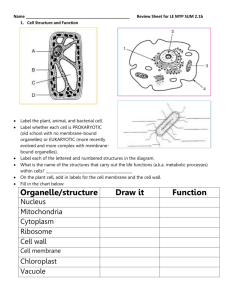
REVIEW GAME The Nerve Impulse TUN
advertisement

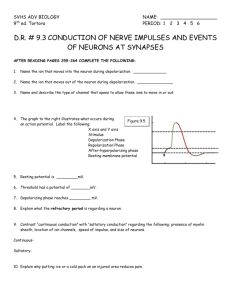
See also the NOTE GUIDES posted online on the wiki, the online self-quizzes posted on the wiki, and USG pages 6 to 10. Main Content: 1. Sodium Potassium Pump 2. Generation of an Action Potential 3. Transmission Across a Synpase with Neurotransmitters Self Quizzes and Animations Action Potential Self Quiz: http://wps.pearsoned.it/fisiologia_umana5/165/42313/10832298.cw/content/index.html Action Potential Self Quiz #2: http://www.siumed.edu/~dwade/phys310/6ap.htm Action Potential Animation: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__the_nerve_impulse.html Action Potential Animation: http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/actionpotential.html Voltage Gated Channels: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__voltagegated_channels_and_the_action_potential__quiz_1_.html Sodium Potassium Pump Animation: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__sodium-potassium_exchange_pump__quiz_3_.html Sodium Potassium Pump Animation: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__sodium-potassium_exchange_pump__quiz_1_.html Transmission Across a Synapse: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__transmission_across_a_synapse.html To remember… Your assessment is all essay so this review game does not represent the format of you test. Be sure to review all class activities and notes to fully prepare. Fill in the blanks in the sentence below with the NAME of the STRUCTURE of a NEURON that provides the described FUNCTION. Signals “come in” to the neuron through the ________, and travel “out” of the neuron along the ________, at the end of which the __________ contact the next neuron in the communication chain. The _________ phase ensures propagation in this direction. Fill in the blanks in the sentence below with the NAME of the STRUCTURE of a NEURON that provides the described FUNCTION. Signals “come in” to the neuron through the dendrites, and travel “out” of the neuron along the axon, at the end of which the axon endings contact the next neuron in the communication chain. The hyperpolarization phase ensures propagation in that direction. The opening and closing of the ____________ causes the characteristic phases of an action potential. The opening and closing of the voltage gated ion channels causes the characteristic phases of an action potential. The refractory period includes both the ________ phase and the _________ phase. It describes a time period in which a neuron ________ generate an action potential. The refractory period includes both the repolarization phase and the hyperpolarization phase. It describes a time period in which a neuron cannot generate an action potential. A ______ causes SOME of the sodium channels on the membrane to open. Once the membrane has reached ______, ALL of the sodium channels open to ______ the membrane. A stimulus (disturbance on the membrane) causes SOME of the sodium channels on the membrane to open. Once the membrane has reached threshold, ALL of the sodium channels open to depolarize the membrane. Match each of the following phases to the description of events that takes place. a. Resting Phase b. Hyperpolarization Phase c. Repolarization Phase d. Depolarization Phase 1. Phase that is characterized by a rapid decrease in sodium permeability and increase in potassium permeability. 2. Phase that is characterized by a prolonged high permeability to potassium due to the slow closing of potassium channels. 3. Phase that is characterized by a high permeability to sodium. Match each of the following phases to the description of events that takes place. a. b. c. d. Resting Phase Hyperpolarization Phase Repolarization Phase Depolarization Phase C 2. B 3. D 1. At the end of the depolarization phase, the ______ channels help restore resting membrane potential. At the end of the depolarization phase, the potassium channels help restore resting membrane potential. When a neuron is at rest, the cytoplasmic side of the membrane has a _____ charge and the extracellular fluid side has a _____ charge due to 3 _____ ions being pumped out and 2 _____ ions being pumped in via the ______ using _____ transport. When a neuron is at rest, the cytoplasmic side of the membrane has a negative charge and the extracellular fluid side has a positive charge due to 3 Na+ (sodium) ions being pumped out and 2 K+ (potassium) ions being pumped in via the sodium-potassium pump using active