W. Geog. U11 Vocab Power Point
advertisement

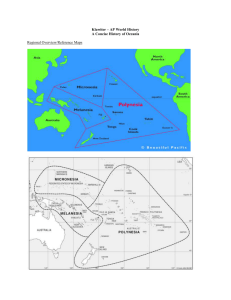
WORLD GEOGRAPHY AUSTRALIA/OCEANIA UNIT 11 VOCABULARY TERMS THE ECOSYSTEM OF THE REGION • Limestone skeletons of a tiny sea animal: coral • Shrimplike animal: krill • Small, sturdy plants: lichen • Small shrub that grows in New Zealand: manuka • Pool of water inside an atoll: lagoon • The formation that lies just off Australia's northeastern coast (the largest living thing on earth) is the _____. Great Barrier Reef The Great Barrier Reef can be seen from outer space – it’s big! A FEW CULTURAL ASPECTS • In some parts of Oceania _____ is spoken. pidgin English • Australians speak _____, a dialect of English. Strine • The _____ was originally a hunting tool.Boomerang • Each aboriginal family group traveled as a _____. Clan • A _____ provides simple shelter on tropical islands. Fale • Some islanders still make their livings by _____. subsistence farming • The arts have enriched life in the South Pacific region by passing on knowledge from generation to generation and now it has many _____, _____, and _____. musicians, writers and artists • Some characteristics of modern lifestyles in Australia, New Zealand, and Oceania include: _____ and _____. Australia and New Zealand are fast paced and island life is slow paced THE ECONOMICS OF THE REGION • New Zealand's main natural resource is _____. Land • The local resources that help to meet New Zealand's main natural resource are: _____. rivers and dams that produce hydroelectric power and geothermal energy provided by water heated underground by volcanoes The beauty of scenic New Zealand is stunning. The sheep like it too! THE PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF THE REGION • Well from which pressurized water flows to the surface: artesian well • Huge crack in an ice cap: crevasse • Low, ring-shaped island: atoll • The three types of islands that are found in Oceania are: _____, _____, and _____. high islands, low islands, and continental islands • The _____ of the cap causes the motion of the Antarctic ice cap. Weight This is an island. It’s an atoll – created by a volcanic explosion leaving a ring SOME POLITICAL FACTORS OF THE REGION • The Micronesian islands became a _____ after World War II. trust territory • In 1901 Australia became a _____ Great Britain. Dominion The Antarctic treaty was established in 1959 because they wanted to preserve Antarctica as a peaceful scientific _____. research site Antarctica is a wasteland of ice, but millions of animals survive their year-round SOME HISTORY OF THE REGION *Geography influenced settlement patterns in the region because a high percentage of the land is unsuited for human _____. Habitation *The ways of life that Pacific indigenous peoples practice is that the Aborigines were nomads and the pacific islanders settled in family groups along the _____. Coasts *European settlement influenced the region by _____, _____, _____, _____ and _____. establishing coastal farms, bringing livestock, building textile industries, bringing diseases, and by ruling the people cruelly *Maori, Aborigines, and people from Asia were the original settlers of _____, _____, and _____. Australia, New Zealand, and Oceania The didgeridoo (also known as a didjeridu) is a wind instrument developed by Indigenous Australians of the North • • • • WEATHER & CLIMATE Windless area near the Equator: doldrums Violent Pacific Ocean storm: typhoon The climate that supports most of Australia's agricultural lands is _____. humid subtropical The factor that prevents temperature extremes in _____ is ocean winds that warm the land in winter and cool it in the summer. New Zealand South Pacific island typhoons can be deadly