Mineral
advertisement

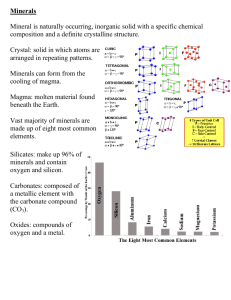
What is a Mineral? • Naturally formed solid substance with a crystal structure What do All Minerals have in Common? • • • • Formed by Natural Processes Are not Alive and Never Were Alive Have a Definite Volume & Shape Are Elements or Compounds with a Unique Chemical Make-Up • Are Crystals (particles arranged in patterns that are repeated over and over) How do Minerals Form? Physical Properties Used to Identify • Color – Can be misleading – Can vary due to impurities Physical Properties Used to Identify • Luster – Surface Reflection – Metallic = Shiny – Non-Metallic = Dull Physical Properties Used to Identify • Streak – The color of the powdered form of the mineral – The color of the streak can be different than the mineral – Minerals must be softer than the streak plate Streak - Quartz • Quartz comes in many colors, but… the streak is always white! Physical Properties Used to Identify • Hardness – A measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched • Mohs Hardness Scale – 1 (Talc) = Softest – 10 (Diamond) = Hardest Simple Hardness Test Method • • • • Test more than one area of each sample Fingernail: Hardness less than 2 Glass: Hardness = 5.5 If you can make a scratch in the mineral with your fingernail: – Hardness < 2. • If you cannot make a scratch in the mineral with your fingernail, but the mineral cannot make a scratch in the glass: – 2 < Hardness < 5.5 • If the mineral scratches the glass: – Hardness > 5.5 Physical Properties Used to Identify • Cleavage and Fracture – Atomic arrangement determine the way the mineral breaks • Cleavage: Minerals break along smooth, flat surfaces and every break has the same general shape • Fracture: Minerals break with random, jagged edges Mica • Mica cleaves in thin sheets, because the weakest joints are between flat sheets of strongly-joined atoms. Galena • Galena cleaves into cubes, because the joints inside are equally strong. Gold • The “nugget” shape of gold is a good representation of random fracture. Physical Properties Used to Identify • Density – Reflects the atomic mass and structure of a material Mass Density Volume – If you had a sample of gold and a sample mica of the same size, the gold would have greater weight Physical Properties Used to Identify • Specific Gravity – the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of an equal volume of water at 4 C. Physical Properties Used to Identify • Magnetism – Minerals often have a strong or weak attraction to a magnetic field. • Most magnetic minerals are opaque, metallic-looking minerals Physical Properties Used to Identify • Smell – Sulfides smell like a struck match or rotten eggs – Arsenic smells like garlic • Taste – Halite and Hanksite are salty – Sylvite is bitter • Texture – Fluorite has a smooth texture – Talc is greasy Physical Properties Used to Identify • Refractive Index – When light travels from one substance to another, it bends • Fluorescence – Some minerals “glow” when exposed to black light Groups of Minerals • About 1,500 unique minerals have been identified • Geologists have classified minerals into groups – Distinct Chemical Nature – Specific Characteristics Groups of Minerals • Silicates – Most abundant group – Contain Silicon and Oxygen – Strongly-bonded Tetrahedron Ions Groups of Minerals • Carbonates – Composed of one or more metallic elements combined with a Carbonate (CO3-) – Typically transparent and lightly colored – A common component of the earth’s inner crust Calcite Rhodochrosite Groups of Minerals • Oxides – Compounds of Oxygen and a Metal – Strong Chemical Bond – Very Hard and Dense – Great sources of iron and rare metals Hematite Groups of Minerals • Sulfides – Sulfur and a Metallic Ion – Highly symmetric, simple structures • Low Hardness and High Specific Gravity Galena Pyrite Groups of Minerals • Sulfates – Composed of Elements with a Sulfate Ion (SO42-) – Delicate and occur near the earth’s surface Barite Gypsum Groups of Minerals • Native Elements – Made up of a Single Element – Highly Ordered Atomic Arrangment Copper Gold What is a Gem? • Mineral or rock that has value – Usually rare • Example: – Mineral: Corundum – Gem: Ruby Mineral Uses – Building a House Mineral Uses – In the Kitchen Mineral Uses – Transportation Mineral Uses – Medical/Dental