transport. The sodium potassium pump uses _____ transport which moves molecules from areas of _____ concentration to areas of _____ concentration using _____. The phoshphoyrlization of the transport protein causes ______. The sodium potassium pump uses active transport which moves molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration using ATP (adensosine triphosphate). The phoshphoyrlization of the transport protein causes a change in conformation (shape change). B A C E D Identify what each part of the reaction is above. B A C E D A = ATP B = water to break ATP molecule by hydrolysis C = inorganic phosphate (will phosphorylate the sodium potassium pump) D = ADP E = energy release with the breaking of bonds The primary neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is ________, an ________ neurotransmitter. A)Dopamine , excitatory B)Glutamate, excitatory C)Acetylcholine, excitatory D)GABA, inhibitory E)Serotonin, inhibitory The primary neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is ________, an ________ neurotransmitter. A)Dopamine , excitatory B)Glutamate, excitatory C)Acetylcholine, excitatory D)GABA, inhibitory E)Serotonin, inhibitory Arrange the following in the proper order in which they occur at the pre-synaptic side of a neuromuscular junction. 1. Calcium ions enter the cell via voltage-gated calcium channels 2. An action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal 3. Neurotransmitter is released A) 1, 2, 3 B) 2, 1, 3 C) 2, 3, 1 D) 3, 2, 1 E) 3, 1, 2 Arrange the following in the proper order in which they occur at the pre-synaptic side of a neuromuscular junction. 1. Calcium ions enter the cell via voltage-gated calcium channels 2. An action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal 3. Neurotransmitter is released A) 1, 2, 3 B) 2, 1, 3 C) 2, 3, 1 D) 3, 2, 1 E) 3, 1, 2 The process by which neurotransmitter molecules detach from a postsynaptic neuron are reabsorbed by a presynaptic neuron so they can be recycled and used again. A. axon terminals B. synaptic transmission C. reuptake D. diffusion The process by which neurotransmitter molecules detach from a postsynaptic neuron are reabsorbed by a presynaptic neuron so they can be recycled and used again. A. axon terminals B. synaptic transmission C. reuptake D. diffusion Arrange the following in the proper order in which they occur at the post-synaptic side of a excitatory synapse. 1. Neurotransmitter binds to a ligand-gated ion-channel. 2. An action potential is propagated along the postsynaptic cell’s axon 3. Depolarization of the post-synaptic membrane. 4. Sodium ions move into the post-synaptic cell. A) 1, 2, 3, 4 B) 2, 1, 3, 4 C) 4, 2, 3, 1 D) 1, 4, 3, 2 E) 3, 1, 2, 4 Arrange the following in the proper order in which they occur at the post-synaptic side of a excitatory synapse. 1. Neurotransmitter binds to a ligand-gated ion-channel. 2. An action potential is propagated along the postsynaptic cell’s axon 3. Depolarization of the post-synaptic membrane. 4. Sodium ions move into the post-synaptic cell. A) 1, 2, 3, 4 B) 2, 1, 3, 4 C) 4, 2, 3, 1 D) 1, 4, 3, 2 E) 3, 1, 2, 4 Generally, neural impulses travel a. electrically between and within each neuron. b. chemically between and within each neuron. c. electrically between neurons and chemically within each neuron. d. chemically between neurons and electrically within each neuron. Generally, neural impulses travel a. electrically between and within each neuron. b. chemically between and within each neuron. c. electrically between neurons and chemically within each neuron. d. chemically between neurons and electrically within each neuron. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is primarily involved in… A. emotional states and sleep B. physical arousal, learning, and memory C. learning, memory, and muscle contractions D. movement, thought processes, and rewarding sensations The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is primarily involved in A. emotional states and sleep B. physical arousal, learning, and memory C. learning, memory, and muscle contractions D. movement, thought processes, and rewarding sensations Neurotransmitters are _______ that travel across the ________ to another cell where they bind to _________. Neurotransmitters are chemicals (not electrical impulses!) that travel across the synaptic cleft to another cell where they bind to ligand gated ion channels. Ligand gated ion channels on the post-synaptic cell that are permeable to chlorine and potassium ions are ______ and channels that