The Digestive System
advertisement
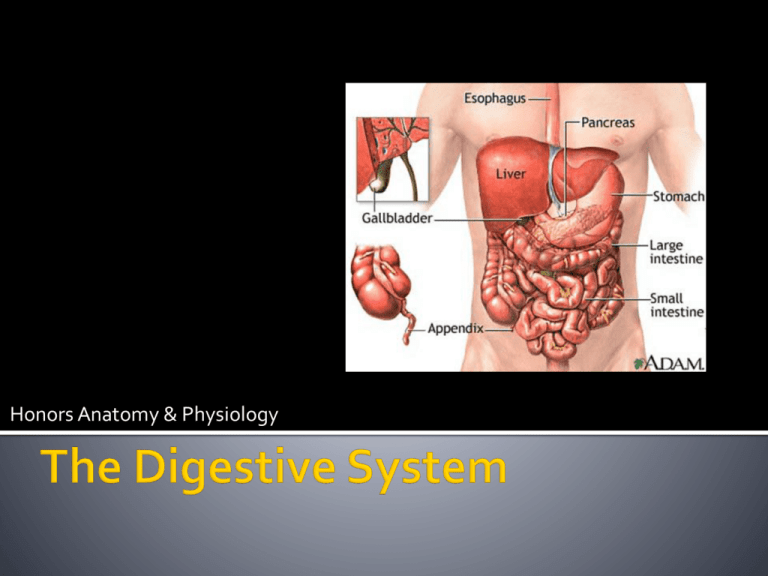
Honors Anatomy & Physiology AKA alimentary canal or gut Continuous muscular digestive tube Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus Ingestion Propulsion Catabolic break down by enzymes Absorption Chewing, mixing w/saliva by tongue, churning food in stomach Segmentation – constriction of intestines mixes food w/juices (see fig b) Chemical Digestion Swallowing -voluntary Peristalsis – waves of involuntary contractions (see fig a) Mechanical Digestion Taking food in Chemical building blocks, vitamins, minerals, and water from lumen of GI into blood & lymph Defecation Eliminates indigestibles Lines w/stratified squamous epithelium Labia (lips) – orbicularis oris (poorly keratinized) Cheeks – buccinators for chewing Hard Palate – rigid surface for tongue to mash food Soft palate – skeletal muscle w/ uvula Tongue- skeletal muscle fibers in various directions, repositions food and mixes w/saliva to form bolus lingual frenulum attaches to floor 1,000 – 1,500 mL per day! Regulated by parasympathetic division of ANS Functions: Composition Cleanses mouth Dissolves food chemicals for taste Moistens food to compact into bolus Amylase breaks down starch 97% water, electrolytes pH 6.75 Amylase, mucin (forms mucus), lingual lipase Antimicrobials: lysozyme, IgA, defensins Multiple Locations: Extrinsic salivary glands Intrinsic salivary glands – continuous secretion Buccal galnds Paratid gland Submandibular gland Sublingual gland Function: Masticate (Chew) voluntary & reflexive 20 Primary (deciduous) or milk teeth by 24 months Roots reabsorbed as adult teeth develop causing them to fall out between 6-12 yrs 32 Permanent teeth (including wisdom teeth) Types: Incisors - cutting Canines – tear/pierce Premolars (bicuspids) – grinding & crushing Molars (4-5 cusps) Structure: Enamel – acellular hardest substance in body (Ca and hydroxyapatite), cannot be replaced Gingiva recedes w/age Dentin – bonelike but avascular Cementum – Ca connective tissue covers root Peridontal liagment anchors to alveolus Oropharynx & laryngopharynx Stratified squamous epithelium w/mucus producing glands 2 skeletal muscle layers: inner layer longitudinal Constrictor muscles encircle Peristalsis propels food into esophagus Collapsed 10” muscular tube Pierces diaphragm to join to cardiac sphincter of stomach Takes 2 (liquids) -8 (solids) seconds 4 layers: Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium Longitudinal folds when empty, flatten when food is in transit Esophageal glands – secrete mucus as bolus moves thru Skeletal & smooth muscle Storage tank where bolus + enzymes = chyme 6-10” long, ‘J’ shaped Mechanical digestion Vigorous peristalsis Chemical digestion HCl denatures proteins Chief cells secrete pepsin & lipase rennin (milk proteins) Absorption Alcohol & aspirin (lipid soluble) pass through stomach mucosa into blood (can cause gastric bleeding) Secretes intrinsic factor to absorb vitamin B12 in small intestine Mucus barrier Rugae – fold when empty Omentum –mesenteries that tether digestive organs to body wall (fat & lymph) 20 ft long, 1.5” diameter, complete trip about 2 hours Simple columnar