BY 124 SI WORKSHEET #4 MULTIPLE CHOICE Which of the
advertisement

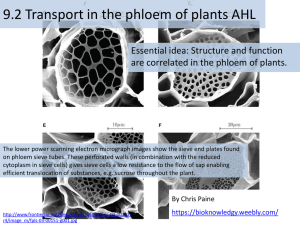
BY 124 SI WORKSHEET #4 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is responsible for the cohesion of water molecules? a. Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atoms of a water molecule and cellulose in a vessel cell b. Covalent bonds between the hydrogen atoms of two adjacent water molecules c. Hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule d. Covalent bonds between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and a hydrogen atom of another water molecule 2. What is the driving force for the movement in materials in the phloem of plants? a. Gravity b. Difference in osmotic water potential between source and sink c. Root pressure d. Transpiration of water that stomates e. Adhesion of water to phloem sieve tubes 3. Water flows into the source end of a sieve tube because a. Sucrose has diffused into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic b. Sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic c. Water pressure outside the sieve tube forces in water d. Sucrose has been dumped from the sieve tube by active transport 4. True or False: Phloem sap is pushed for transport by negative pressure. 5. According to the pressure flow hypothesis of phloem transport: a. Solute moves from high concentration in source to lower concentration in the sink b. Water actively transported into the source region of phloem to create needed turgor pressure c. Formation of starch from sugar in the sink increases osmotic concentration d. Pressure in phloem of a root is greater than the pressure of phloem in the leaf 6. True or False: Transpiration raises water potential in the leaf by producing a positive pressure potential. This higher water potential draws water from the xylem. SHORT ANSWER/APPLICATION QUESTIONS 1. Discuss the structure and function of the 2 cell layers of Phylum Porifera, including their cell components and location. Sponge body has 2 cell layers separated by gelatinous mesohyl. Amoebocytes: manufacture spicules, digest and transfer nutrients from choanocytes to other cells Choanocytes: have flagellum & engulf food by phagocytosis 2. Discuss the 1 phyla & 2 classes of Lophotrochozoans talked about in class, including their common names and one characteristic of each. Platyhelminthes: flatworms, triploblastic, acoelomates Trematoda: flukes, parasitic, schistosomiasis Cestoda: parasitic tapeworms, scolex, proglottids 3. Describe in detail the life cycle of the pork tapeworm. ** see handout given in class 4. Discuss the organization of tissues in the Cnidarians and any special cells they may possess. *cnidocytes, nematocysts