SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
advertisement
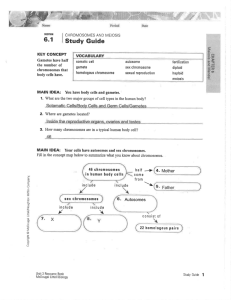
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Quiz 6B sexual reproduction • the joining of haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote, which develops into a new individual • each offspring receives genes from both its parents • get genetic variety Information about genes most organisms have 2 genes for every trait Information about genes genes are parts of chromosomes Information about genes most genes come in pairs Information about genes most chromosomes come in pairs Diploid •having 1 pair of each type of chromosome in an organism •have 2 of every kind of chromosome •symbol is 2n Haploid •a cell that has only 1 chromosome of every pair •symbol is 1n Diploid vs Haploid Normal human cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes which is a total of 46 chromosomes. Human diploid number is 46 Human haploid number is 23 Diploid & Haploid Examples Haploid Diploid Honey bee 16 32 Crayfish 100 200 Rabbit 22 44 Watermelon 11 22 Corn 10 20 Meiosis •the process whereby 1 diploid cell forms haploid cells (gametes) •a dividing process during which the # of chromosomes is cut by 1/2 in each resulting cell •also called reduction division Meiosis Gamete •a cell that contains only 1 of each type of chromosome found in an organism •a reproductive cell •in order to form a haploid cell (gamete)- meiosis occurs •in most organisms meiosis produces 1 of 2 types of gametes 2 types of gametes •Ova (singular-ovum) female gametes; usually larger than the male gamete and does not have that power to move itself •Sperm - male gametes; usually smaller than ova, but they have some means of moving themselves 2 types of gametes ovum sperm Spermatogenesis Oogenesis Where are gametes formed? In reproductive organs • Testes – male reproductive organs • Ovaries – female reproductive organs Fertilization the formation of a zygote from the union of 2 gametes Zygote a diploid cell formed by the union of 2 gametes