epithelium w/goblet cells and T cells Intestinal crypts w/defensins & lysozyme & stem cells 2 layers of muscle for segmentation Peyer’s patches Huge SA for absorption Villi – 1mm fingerlike projections w/capillary bed & lacteal (lymph) Microvilli – brush border projections of plasma membrane w/ bound enzymes to complete carb & protein digestion 3 subdivisions: Duodenum - 10” curves around pancreas ▪ Bile duct ▪ Pancreatic duct ▪ Duodenal glands produce bicarbonate mucus to neutralize acidic chyme Jejunum – 8’ long Ileum – 12’ long Liver Largest gland in body (3lbs), 4 primary lobes Produces 500-1,000 mL bile/day – fat emulsifier Gallbladder 4” long, inferior surface of right lobe Store bile (yellow-green alkaline solution) Salts, pigments (bilirubin), cholesterol, triglycerides, phospholipids & electrolytes Pancreatic juice (12001500mL/day) released via pancreatic duct which fuses w/bile duct as enters duodenum Acini – clusters of secretory cells Pancreatic proteases: trypsin, carboxypeptidase, chymotrypsin Amylase, lipases, nucleases Islets of Langerhans β cells secrete – insulin (↓ blood glucose) α cells secrete – glucagon ( blood glucose) Bicarbonate ions – pH 8 7cm diameter, 1.5 meters Function: reabsorb remaining water from indigestible food residue & eliminate as feces 12-24 hours to reclaim water & electrolytes Simple columnar epithelium Deep crypts w/goblet cells to ease passage of feces Mass movements: slow powerful contractive waves, fiber increases strength contractions Subdivisions: Cecum - pouch Appendix – lymph tissue Colon – ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid Rectum – has valves to separate feces from flatus! Anal Canal – 2 sphincters (1 involuntary & 1 voluntary), stratified squamous epithelium Over 700 species! Survivors from small intestine or enter via anus Ferment indigestible carbs (cellulose, xylan) Metabolize proteins (mucin, heparin, hyaluronic acid) Release 500mL gasses/day (H2, N2, CH4, CO2, and smelly dimethyl sulfide) Synthesize vitamin B & K Lymph cells moniter to ensure they do not stray Catabolic process: polymers hydrolyzed monomers Complete Enzyme Chart: Carbs: Amylase, dextrinase, glucoamylase, maltase, sucrase, lactase Proteins:Pepsin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, aminopeptidase, dipeptidase Lipids: bile, lipase Nucleic Acids: ribonuclease, deoxyribonuclease, phosphatases Endoderm forms lining GI tract Rest develops from mesoderm Nutrients – promote growth, maintenance & repair Carbohydrates Lipids Organic compounds function as coenzymes Classified as fat or water soluble Minerals Structural uses: keratin, collagen, elastin, muscle proteins, etc Functional uses: enzymes, hormones, pigments, and transport Can be oxidized for energy in liver RDA: 0.8%g/kg of body weight Vitamins Utilized for phospholipids, myelin, insulation, cushion, stored energy, steroid hormones, absorb fat-soluble vitamins RDA: 80-100g plant/animal fats; <250mg cholesterol Proteins Glucose oxidized to ATP (mitochondria) Energy measured in kilocalories or Calories (heat energy required to raise 1kg of water 1OC) RDA: 130g digestible, 25-30g of fiber Inorganic Ionized or bound to organic compounds Water