to generation. When species do this they tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. OVERPRODUCTION 2. Darwin noted many differences in the species he observed on his trip to the Galapagos Islands. VARIATION • Ex: Polar bears with thicker fur • Darwin wasn’t able to explain where variations came from TOPIC: Evolution AIM: Explain the theory of Natural Selection. Do Now: Pass up your Punnett Square Lab HW: Selective Breeding ISN CL Genetics due Monday Genetics Exam Tuesday 1. The letter X most likely represents (1.) bacterial cells that are unable to synthesize insulin (2.) human cells that are able to synthesize antibodies (3.) bacterial cells that are able to synthesize insulin (4.) human cells that are unable to resist antibiotics 2. What is this process an example of? Genetic engineering Which sequence shows the largest structure to the smallest structure? 1.gene – DNA – chromosome 2.DNA – gene – chromosome 3.gene – chromosome – DNA 4.chromosome – gene – DNA White short-horned cattle and Black Angus cattle have been crossed to produce offspring with superior beef and rapid growth qualities. Identify technique used. Support your answer. 3. The lack of resources to nourish these individuals places pressure on the size of the species population, and the lack of resources means increased competition and as a consequence, some organisms will not survive. COMPETITION 4. The organisms that die as a consequence of this competition were not totally random. Darwin found that those organisms more suited to their environment were more likely to survive. SURVIVAL OF THE FITTEST 5. Overtime, the offspring of individuals with helpful variations make up more of a population and eventually may become a separate species. SPECIATION 2. Describe • Not suited for the environment. the reason • Not able to compete why organisms do not survive, according to Darwin. 3. Identify an example of variation you have observed in a species. 4. Why does Darwin believe organisms “evolve?” • They evolve to suit their environment. 5. State Darwin’s Theory of natural Selection. • Organisms with favorable adaptations survive, reproduce, and pass on the trait to offspring. • Organisms with unfavorable adaptations do not survive. TOPIC: Evolution AIM: Explain the theory of Natural Selection. Do Now: Take out your Selective Breeding ISN. Pedigree chart Ditto #’s 1 and 2 HW: Right side of genetics ditto. 1. Beth does not have green hair. Is she a carrier? Explain. Yes she is a carrier. All of her offspring have green hair, so she is carrying one recessive allele. 2. Bunny, who has blond hair, is a carrier of the green hair gene. She claims to be the long lost child of Great Grandma and Great Grandpa Berg. Should they include her as a daughter in their will? Explain. No. Great Grandma and Great Grandpa Berg are homozygous recessive so Bunny should have green hair if she is their daughter. 1. What are the genotypes of the individuals from generation 1? 2. Could generation 2 have any carriers? 3. What are the genotypes of the parents in generation 3? Y 1. What process is represented in the diagram? Genetic engineering. 2. Identify structure Y. Recombinant DNA 3.What does X represent? Bacteria that produce insulin 4. Identify the cell division occurring in this process. Mitosis 1. Identify the finch that lives on an island with fruit as the main source of food. 2. Identify the finch that lives on an island with cacti as the main source of food. 3. Describe what occurs on an island inhabiting small ground finches and medium ground finches. 4. Can vegetarian finch and large ground finches inhabit the same island? Support your answer. 1. Identify the finch that lives on an island with fruit as the main source of food. Support your answer. Vegetarian finch They have parrotlike beaks. 2. Identify the finch that lives on an island with cacti as the main source of food. Support your answer. Cactus ground finch They have probing bills. 3. Describe what occurs on an island inhabiting small ground finches and medium ground finches. The finches will compete for food. 4. Can vegetarian finch and large ground finches inhabit the same island? Support your answer. Yes. They eat different types of food. Overproduction Competition Survival of the Fittest Speciation 6. There are 2 types of worms: worms that eat at night (nocturnal) and worms that eat during the day (diurnal). Birds eat during the day and seem to be eating only the diurnal worms while the nocturnal worms are in their burrows. Each spring when the worms reproduce, that have about 500 babies but only 100 of these ever become old enough become old enough to reproduce. a. Identify the worm that natural selection selected AGAINST and support your answer. Diurnal worms. Birds come to eat the worms during the day. The nocturnal worms are in the soil during the day. 6. There are 2 types of worms: worms that eat at night (nocturnal) and worms that eat during the day (diurnal). Birds eat during the day and seem to be eating only the diurnal worms while the nocturnal worms are in their burrows. Each spring when the worms reproduce, that have about 500 babies but only 100 of these ever become old enough become old enough to reproduce. b. Identify the points of Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection below from the scenario above. • Variation: Two types of worms (Nocturnal and diurnal) • Overproduction: Worms produce 500 babies, but only 100 become old enough to reproduce. • Competition: Worms competing for food • Survival of the fittest: Nocturnal worms have the favorable adaptation. c. If speciation were to occur, identify the characteristic that the species would have. Worms would be nocturnal because they were not eaten by the birds. 