The Nervous System
advertisement

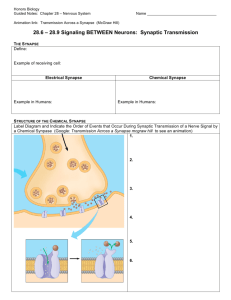
The Nervous System By Nate Levin, Cedric White, and Andrew Boon Chemical Synapse Chemical synapses are specialized areas through which neurons (nerve cells) signal each other. A junction that permits a neuron to pass a chemical signal to another cell. A space in between two neurons(1). Chemical Synapse Animation QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Neurotransmitter Neurotransmitters are chemicals created within the cells that transmit signals from a neuron to a cell across a synapse(2). Neurotransmitter Animation QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Acetylcholine Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter that has inhibitory and excitatory effects on the brain, spinal cord, glands, and muscles. ACh is released from the motor neuron, diffused across the cleft, and binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane(3). Dopamine Dopamine is a neurotransmitter present in the brain that functions by activating the five types of Dopamine receptors. It is produced in the brain. Crossing the Neural Membrane An electrical impulse called an action potential travels along the axon in the pre-synaptic neuron toward the axon terminal. The action potential can not cross the synaptic space because electrical signals can not cross gaps. The vesicle holding the neurotransmitters then moves to the end of the pre-synaptic neuron. Crossing the Neural Membrane The neurotransmitters released move across the synaptic space to receptors on the post-synaptic neuron. The binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptors triggers an action potential within the post-synaptic neuron. At this point, the neurotransmitters release and either are degraded by enzymes in the synaptic space or move back into the vesicles in the pre-synaptic space through transporter proteins. Electrical to Chemical Question: Why do the electrical signals (action potential) need to be converted to chemical signals (neurotransmitter) to be transported across the membrane? Answer: The electrical signals are unable to cross the synaptic space without direct contact to the post-synaptic neuron. (Think plugging into a socket. It must be fully plugged in to work) Because the electrical signals are unable to cross the synaptic space, the actions that must be relayed would be stuck in the pre-synaptic membrane. Electrical to Chemical Due to the electrical signal’s inability to cross the synaptic space, the signal is relayed through neurotransmitter in the form of chemical energy. Without this conversion, it would be impossible for the message to move from neuron to neuron. Now, watch the animation again and pay close attention to how neurotransmitters cross the synaptic space and the importance of converting electrical signals to chemical. Review of Neurotransmission Alzheimer’s The lead cause for Alzheimer’s, doctors believe, is that the neurotransmitter acetylcholine is becoming useless, making it impossible for neurons to interact. There are no known medicines for Alzheimer’s because doctors can not stimulate the now-useless neurotransmitters(4). References 1. McGraw-Hill. "Animation: Chemical Synapse (Quiz 1)." Animation: Chemical Synapse. 2006. Web. 04 Nov. 2010. <http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter14/animation__chemical_synapse__qu iz_1_.html>. 2. "The Brain - Lesson 2 - How Neurotransmission Works." The Brain: Understanding Neurology. 2000. Web. 04 Nov. 2010. <http://science.education.nih.gov/supplements/nih2/addiction/activities/lesson2_neurotr ansmission.htm>. 3. "Acetylcholine - Chemistry Encyclopedia - Structure, Reaction." Chemistry: Foundations and Applications. 2008. Web. 04 Nov. 2010. <http://www.chemistryexplained.com/A-Ar/Acetylcholine.html>. 4. "Alzheimer's Association - What Is Alzheimer's." Alzheimer's Association. 1 Nov. 2010. Web. 05 Nov. 2010. <http://www.alz.org/alzheimers_disease_what_is_alzheimers.asp>.