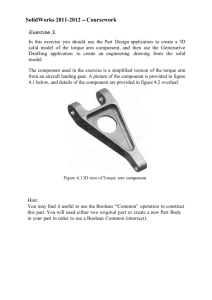
Lecture 3
advertisement
PHYS16 – Lecture 24 Simple Machines II and Static Equilibrium November 3, 2010 Review of last time… Practice Question 1 • In a spin, why do ice skaters decrease their ang. velocity when they hold their arms out? A) B) C) D) E) It decreases ang. momentum. It decreases rot. inertia. It increases rot. inertia. It increases the centripetal force. None of the above. http://www.corbisimages.com/images/67/7760610C-6DF3-4A39-ACD6-C3CDEFF73296/PN015983.jpg Kristi Yamaguchi Practice Question 2 • A lawn tractor tire turns at 65.0 rpm and has a radius of 13.0 cm. Find the linear speed of the tractor in m/s. A) B) C) D) 0.141 m/s 0.885 m/s 88.5 m/s 186 m/s Practice Question 3 • A ball attached to the end of a string is swung in a vertical circle. The angular momentum of the ball at the top of the circular path is: A) > ang. momentum at the bottom B) = ang. momentum at the bottom C) < ang. momentum at the bottom Practice Question 4 • The turbine of a jet engine has a moment of inertia of 25 kg∙m2. If the turbine is accelerated uniformly from rest to an angular speed of 150 rad/s in a time of 25 s, what is the torque? 0 t ( 0 ) / t I I ( 0 ) / t (25)(150) / 25 150 J This Week • Simple Machines II – gears, belts, and levers • Static Equilibrium – Center of Gravity – Newton’s Second law for torques and forces Simple Machines II Simple Machine = Gears and Belts • Gears are machines that transfer rotational motion • Gear/belt system linear velocity is equal v1 v2 1r1 2 r2 r1 2 gear ratio r2 1 Trade radius for rot. speed Gear Ratio • Gears with Teeth r1 # of teeth 2 gear ratio r2 # of teeth 1 • Belts or Smooth disks r1 f 2 gear ratio r2 f1 Gears/Belts: What are they good for? 1) Transfer rotational motion 2) Adjust the direction of motion 3) Change the torque…. Torque and Power • Torque (rotational equivalent of force) changes with radius rF sin( ) • Power depends on both torque and rotational speed dW P dt t Example Question: Bicycle • A bike is set such that it has 44 teeth on the front gear and 11 teeth on the rear gear – What is the use of this setting? Going downhill or fast! • Then in a “Granny” setting it has 15 teeth on the front gear and 30 teeth on the rear gear – What is the use of this setting? Going uphill! Example Question: Gears • Which way does Gear C turn? • What is the ang. velocity of Gear C in rev/min? Simple Machine: Lever • Lever is a machine that improves mechanical advantage by using rotation • In a lever the applied force can be reduced by increasing the distance between force and fulcrum rF sin( ) Increasing r allows for decreasing F Example Question: Lifting students • If the fulcrum is placed in the middle it takes me 1 kN of force to lift two students. Now, if I place the fulcrum such that it is ¾ of the way from my end, how much force do I need? A third of the force! Three kinds of levers: Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PW7ztbwJ KBk • This movie reminds me of a high school film strip, but is useful… Static Equilibrium • Forces should not cause linear acceleration F ma 0 • Torques should not cause rotational acceleration I 0 • Object has no rotational or linear motion Example: Wheelbarrow • I want to use a wheelbarrow to move 30 kg of yard waste with a center of mass 0.2 m from the wheel axle. If the handle is located at 1 m from the wheel axle how much force should I use to keep the wheelbarrow lifted? F=(30kg)(9.8 m/s^2)(0.2 m)/(1 m) = 60 N • What is my mechanical advantage? MA=(30kg)(9.8 m/s^2)/(60 N) = 5 Main Points • Gears transfer rotational motion, as the radius of the gear increases there is more torque for the same amount of force • Levers use torque to lift a load, as the length of the lever arm increases the force needed decreases • Static Equilibrium – both forces and torques on an object have to sum to zero

![Machine Elements [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009054465_1-76bd66345967cd60934cd86eccae6fad-300x300.png)