Lisa Mancino
advertisement

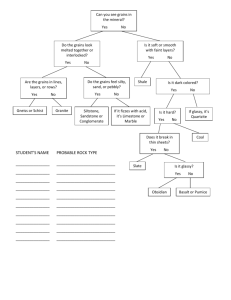
Factors affecting grains consumption: The evidence from NHANES survey data Lisa Mancino, ERS-USDA Andrea Carlson, CNPP-USDA National Health and Nutrition Exam Survey Collected by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics • First collected in 1960. Became ‘continuous’ in 1999 • For any given year is ~ 5,000 people around the US (15 counties each year) • Oversamples: Certain age groups: 12-19, 60+ Specific minorities: African Americans, Mexican Americans Low income persons (< 130% of poverty level) Pregnant women NHANES 1999-2001 NHANES (1999-2000) Diet Information Health Information Demographic Information What it has What it lacks • 1 24 hr recall • What was eaten, when and where • Measured BMI • Waist circumference • Weight and diet history • Detailed physical activity • Gender • Age • Race ethnicity • Marital status • Household income • A second recall • Where food was purchased • Diet and nutrition knowledge • Household size • Ability to link children’s information with parents’ • Geographic information NHANES (1999-2000) Provides a snap shot of consumption: What When Where Who What Dietary Patterns Servings, cups or ounces 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Whole Grains Other Grains Fruits Vegetables Lean Meat Equivalent (oz) Dairy Proposed Recommended Intake* Average Intake *US Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee Added Sugar (cups) Solid Fats (ozs) What Broad Categories Pancakes, waffles, french toast Quick breads 2.0% 5.5% Ready to eat cereals 5.8% Flour mixes/meat substitues 0.02% Breads & rolls 27.6% Cakes, cookies, pies, pastries 9.0% Pastas, cooked cereals, rice 9.8% Crackers & salty snacks 10.7% Grain mixtures 18.2% Other 11.3% What Specific foods Mixtures Other Pizza Burgers Noodle Soups Chicken patties Macaroni and Cheese Corn Dogs Spaghetti with sauce Fish Sandwiches Rice & tomato sauce Pot Pies Snacks Corn chips Pretzels Corn puffs and twists Crackers Popcorn What Whole Grains Breads & rolls, 2% Pastas, cooked cereals, rice, 2% Ready to eat cereals, 3% Crackers & salty snacks, 5% Non whole grains, 86% When % All Grains (% of all calories) Brunch 1% 19% (15%) 36% Breakfast (35%) Dinner Snack 19% (26%) Lunch 25% (23%) When Whole Grains Brunch 1% 19% Dinner 33% Breakfast 1% 19% 33% 18% 29% Lunch 18% Snack 29% Where Specific Places: % of All Grains (% of all calories) 0% 20% Home Work 64% 9.1% 7.2% 4.9% 14.8% (62%) (9%) (9%) (5%) (15%) 40% Restaurant 60% Fast Food 80% 100% All Others Who By types of grains reported 8 7 0.97 1.6 Number of Servings 6 5 5.7 5.7 5.8 4 3 2 1 0 Full Sample Whole Grains Reported Whole Grains Reported No Whole Grains All other Grains Who Do the amounts and types of grains consumed vary by Socioeconomic factors Income, Marital status, Education, Ethnicity Biological factors Gender, Age, Body weight, Lifestyle factors Physical Activity, meal patterns, health behaviors, diet history Who Socioeconomic factors Amount of all grains Any whole grains Adults Education Non-Hispanic black Hispanic 0.37 -0.66 -0.78 -0.48 0.19 0.05 Children Income Who Biological Factors Amount of all grains Any whole grains Adults Age -0.04 0.01 Men 2.19 -0.22 Waist Measure -0.64 Children Age 0.19 Boys 1.96 BMI -0.06 0.09 -0.01 Who Lifestyle Factors Amount of all grains Any whole grains Adults Cigarettes -0.01 Alcohol -0.03 -0.13 Breakfast 1.90 Snacking 0.02 Optimism (Weight) -0.41 Portion Control Extreme Measures -0.89 -1.17 0.71 Who Lifestyle Factors Amount of all grains Any whole grains Children Breakfast 1.54 0.90 Snacking 0.03 0.01 So…. Can we say anything about shifts in grain consumption? • Changing Demographics – – – – Age Ethnicity [whole grains] (adults) Education [whole grains] (adults) Income (children) • Changing diets and lifestyles – More health conscious ? For More Information ERS-www.ers.usda.gov CNPP-www.cnpp.usda.gov NHANES-www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm Lisa-Lmancino@ers.usda.gov Andi-Andi.carlson@cnpp.usda.gov The End