Test 5 Review Guide Name: Honors Chemistry Chapter 15 Answer

Test 5 Review Guide
Honors Chemistry Chapter 15
Name:
Answer the following questions, give examples and explain your answers where indicated:
(1) What is energy?
(2) What are the two types of energy?
(3) What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy? Give an example of each.
(4) What are heat and its symbol?
(5) How is a calorie defined?
(6) What is the difference between a calorie and a nutritional Calorie?
(7) What is a joule?
(8) What is the relationship between joules and calories?
(9) When chemicals are mixed in a test tube, the test tube becomes hotter. What kind of reaction has occurred?
(10) A negative ∆H (-∆H) indicates that a chemical reaction is what?
(11) Give an example of an endothermic reaction.
(12) When there are physical, chemical, or phase changes, you also have what changes?
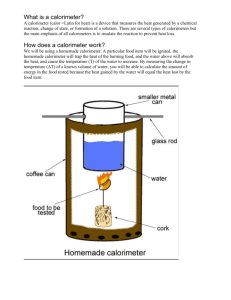
(13) To measure the heat change in a calorimeter, what information is needed?
(14) I
2
+ Cl
2
+ 4.3 kcal → ICl : The reaction shown is known as what kind of equation?
Vocabulary, write the correct term on the line next to the definition
(15) ____________________ the ability to do work or produce heat
(16) ____________________ states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed
(17) ____________________ energy stored in a substance because of its composition
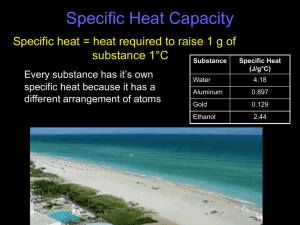
(18) ____________________ heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius
(19) ____________________ the SI unit of heat and energy
(20) ____________________ type of equation that shows the states of matter and the amount of energy gained or lost
(21) ____________________ type of reaction that releases energy
(22) ____________________ type of reaction that absorbs energy
(23) ____________________ forces holding together a solid are broken, and the phase changes from a liquid to a solid
(24) ____________________ the part of the universe that is being studied during a chemical process
(25) ____________________ a form of energy that flows from a warmer object to a cooler object
(26) ____________________ a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance
(27) ____________________ the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by 1°C
(28) ____________________ an insulated device that is used to measure the amount of heat released or absorbed during a physical or chemical process
(29) ____________________ the study of heat changes that accompany chemical reactions and phase changes
(30) ____________________ the heat content of a system
Solve the following problems. Please show your work and circle your answer.
(30) Write the energy conversions here:
(31) Convert 15 calories to joules.
(32) Convert 3000 joules to Calories.
(33) Convert 10 kilojoules to kilocalories.
(34) The specific heat capacity of water is: _______________ and the formula used for specific heat calculations is:
______________________________
(35) If the temperature of 34.4 g of ethanol increases from 25°C to 78.8°C, how much heat has been absorbed by the ethanol?
The specific heat for ethanol is 2.44 J/g°C.
(36) A 4.5 g nugget of pure gold absorbed 276 J of heat. What was the final temperature of the gold if the initial temperature was 25°C? The specific heat for gold is 0.129 J/g°C.
(37) A 155 g of an unknown substance was heated from 25°C to 40°C. In the process, the substance absorbed 5696 J of energy.
What is the specific heat of the substance?
(38) What is the mass of a substance that has a specific heat of 0.362 J/g°C and raises its temperature from 25°C to 110°C when it absorbs 8700 J of energy?
(39) A calorimeter contains 195 g of water at 20.4°C. A 37.8 g sample of an unknown metal is heated to 133°C and placed into the water in the calorimeter. Heat flows from the metal to the water until both reach a final temperature of 24.6°C. What is the specific heat of the metal?
(40) A 77.5 g sample of an unknown solid is heated to 62.5°C and placed into a calorimeter containing 93 g of water at 23.3°C. If the final temperature of the solid sample and the water is 26.2°C, what is the specific heat of the solid?
(41) A milkshake from Zaxby’s contains 3172 kJ of energy. If you drank a milkshake every day for four weeks and continued to eat and exercise normally, how much weight would you gain? (1 lb of body fat = 4000 Calories)
(42) Convert 10 kilojoules/minute to kilocalories/hour.
Complete the following table of phase changes:
Name of Change of State
Deposition
Condensation
Solidification/crystallization
Change solid to gas liquid to gas solid to liquid
Endothermic or Exothermic?
Use the heating curve above to answer the following questions:
(43) Which letter on the curve represents the liquid phase?
(44) Which letter on the curve represents melting, ∆H fusion
?
(45) At letters b and d on the curve, the temperature does not increase until after enough heat is absorbed. Why does the temperature not increase in these areas?
(46) At what temperature does this substance vaporize?
(47) Is this graph showing an endothermic or an exothermic process?
(48) What phase or phases are present during segment d?
(49) What is happening to the energy being absorbed from the heat source (in terms of potential and/or kinetic energy?
(50) What phase or phases are present during segment a?
(51) Explain why segment d is longer than segment a.
Use the graph above to answer the following questions:
(52) What type of energy flow does this graph represent?
(53) Is the ∆H negative or positive for this process?
(54) Which letter represents the amount of energy of the products?
(55) Which letter represents the amount of energy of the reactants?
(56) Which letter represents the transition state?
(57) Which letter represents the change of energy of the system?
(58) Which letter represents the change of enthalpy of the system?