Citizen Participation
advertisement

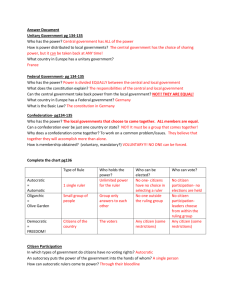
Government Citizen Participation Autocratic/ Autocracy Oligarchic/ Oligarchy Democratic/ Democracy Definition Definition Definition Characteristics: Characteristics: Characteristics: Autocratic/ Autocracy Oligarchic/ Oligarchy Democratic/ Democracy Examples Examples Examples Picture Picture Picture Citizen Participation • Different governments decide a citizens’ role in government differently • The government can share none, little, or most of its power with its citizens 3 main ways governments determine citizen participation . . . 1. autocratic 2. oligarchic 3. democratic AUTOCRATC rule by one OLIGARCHIC rule by the few DEMOCRATIC rule by all Citizen’s Role in Government Autocratic Oligarchic Democrati c (one) (few) (all) LEAST citizen MOST citizen participation participation Low or No Participation Autocratic Low or No Participation Oligarchic Citizen Participation Government Power General Citizens’ Participation Select Citizens’ Participation Government Power Citizen Participation Government Power How Governments Determine High Participation High Participation Citizen Participation Low or No Participation Democracy Autocratic • One person (ex. King, Emperor, Czar) possesses unlimited power • The citizen has limited, if any, role in government Autocratic cont. • Ruler gets power through inheritance or ruthless use of military & police power • The oldest form of government • One of the most common forms of government Examples of Autocratic Gov’ts Totalitarianism & Dictatorships • Ideas of a single leader glorified • Gov’t tries to control all parts of social & economic life • People lack the power to limit their rulers • Examples- Hitler (Germany), Mussolini (Italy), Stalin (Russia), Bashir (Sudan), Hussein (Iraq) Examples of Autocratic Gov’ts • • • • • Absolute Monarchy King, queen, or emperor has unlimited power Position is usually inherited (from parents or other relatives) People lack the power to limit their rulers Absolute monarchs are rare today but from the 1400s to the 1700s they ruled most of Western Europe Example - King of Jordan Oligarchy • Government by the few (a few powerful individuals make decisions) • A small group exercises control, especially for corrupt and selfish purposes • The citizen has a very limited role Oligarchy •The ruling group gets its power from military force, wealth, religion or a combination. •Political disagreement is usually suppressed (sometimes violently) Examples of Oligarchy Theocracy • a government run by religious authority • A Deity (god) is recognized as the highest ruler • The Deity's laws are interpreted by religious experts (priests, mullahs, etc.) Examples of Oligarchy Communism • Gov’t plans & controls the economy • a single political party holds power • state controls are forced • NO private ownership of property • All goods are to be equally shared by the people (ex. classless society) WARNING! Autocracy & Oligarchy • Sometimes claim they rule for the people. • In reality, the people have very little say in both types of government. • Example - may hold elections with only one candidate or control the results of elections • Example - even when these governments have a legislature (branch that makes laws), they often only approve decisions made by the leaders. Democracy • Citizens vote on government representatives & on specific issues • People have the most power Examples of Democratic Gov’t Republic the people elect representatives, not the people themselves, to govern and make laws Examples of Democratic Gov’t Constitutional Monarchy • monarch must follow the laws of the constitution • monarch is usually a figure-head, the real power rests with the legislature (Parliament/Congress) who is elected by the citizens 2 main forms of democratic governments . . . 1. Presidential 2. Parliamentary Types of Democratic Gov’ts Presidential Democracy Parliamentary Democracy Definition Definition Characteristics Characteristics Examples Examples Picture Picture Branches of Government Enforces the laws of the EXAMPLES Constitution & legislature President or Prime Minister Police, FBI, Military, Dept. of Ed, Treasury, Dept. of Justice (prisons), Dept. of Agriculture Decides who is or isn’t following the laws of the Constitution & legislature Makes the laws (legislature) EXAMPLES Congress (Senate & House of Representatives) Parliament EXAMPLES courts & juries Supreme Court Presidential Democracy (definition) • Executive branch is independent from the legislature • Head of the executive branch (president) elected by citizens, not the legislature Presidential Democracy Citizens vote for EVERY branch of gov’t Presidential Democracy (characteristics) •Different branches of government (executive, legislative, judicial) are equal in power •EXAMPLE U.S.A., Mexico, Brazil Parliamentary Democracy (definition) • executive branch is dependent on legislative branch • Head of executive branch (Prime Minister) elected by the legislature, not the citizens Parliamentary Democracy Citizens DO NOT vote for Executive Branch Prime Minister Parliament Parliamentary Democracy (characteristics) •NO clear separation of powers between the executive and legislative branches •Legislature makes most decisions Examples of Parliamentary Democracy U.K., Canada, Germany, Australia What do you know? 1. What is the main difference between a Presidential Democracy and a Parliamentary Democracy? • Presidential = executive branch (ex. President) is chosen by the citizens, not the legislature • Parliamentary = executive branch (ex. Prime Minister) is chosen by the legislature (parliament) 2. Which form of democracy do you think allows for more citizen participation? Why? • Presidential b/c citizens get to vote for all 3 branches of gov’t AUTOCRATIC OLIGARCHIC DEMOCRATIC Rule by one Rule by the few Rule by all/many •One person (ex. King, Emperor, Czar) possesses unlimited power •The citizen has limited, if any, role in government Ruler gets power through inheritance or ruthless use of military & police power Examples Totalitarianism & Dictatorships- Hitler, Mussolini, Stalin, Sudan Absolute Monarchy – King, queen, or emperor has unlimited power Position is usually inherited (from parents or other relatives) •A small group exercises control, especially for corrupt and selfish purposes •The citizen has a very limited role •The ruling group gets its power from military power, wealth, religion or a combination. Political disagreement is usually suppressed (sometimes violently) Examples Theocracy - a government run by religious authority Communism - NO private ownership of property •Citizens vote on government representatives & on specific issues •People have the most power Examples Republic – the people elect representatives, not the people themselves, to govern and make laws Constitutional Monarchy –monarch must follow the laws of the constitution monarch is usually a figure-head, the real power rests with the legislature (Parliament/ Congress) who is elected by the citizens