Measurement & Density Worksheet: Middle School Science
advertisement
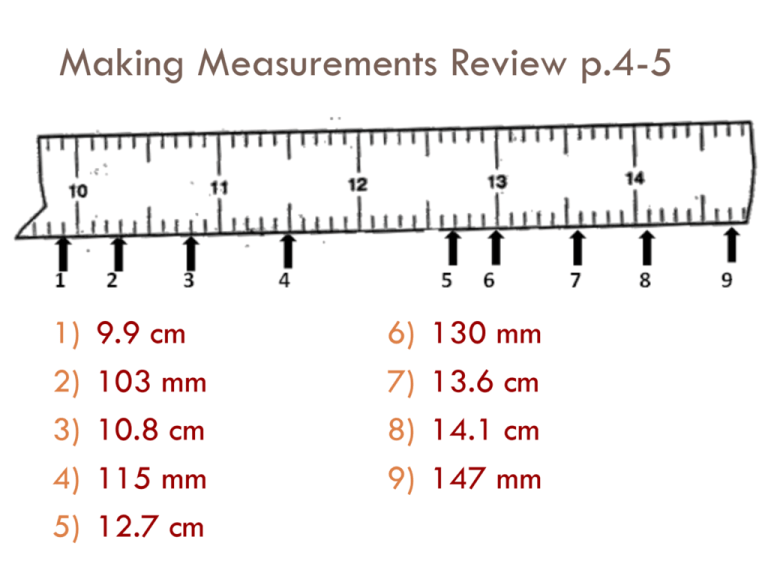
Making Measurements Review p.4-5 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 9.9 cm 103 mm 10.8 cm 115 mm 12.7 cm 6) 7) 8) 9) 130 mm 13.6 cm 14.1 cm 147 mm Measuring Mass 10. 324.2 g 11. 117.1 g 12. 51.4 g 13. 403.5 g Measuring Volume 41ml 244 ml 7.9 ml 28 ml 208 ml 1.1 ml 159 ml 8.8 ml Measuring Temperature 77 ˚ 63 ˚ 5˚ 66 ˚ What is Density? p.6 What is VOLUME? • How much space matter takes up What is MASS? • How much matter (stuff) there is in an object. How could volume and mass determine if something sinks or floats in water? • Write your own ideas. Don’t be afraid to be wrong. Part A: Cola Demo Observations: • What are the different characteristics of each can of coke? • Which are the differences between mass and volume of the two cans? Hypothesis: Data: Was your prediction correct? Why or why not? What is Density? • How much matter (mass) there is in a certain amount of space (volume). • If you drop an object into a lake it would do one of two things- sink or float. Explain what is necessary for something to float or sink in a substance. • Explain what happened in the demonstration using the words volume, mass, density, sink, and float. Sink or Float Lab • Problem: What materials will sink, swim, or float in water. • Materials: 3 film canisters, a tub of water, and various objects. • Objective: You must create three film canisters. One that sinks, one that Canister 1 – Float (at least part if floats, and one that is it is above the surface) suspended in water. Canister 2 – Swim (suspended) Canister 3 – Sink (all the way) General Procedure • Modify 3 film canisters using the 8 objects available. • Use cup to gather your objects from the back table. • You may use only one type or a combination of objects • Your canister must be filled with objects. • Write the materials and procedure your group followed. • Fill out data table. • Clean up: ▫ Empty out all canisters and return materials to back table (If cotton balls are wet, throw them away) ▫ Dry you are and leave it cleaner than you found it. • You have 15 minutes to complete! GO!!! Density Notes and Activities p.8 What is density? • Density is a comparison of how much matter there is in a certain amount of space. ▫ Higher density = more crowded molecules (packed together) ▫ In general, density of matter gets lower as it moves from solid to gas and higher as it moves from gas to solid. Why? • You need to know the mass of the object or substance • You need to know the volume of the container or the object Note: 1 mL = 1 cm³ Density formula and Units • Density = mass OR mass ÷ volume volume • Units for density: g cm3 or g or Kg ml L • Why are these the units for density? ▫ They are the units for mass (g) divided by the units for volume (cm3, ml). ALWAYS REMEMBER UNITS! D= Which one is more dense (denser)? • Which square has higher density? Why? • Why? Same volume greater mass Which one is more dense (denser)? • Now which one has higher density? Why? • Why? Same mass less volume Density of water • The density of water is 1g/ml (or one gram per milliliter) • If a substance has a lower density (less density) than water it will float. • If an object or substance has a higher density (greater density) than water it will sink. Let’s Practice (we’ll do these together) • Frank has a paper clip. It has a mass of 1g and a volume of 1cm3. What is its density? 1 g ÷ 1cm3 = _____ Answer: 1 g/cm3 Will it sink, swim, or Float in water? • Frank also has an eraser. It has a mass of 5g, and a volume of 9cm3. What is its density? 