are permeable to sodium and potassium are _______. Chlorine ions (enter/exit) the membrane and _____ it. Sodium ions (enter/exit) the membrane and ______ it. Ligand gated ion channels on the post-synaptic cell that are permeable to chlorine and potassium ions are inhibitory and channels that are permeable to sodium and potassium are excitatory. Chlorine ions (enter/exit) the membrane and hyperpolarize it. Sodium ions (enter/exit) the membrane and depolarize it. List the following in order of their occurrence: A. Action potential travels along axon of sending neuron B. The neurotransmitter must fit perfectly into the receptor C. Synaptic transmission occurs when the action potential causes neurotransmitters to be released by the synaptic vesicles in the axon terminals D. The neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap and bind with the correctly shaped receptor sites on the receiving neuron. A)ABCD B)ACDC C)ADCB D)ACDB List the following in order of their occurrence: A. Action potential travels along axon of sending neuron B. The neurotransmitter must fit perfectly into the receptor C. Synaptic transmission occurs when the action potential causes neurotransmitters to be released by the synaptic vesicles in the axon terminals D. The neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap and bind with the correctly shaped receptor sites on the receiving neuron. A)ABCD B)ACDC C)ADCB D)ACDB Which of the following statements about the action of drugs is TRUE. A. Drugs can mimic the function of neurotransmitter at the synaptic cleft. B. Drugs can block the ligand-gated ion channel site on the membrane of the post-synaptic neuron. C. Drugs can block the reuptake of the neurotransmitter by the pre-synaptic neuron. D. All of the above Which of the following statements about the action of drugs is TRUE. A. Drugs can mimic the function of neurotransmitter at the synaptic cleft. B. Drugs can block the ligand-gated ion channel site on the membrane of the post-synaptic neuron. C. Drugs can block the reuptake of the neurotransmitter by the pre-synaptic neuron. D. All of the above Low levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine are often associated with A)Depression B)Multiple sclerosis C)Parkinson’s Disease D)Alzheimer’s Disease Low levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine are often associated with A)Depression B)Multiple sclerosis C)Parkinson’s Disease D)Alzheimer’s Disease Muscular tremors and rigidity in Parkinson's disease results from which of the following? A)Damage to acetylcholine pathway in the thalamus B)Damage to a dopamine pathway in the substantia nigra C)Excitotoxicity due to excess levels of glutamate D)Loss of GABA in the spinal cord Muscular tremors and rigidity in Parkinson's disease results from which of the following? A)Damage to acetylcholine pathway in the thalamus B)Damage to a dopamine pathway in the substantia nigra C)Excitotoxicity due to excess levels of glutamate D)Loss of GABA in the spinal cord Neurotransmitters are contained in _____ that are located in _____ of the pre-synaptic neuron. A. vesicles; axon terminals B. axon terminals; dendrites C. receptor sites; synapses D. cell membranes; synaptic gaps Neurotransmitters are contained in _____ that are located in _____ of the pre-synaptic neuron. A. vesicles; axon terminals B. axon terminals; dendrites C. receptor sites; synapses D. cell membranes; synaptic gaps Low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin are often associated with A)Depression B)Multiple sclerosis C)Parkinson’s Disease D)Alzheimer’s Disease Low levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin are often associated with A)Depression B)Multiple sclerosis C)Parkinson’s Disease D)Alzheimer’s Disease Which of the following mechanisms can serve to remove neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft? A)Reuptake by the axon terminus of the pre-synaptic cell B)Breakdown by enzymes C)Diffusion away from the synaptic cleft D)All of the above Which of the following mechanisms can serve to remove neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft? A)Reuptake by the axon terminus of the pre-synaptic cell B)Breakdown by enzymes C)Diffusion away from the synaptic cleft D)All of the above Which of the following is a primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system? A)Acetylcholine B)Glutamate C)GABA D)Norepinephrine Which of the following is a primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system? A)Acetylcholine B)Glutamate C)GABA D)Norepinephrine