Evolution Notes Outline 2014
advertisement
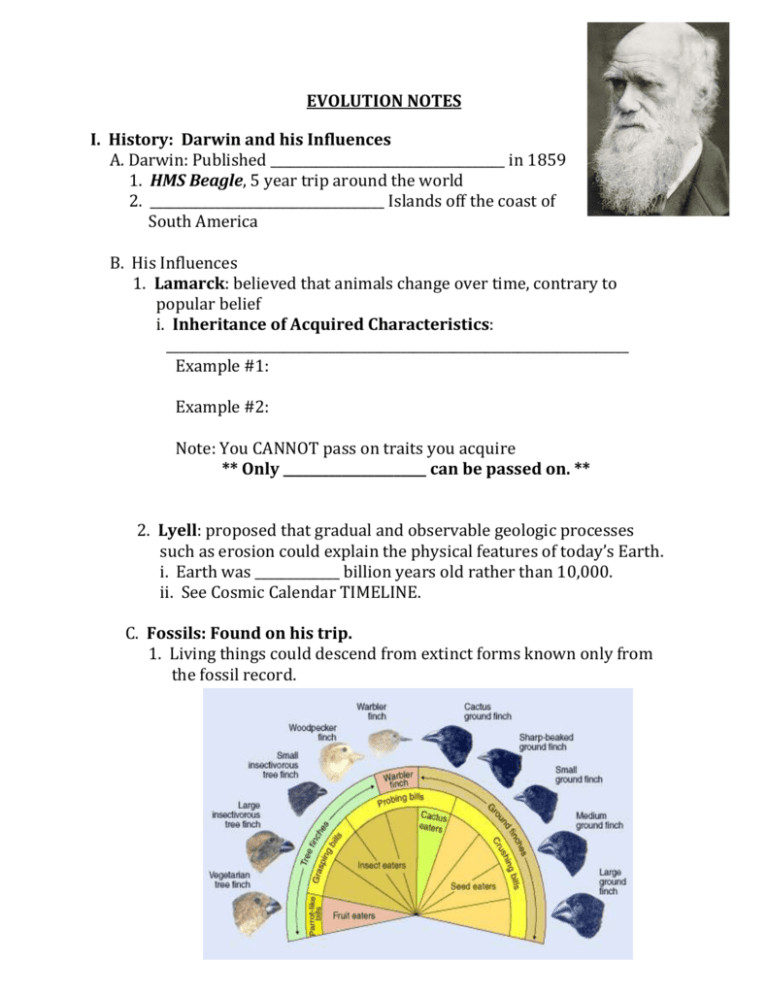
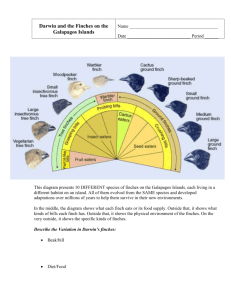
EVOLUTION NOTES I. History: Darwin and his Influences A. Darwin: Published ____________________________________ in 1859 1. HMS Beagle, 5 year trip around the world 2. ____________________________________ Islands off the coast of South America B. His Influences 1. Lamarck: believed that animals change over time, contrary to popular belief i. Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics: _______________________________________________________________________ Example #1: Example #2: Note: You CANNOT pass on traits you acquire ** Only ______________________ can be passed on. ** 2. Lyell: proposed that gradual and observable geologic processes such as erosion could explain the physical features of today’s Earth. i. Earth was _____________ billion years old rather than 10,000. ii. See Cosmic Calendar TIMELINE. C. Fossils: Found on his trip. 1. Living things could descend from extinct forms known only from the fossil record. II. Darwin’s Finches A. Biogeography: B. Galapagos Islands: volcanic islands off the coast of South America 1. Species were slightly different than the ones on the ____________________ C. Finches: different beaks depending on the food available i. Cactus-eating finch: more pointed beak ii. Insect-eating finch: sharp (trees) iii. Types of seeds: varying beak thickness D. All descended from one mainland finch ____________________________________________________________________ from a __________________________ _________________________ III. Natural Selection A. Definition: mechanism for evolutionary change. B. Components: 1. ________________________________________ - Mutations - Meiosis (crossing over, independent assortment) 2. ________________________________________ 3. Adaptations (____________________________________________________________) to increase survival and reproductive success (Fitness: ________________________________________________) 4. _________________________________________ - The results of natural selection is a population adapted to the local environment. ** LACKS DIRECTION: not always towards a “best” or “strongest” ** ** EXTINCTION- previous adaptations are no longer suitable to changed environment ** IV. Artificial Selection A. The selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to produce offspring with genetic traits that HUMANS value. 1. Examples: V. Evidence For Evolution A. Fossils: living things could descend from extinct forms known only from fossil record. 1. Example: B. Biogeographical: geographic distribution of life forms 1. Related forms evolved in one locale and then spread to other accessible regions. i. Example: C. Anatomical: 1. Homologous structures: structures that are similar because they are inherited from a __________________________________ 2. Analogous structures: features are similar in function but NOT in structure. They do not derive from a recent common ancestor but in response to a similar ______________________________________ 3. Vestigial structures: no longer have function. They occur because inherit anatomy from their ancestors. Ex:. D. Biochemical/Molecular 1. Living organisms use DNA and many identical enzymes. 2. _________________________________ of DNA sequence or amino acid structure based on how closely related E. Embryology 1. ____________________________ of closely related organisms often have similar stages during development F. Present day examples: Antibiotics Tuberculosis/MRSA and Antibiotic Resistance Video