5 g ÷ 9 cm3 = ________ Answer: 0.6 g/cm3 Will it sink, swim, or Float in water? Work on these problems with your neighbor. • Jack has a rock. The rock has a mass of 10g and a volume of 5cm3. What is the density of the rock? 10g / 5cm3 = 2g/cm3 Will it sink, swim, or Float in water? • Jill has a gel pen. The gel pen has a mass of 8g and a volume of 4cm3. What is the density of the gel pen? 8g/ 4cm3 = 2 g/cm3 Will it sink, swim, or Float in water? Now, try these on your own. • Alicia has a watch. It has a mass of 50g and a volume of 25cm3. What is the density of the watch? 50g/25cm3 = 2 g/cm3 Will it sink, swim, or Float in water? • Mia has a wallet. It has a mass of 25g and a volume of 40cm3. What is the density of the wallet? 25g/40cm3= 0.63 g/cm3 Will it sink, swim, or Float in water? Eggciting Density Demo • Explain how the density of freshwater is different from the density of saltwater. • Predict what will happen (sink, or float) to an egg in freshwater?______ Salt water? ______ • Watch Teacher demo • Draw what happened. • Why did that happen? Review 1. What is the formula for density? D=m/v 2. How do we know if an object will float or not? Less dense than the substance = float 3. If two objects have the same mass but different volumes, which one will have a greater density? The object with the smaller volume (more crowded) 4. If two objects have the same volume but different mass, which one will have a greater density? The object with the greater mass (more crowded) 5. Jake has a book, a ruler, and a balance. How can Jake find the DENSITY of the book with the tools he has? Use the balance to figure out mass, and the ruler for volume (LxWxH). Then take mass and divide it by volume. • Water Displacement Review. (Show your work!) • Work on DENSITY PRACTICE (Show your work!) • HOMEWORK: Riddle me this…Density! Water Displacement Review p.7 1. 2. 3. 4. 35 – 30 = 5 ml 150 – 100 = 50 ml 22 – 20 = 2 ml 38 – 32 = 6ml B. 40 – 30 = 10 ml DENSITY PRACTICE P7 1. 5g/1mL = 5 g/mL 2. 0.5g/mL 3. 3g/mL 4. 0.5g/cm3 • Object more likely to be wood (floats, less dense than water) 5. 4mL 6. 3g/mL 7. Density of A = 8g/cm3 Density of B = 4g/cm3 Which material would make the bag for Alex? Why? • B, it is less dense In which material are the atoms closer together? How do you know? • A, it is more dense RIDDLE ME THIS…DENSITY P8-9 Letter #1 - 6.00g/mL : D Letter #8 - 0.01Kg/L : S Letter #2 - 6.81g/cm3 : Y Letter #9 - 247.50g/L : M Letter #3 - 2.36Kg/L : O Letter #10 - 0.11g/mL : H Letter #4 - 4.45g/mL : I Letter #11 - 3.15g/mL : B Letter #5 - 131.43mg/mL : L Letter #12 - 8.80g/mL : N Letter #6 - 3.57g/mL : R Letter #13 - 0.65g/mL : A Letter #7 - 0.46g/mL : U Letter #14 - 0.73Kg/L : T Letter #15 - 19.07g/mL : E RIDDLE ME THIS…….DENSITY CONT. • What did the gas say to the solid? • Boy, you sure are dense! • What was the solid’s response? • At least I’m not an airhead! The Great Density Field Trip • Intro • Question: Where is density the greatest given the different areas/volumes? • Hypothesis (ITB): D= m/v LOCATION Classroom Stair Landing Between doors Main entry way Hallway Square Lunch Room MASS (higher, same, or lower than classroom) VOLUME (higher, same, or lower than classroom) # of students x 1 kg= L=10 m W= 11 m H= 3 m V= ? DENSITY (higher, same, or lower than classroom) D=m/v Density Field Trip – Analysis Questions 1. Where was our density the greatest? Where was it lowest? – Stair landing, lunch room 2. If an object has a larger volume and a smaller mass, what does that mean for its density? Explain. – Lower density, because there are less particles in a larger space. 