8. There are 2 types of rabbits: those that strictly eat grass and those that strictly eat berries and flowers. A drought occurs one year, and the plants have difficulty producing any extras (flowers, berries, etc.) and remain green. The rabbits have reproduced all year, but many are eaten by foxes or hawks. Due to the drought, many rabbits have starved to death. a. Identify the rabbits that natural selection selected AGAINST and support your answer. The rabbits that strictly eat berries and flowers were selected against. Because of the drought, berries and flowers were not produced. Therefore, these flowers did not have food to eat, 8. There are 2 types of rabbits: those that strictly eat grass and those that strictly eat berries and flowers. A drought occurs one year, and the plants have difficulty producing any extras (flowers, berries, etc.) and remain green. The rabbits have reproduced all year, but many are eaten by foxes or hawks. Due to the drought, many rabbits have starved to death. b. Identify the points of Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection below from the scenario above. Rabbits that eat grass and rabbits that eat berries • Variation: and fruit • Overproduction: Rabbits have reproduced all year. • Competition: Rabbits compete for food • Survival of the fittest: Rabbits that eat grass had the favorable adaptation and, as a result, survived and passed on their trait to offspring. c. Describe which rabbits would have greater population during the drought. Support your answer. The rabbits that eat grass will have a greater population during the drought because they have food to eat. Let’s summarize… 1. According to Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection, which organisms survive? 2. Identify the main points to Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection. The diversity within the wild bird species in the diagram below can best be explained by which process? (1) natural selection (3) ecological succession (2) asexual reproduction (4) mitotic cell division Which concept would be correctly placed in box X? (1) use and disuse (2) variation (3) transmission of acquired traits (4) changes in nucleic acids Which statement is not part of the concept of natural selection? (1) Individuals that possess the most favorable variations will have the best chance of reproducing. (2) Variation occurs among individuals in a population. (3) More individuals are produced than will survive. (4) Genes of an individual adapt to a changing environment According to the theory of natural selection, why are some individuals more likely than others to survive and reproduce? (1)Some individuals pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes. (2)Some individuals are better adapted to exist in their environment than others are. (3)Some individuals do not pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes. (4)Some individuals tend to produce fewer offspring than others in the same environment. Charles Darwin proposed that organisms produce many more offspring than can possible survive on the limited amount of resources available to them. According to Darwin, the offspring that are most likely to survive are those that (1.) are born first and grow fastest (2.) are largest and most aggressive (3.) have no natural predators (4.) are best adapted to the environment Darwin's studies of finches on the Galapagos Islands suggest that the finches' differences in beak structure were most directly due to (1.) acquired characteristics in the parent finches (2.) the size of the island where the finches live (3.) mating behaviors of the different finch species (4.) adaptations of the finches to different environments According to Charles Darwin, one factor that affects the evolution of a species is (1.) variation due to genetic mutations (2.) rapid fossil formation (3.) survival of the fittest (4.) exposure to environmental pollutants 1. How many people in this pedigree chart have the recessive trait? 2. How many people in this pedigree chart are carriers? 3. How many offspring are found in generation 2? 4. What is the chance of the individuals in generation 1 having a child with the recessive trait? 1. How many individuals make up generation 2? 2. What are the genotypes of the individuals in generation 1? 3. How many individuals make up generation 3? Gorillas Habitat: Tropical forest Adaptations: •Opposable thumb enables manipulation of objects; big toe also opposable for grasping. •Large and powerful arms used to break stalks or uproot vegetation while foraging. •High intelligence probably an adaptation for finding scarce or isolated fruit plants in the rain forest. Cactus Habitat: Dry deserts Adaptations: •The spines serve a number of purposes in addition to protection from hungry and thirsty animals. •They provide shade, serve as a windbreak to prevent dehydration from dry winds, and help trap warm air close to the plant. •The root systems of cacti are very close to the surface of the soil, making it possible for them to take advantage of the slightest rain shower.