Gemstones Lesson
advertisement
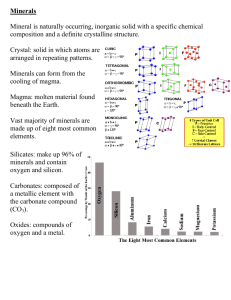
SETON HILL UNIVERSITY TOPIC Name Subject Grade Level Date/Duration Big Ideas Essential Questions PA/Common Core/Standards DETAILS Katelyn Pratt Gemstones 7th Grade 20 minutes Critical thinking enhances problem solving skills. There is more than one solution to a problem. Objective Bloom's Taxonomy Webb's Depth of Knowledge (DOK) Formative & Summative Assessment Evidence ISTE Standards for Students Framework for 21st Century Learning What are gemstones? What do they come from? What physical properties help distinguish one from another? S6.D.1.1.2: Identify the three basic rock types and describe their formation (i.e., igneous [granite, basalt, obsidian, and pumice]; sedimentary [limestone, sandstone, shale, and coal]; and metamorphic [slate, quartzite, marble, and gneiss]). S6.C.1.1.1: Describe how characteristic physical properties of matter can be used to distinguish one substance from another While creating a poster, SWBAT accurately explain their gemstone’s appearance, properties, and chemical makeup in a minimum of 3 sentences. While participating in a group discussion, SWBAT accurately explain the definitions of minerals and gemstones 2/2 times. While completing an online quiz, SWBAT demonstrate knowledge of minerals and properties of diamonds with at least 90% accuracy. Monitor student understanding of minerals and gemstones Use the three-point rubric to evaluate students' work during this lesson. o Three points: Students were highly engaged in class discussions; demonstrated a thorough understanding of the properties of minerals; developed a clear, coherent presentation with answers to all of the assigned questions. o Two points: Students showed satisfactory participation in class discussions; demonstrated a satisfactory understanding of the properties of minerals; developed an adequate presentation with answers to most of the assigned questions. o One point: Students participated minimally in class discussions; demonstrated a weak understanding of the properties of minerals; developed a simplistic presentation with answers to few of the assigned questions. Diamond Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vHPOp69SO9E Possible Websites for Research http://www.minerals.net/gemstone/gem_abc/gem_abcd.htm http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/gemstones/mineral.html http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/gemstones/formulas.html CK Materials http://rocksforkids.com/RFK/identification.html http://www.minerals.net/resource/property/properti.htm Computer with Internet access Print resources about mineral gemstones Poster board and markers SUPERVISING TEACHER’S SIGNATURE Seton Hill University Lesson Plan Template Step-by-Step Procedures RATIONALE for the Learning Plan Methods & Watch video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vHPOp69SO9E Procedures As a class, review what was learned about diamonds in the video. o What is a diamond made of? (The element carbon.) o How are diamonds formed? (They form under very high pressures deep within the earth.) o How do they come to the surface? (In rocks released during volcanic eruptions.) o What are some properties of diamonds? (They are very hard, durable, reflect light well, and refract light into many colors.) If students want to learn more about diamonds, visit The Nature of Diamonds feature on the American Museum of Natural History's Web site: http://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/diamonds Next, explain that o diamonds are a mineral — a solid substance that occurs naturally in rocks or in the ground. o Every mineral has a unique chemical makeup and distinct characteristics. o Some minerals are treasured for their beauty, durability, and rarity. These minerals, called gemstones, are often cut, polished, and used for jewelry or decoration. Gemstones include emeralds, rubies, and sapphires, as well as diamonds. Explain that all minerals, including gemstones, are described by their properties, which include the following. o Color: A mineral can vary in color, depending on its chemical makeup. o Streak: When a mineral is crushed or rubbed against another surface, the resulting color is its streak. A mineral's streak is often different from the mineral's color. o Specific Gravity (or SG): A mineral's density or weight is calculated by how heavy it is relative to water. If a mineral has an SG of 3.5, it is 3.5 times heavier than the same amount of water. Most minerals have an SG between 2 and 4.5. o Luster: This property describes how the mineral's surface reflects light-for example, "dull," "metallic," or "brilliant." o Hardness: How well a mineral resists scratching by another CK mineral is determined by its hardness. Diamonds, the hardest mineral, can scratch talc, the softest. Talc cannot scratch diamonds. Two minerals that scratch each other are the same hardness. Divide the class into pairs of students and assign or have them chose a gemstone, such as the following: o Amethyst o Aquamarine o Diamond o Emerald o Jade o Opal o Ruby o Sapphire o Topaz o Turquoise Next, tell students that they will be creating a gemstone poster, which they will use to give their class report. The poster should have at least two images and include answers to the following questions: o Is this mineral part of a larger mineral group or mineral class? If so, which one? What, if any, other popular gemstones belong in this group? o What chemical elements make up this gemstone? o What is this gemstone's relative hardness? o What is its specific gravity? o What color (or colors) is this gemstone? o Describe the luster of this gemstone. Give students the list of sites to look for information. Evaluation of the Learning/Mastery of the Concept Formal Evaluation Presentation rubric 10 point quiz with tier one and tier two questions Closure Summary & Review of the Learning Poster presentations and after an exit slip with something they learned from another group’s presentation Homework/Assignments none Teacher Self-reflection