3. If you have 3 items of the same size (one is rubber, one is foam, and one is steel), which one would have the greatest density? Why? – Steel, because it has more mass so the particles would be closer together. 4. If you have 20 atoms of oxygen in a small, medium, and large balloon, which one will have the least density? Why? – The large balloon because there is more space for the same mass. Particles are further apart. 5. Was your hypothesis supported or not? Explain. – Answers will vary. Bell Ringer: Density Quiz 1. What is the density of a log that is floating in a lake? A. less than water B. less than air C. the same as water D. more than water 2. A rock and a lead weight both sink when dropped into a lake. What do you know about their densities? A. B. C. D. They have the same density. They have different densities. They are more dense than water. They are less dense than water cm3 3. If the volume of a rock is 8 and its mass is 16 g, what is its density? A. B. 0.5 16g/8cm3 g/ cm3 C.= 1.0 g/ cm3 2 g/ cm3 D. 128 g/ cm3 2 g/cm3 4. A rock dropped in a graduated cylinder raises the level of water from35ml-20ml=15 20 to 35 mL. Theml rock has a mass45 of g/15 45 g. What is the density of ml = the rock? A. B. C. D. 1.3 g/3.0 mL g/ml 2.3 g/ mL 3.0 g /mL 4.5 g/ mL 5.A square chunk of plastic has a length of 5 cm, width of 5 cm and height of 5 cm. It has a mass of 200 x 5cm x 5cm = 125 cm3 g.5cm What is its density? A. 2.3 g/cm3 200 g/ 125 cm3 B. 0.12 g/cm3 C. 1.0 g/cm3 D. 1.6 g/cm3 = 1.6 g/cm3 Density Lab p 11-12 • Question/Problem: Which object has the least density? Which is the densest? (Hypothesis must have prediction for both) • What are the two ways to measure volume? How will you determine density? – Volume: water displacement or LxWxH – Mass: triple beam balance – Density: Mass/Volume Object Mass Volume • Data Table (don’t forget units) 1. Dice 5.5 g 3 mL Density 1.83 g/mL 2. Clay Ball 3.5 g 2 mL 1.75 g/mL 3. Penny 2.5 g 1 mL 2.5 g/mL 4. Rock 3.2 g 1.5 mL 2.13 g/mL 5. Eraser 2g 2 mL 1 g/mL 6. Density Lab-Analysis Questions 1. Densest? 2. Least dense? 3. Which ones float on water? How do you know? a. More mass = more density b. Less mass = less density c. More volume = less density d. Less volume = more density 1. More mass, less volume? = very high density 2. Less mass, more volume? = very low density 7. Draw particles VERY DENSE LESS DENSE 8. Conclusion: Start with restating the question, end with the answer. Use the 5 sentence format we learned in class (poster and on my website) The GOLDEN Crown Dilemma p14 • What is density? – How much mass is in a certain amount of volume • Complete Data table Crown # 1 2 3 4 5 Mass 1890 g 486 g 1404 g 3474 g 2034 g Volume 180 cm3 180 cm3 180 cm3 180 cm3 180 cm3 Density 10.5 g/cm3 2.7 g/cm3 7.8 g/cm3 19.3 g/cm3 11.3 g/cm3 TGCD - Analysis Questions 1. What is each crown made of? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Silver Aluminum Steel Gold Mercury 2. Conclusion: 5 sentence composition persuading the king. HW: How dense can you get? P16-17 1 a. Float b. 19.5 g/150 cm3= 0.13 g/cm3 6 a. It’s less dense than water b. 0.9 g/cm3 2 a. 7.9 g/cm3 b. sink 7 a. 3.18 g/cm3 b. Sand is denser than water 3 a. Water displacement b. 2.67 g/mL 8 a. 19.3 g/cm3 b. Gold is denser than sand 4 a. more dense b. 2.92 g/cm3 c. YES 9 a. 8.96 g/cm3 b. No, gold is denser 5. 605,666 g 10 a. 0.013 g/cm3 b. Oxygen is less dense than water , so air bubbles float to top Shake it up, Sort it Out • Answer Analysis Questions 1. Rocks, bigger soil particles. They settled first. 2. Larger, denser objects are at the bottom and smaller, less dense particles are towards the top. 3. Smaller particles, less dense 4. Yes, wood and plant material. Because it is less dense than water. 5. They have about the same density as the water 6. You should talk about density and particle size 7. Conclusion: Natural Sorting p6 Nature likes to sort things! Nature has a way of naturally arranging itself in a predictable manner Natural sorting is when particles are arranged with dense, larger objects on bottom and small, less dense objects on top Water is an excellent natural sorter. Other natural sorters are wind, lava, ice/glaciers. Sorting occurs based on density and the size of particles. This causes particles to settle (sink to the bottom) at different rates, forming layers. Sorting our Earth The Earth is a naturally sorted sequence. The inner core is the most dense (at the center/bottom) and the densities get smaller as you move outwards to the atmosphere which is the least dense of all the layers REAL LIFE SORTING: Sorting really is seen outside! Picture 1: 1. Describe any differences you see in color or texture of the cliffs. 2. Does this rock shows sorting? How so? Picture 2: This section of rock was deposited by water. Remember… water sorts by density and size. D C B A 3. Which layer settled first? How do you think its density compares to the other layers? 4. Which layer has the least dense particles? In what order did it settle out? Picture 3: Look at the texture of the rock. 5. How many different grain sizes do you see? 6. Is this deposit naturally sorted? Explain. B A B A Picture 4: This is a beach deposit. 7. How many general grain sizes do you see? 8. Does it show natural sorting on each half? Explain. Picture 5: Density = 1.025 gram/cm3 Density = 3.2 gram/cm3 9. Based on density, why does the ocean sit on top of the ocean floor (sand)? Picture 6: 10. Is this deposit sorted? How do you know? Picture 7: 11. Does this scene show sorting based on density? Explain. 12. Which element (ice, water, or air) is least dense? Explain. Picture 8: A: Balsa Wood B: Iron Density Density .13 grams/cm3 7.9 grams/cm3 C: Quartz Sand Density 3.2 grams/cm3 D: Gold Density 19.3 grams/cm3 You pick up these items while you are panning for gold in the Provo River. 13. Based on density, tell me what you would find in your pan from top to bottom. Picture 9: A B C D E F This is a diagram of the earth’s layer 14. List the layers from most dense to least dense? 15. Why is the Earth layered? Mastery Quiz 6.1 • Match the correct substances with the Earth layers they would belong to: Substance Density Layer of the earth A 0.0133g/ml 1. Core _____________ B 1.0g/ml C 4.47g/ml D 14g/ml 2. Atmosphere ___________ 3. Hydrosphere ____________ 4. Mantle ______________ 5. A substance/object is found to have a volume of 5 ml and a mass of 10g. Where would this substance settle with the other earth materials above? A. Between the hydrosphere and the mantle B. Between the core and the mantle C. Between the atmosphere and core D. Above the atmosphere Mastery Quiz 6.1 6. Natural sorting is defined as: A. How nature sorts materials by size and weight. B. The way nature sorts things by size only C. Nature sorts by size and density. 7. The layers of the earth from most to least dense are: A. Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core B. Hydrosphere, Atmosphere, Crust, Mantle, Inner Core, Outer Core C. Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, Crust, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere 8. A jar contains layers of gravel, sand, clay, and silt. Which substance would most likely be at the bottom of the jar? A. Clay B. Sand C. Silt D. Gravel Density of liquids Liquid Layers If you pour together liquids that don’t mix and have different densities, they will form liquid layers. The liquid with the highest density will be on the bottom. The liquid with the lowest density will be on the top. Liquid Layers Check out this picture. Which layer has the highest density? Which layer has the lowest density? Imagine that the liquids have the following densities: 10 g/cm3 3 g/cm3 6 g/cm3. 5 g/cm3. Which number would go with which layer? 3 g/cm3 5 g/cm3 6 g/cm3 10 g/cm3 Liquid Layers – Try with your neighbor Which liquid has the highest density? Which liquid has the lowest density? Golden Syrup Oil Which liquid has the middle density? Water Liquid Layers – Try on your own! Imagine that the liquids on the right have the following densities: 15 g/cm3 10 g/cm3 3 g/cm3 9 g/cm3 7 g/cm3 12 g/cm3 Match the colors to the correct densities. 3g/cm3 7g/cm3 9g/cm3 10g/cm3 12g/cm3 15g/cm3 Demo: Watch as your teacher pours different liquids into beakers. Color what you see. All 3: Mastery Quiz 6.2 1.Which choice below gives the layers of the earth in order from highest to lowest density? A. Crust, Core, Atmosphere, Hydrosphere B. Core, Crust, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere C. Hydrosphere, Crust, Core, Atmosphere 2. Layers of the Earth LAYERS OF THE EARTH p23 1. Atmosphere Hydrosphere Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core The Atmosphere 2. The atmosphere is a layer of gases that surrounds the earth. 3. The atmosphere is the least dense layer of the Earth. 4. The mass of the atmosphere is 1.33 g for every 100 cm3. What is its density? 0.0133 g/cm3 5. The atmosphere is composed gases. - 78% Nitrogen - 21% Oxygen - 1% other gases The Hydrosphere (Water) 6. The water part of the crust is called the hydrosphere. 7. Water is more dense that the atmosphere, but less dense than the continental crust and interior layers. 8. Where is the hydrosphere the thickest? At the Mariana trench in the pacific ocean. The Crust 9. The crust is both solid and rocky. 10. The continents and ocean floor are part of the crust. 11. Which is thicker continental crust or oceanic crust? The Mantle 12. The mantle is a thick gel or tar-like layer of molten rock found beneath the earths crust. 13. The mantle is denser than the crust because it contains much more iron and other heavy elements and minerals. 14. A 100 cm3 sample of the mantle has a mass of 447 grams. What is its density? 4.47 g/cm3 The outer Core 15. Why would it be impossible to travel to Earth’s core? Because of the intense heat and pressure of the core. 16. The outer core is the layer of liquid iron and nickel that surrounds the solid center of the Earth. 17. What is the density of the outer core? (A 100 cm3 sample from the core can have a mass around 800 g) 8 g/cm3 The inner Core 18. The inner core is the solid, dense center of our planet. 19. The inner core is super dense. How dense is it? 14 g/cm3 20. Why does the core stay solid even though the temperature at the center of the Earth is so high? Because of the extreme pressure of the other layers LABEL! Name: (name of layer) Density: (g/cm3) Phase: (solid, liquid, gas) Composition:(What is it made of) Atmosphere Name: Density: Phase: Composition: Density:(g/cm3) Phase: (solid, liquid, gas) Composition: (What is it made of) Name: Density: Phase: Composition: Name: Density: Phase: Composition: COLOR! Name: Density: Phase: Composition: Name: Density: Phase: Atmosphere Hydrosphere Crust Name: ATMOSPHERE Density: 0.0133 g/cm³ Phase: Gas Composition: Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Gases Name: HYDROSPHERE Density: 1 g/cm³ Phase: liquid Composition: water Mantle Outer Core Inner Core Name: CRUST Density: 2.93g/cm3 Phase: Solid (rocky) Composition: Si, Al, O, Mg, granite, basalt, Name: MANTLE Density: 4.47 g/cm³ Phase: Gel or tar-like liquid Composition: Iron and other heavy elements and minerals Name: OUTER CORE Density: 8 g/cm³ Phase: Liquid Composition: iron and nickel Name: INNER CORE Density: 14 g/cm3 Phase: Solid (under pressure) Composition: iron and nickel ANALYSIS QUESTIONS P25 1. THICKEST? THE MANTLE THINNEST? THE CRUST WITH THE HYDROSPHERE 2. DENSITY TOWARD CENTER? IT GETS DENSER 3. ELEMENTS SINK TO THE CENTER? THEY WERE DENSER THAN THE OTHERS 4. OUTER CORE A LIQUID? THE TEMPERATURES ARE VERY HIGH SO THE METAL HAS MELTED INTO A LIQUID 5. INNER CORE A SOLID? EVEN THOUGH IT IS REALLY HOT THE PRESSURE FROM THE OTHER LAYERS KEEP THE MOLECULES FROM MOVING AROUND. 6. GOOD MODEL OF THE EARTH? RELATIVE SIZE OF LAYERS, CORRECT ORDER OF LAYERS 7. THINK OF SOME OTHER MODELS OF THE EARTH YOU’VE SEEN (MAPS, GLOBES, ETC.). a) WHAT ABOUT THEM IS ACCURATE? o RELATIVE SIZE, POSITIONS, SHOW MOUNTAINS b) WHAT ABOUT THESE OTHER MODELS IS INACCURATE? o DON’T SHOW INSIDE OF EARTH o DON’T SHOW ATMOSPHERE o CONTINENTS ARE NOT PROPORTIONED CORRECTLY Orange (A) Yellow (B) Green (C) Red (D) Blue (E) YELLOW ON TOP ORANGE ON TOP YELLOW ON TOP RED ON TOP YELLOW ON TOP BLUE ON TOP BLUE ON TOP RED ON TOP BLUE ON TOP Yellow (B) NOTHING GOES HERE Green (C) NOTHING GOES HERE NOTHING GOES HERE NOTHING GOES HERE NOTHING GOES HERE Red (D) NOTHING GOES HERE BLUE ON TOP Number 3 and 4 BLUE (E) YELLOW (B) RED (D) ORANGE (A) GREEN (C) 5. HIGHEST: C (GREEN) LOWEST: E (BLUE) P 34 Liquid Lab analysis questions Substance Density Which substance is it? (A - E) Water 1.00 g/ml D red 0.79 g/ml E blue 1.33 g/ml C green Vegetable oil 0.92 g/ml B yellow Dish Soap 1.06 g/ml A orange Rubbing Alcohol Light Corn Syrup 2. Different densities 3. E/Alcohol/Blue (least dense, lowest density) 4. C/Syrup/Green (most dense, highest density) 5. Wrong colors! (should be blue on top, then yellow, then red, then orange, then green) Atmosphere Crust/hydrosphere Mantle Outer Core Inner Core 6. 7. Paragraph with data 1. Oil, plastic, water, aluminum, marble 2. 14g/20mL= 0.7 g/mL, so it would settle at the top 3. 20g/15mL=1.33g/ml, so it would settle between water and aluminum 4. Measure water in a graduated cylinder, put the rock in the water, see how much the water rises 23. 24. 16g/8mL = 2 g/mL 35mL-20mL = 15 mL 25. 5cm x 5cm x 5cm = 125 cm³ 26. 27. 28. 29. 45g/15mL= 3g/mL 200g/125cm³ = 1.6 g/cm³ B Different densities Most = gravel, least = silt Silt It is small and has low density (about the same density as water) 30. Gold is the most dense 31. Atmosphere, hydrosphere, crust, mantle, outer core, inner core 32. Most dense settled to the bottom (middle) of the Earth first. Most dense in the middle 33. Atmosphere is less dense than the crust 34. An egg will sink in freshwater and float in salt water because the salt adds density to the water, making it more dense than the egg 30. 35. 50g/5mL = 10g/mL This fits in the outer core because it is between 9-12g/mL 36. 20g/5.8mL= 3.45g/mL This fits in the mantle because it is between 3.3-5.7g/mL 37. R S R T S T R S T Lowest to highest density: R, S, T Density Practice Test Answers 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. B 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. B 9. B 10. D 11. B 12. B 13. B 14. C 15. A 16. A 17. C 18. D 19. D 20. C





