Pre Civil War North
advertisement
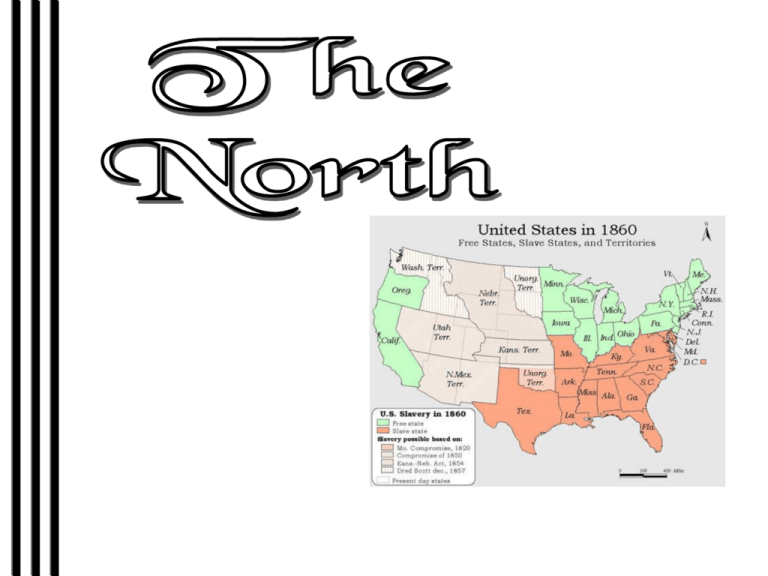
• More than 20 million people living in the North and growing…. • Most immigrants such as Irish and German new to the United States settled in the North to work in factories. • Northerners were leaving their farms and moving to cities to get jobs in newly developed factories. – This created a wage-based economy that resulted in a large middle class. This group lead a lot of social reforms. • Increasing railroad made shipments and travel quicker and easier. By1850, 30,000 miles of tracks connected distant parts of the United States. Most of the new rail lines were in the North. Economy in the North • . The North had more small manufacturing industries, capitalists and banking then the South. – By 1840 there were 1,200 cotton factories in the United States, two-thirds of them in the North. – By 1850 the North had more than 1,500 woolen mills, most of them individually owned, producing blankets, flannel and worsteds. – Firearms and furniture were being produced in the North. – People were investing in labor saving machinery -- advancing technology in order to reduce manual labor or labor costs. Factory Workers The North was also the heart of sea born trade in the United States. By the late 1840s, ships powered by steam engines had replaced sailing ships in hauling freight and passengers across the Atlantic Ocean, the new technology and competition reducing shipping rates. Foreign commerce grew dramatically in the 1840s and 1850s. The North was manufacturing power looms and exporting them to Europe. Ships owned by Northerners were shipping the South's cotton to Europe, mainly to Britain -- cotton being two-thirds of U.S. exports. . Life as a Northern Factory Worker • Small factories employed families, relying primarily on the labor of children (usually between the ages of 10 and 20) to work in factories. • Factory managers argued that these groups of people needed close supervision because they could not be trusted to take care of themselves. • In the North, factory owners paid wages to their workers. • Workers experienced lots of abuse, long hours, no safety programs, unsafe machinery, no worker's comp, the use of child labor, etc, • Many northern factory workers were no more enamored of their jobs than slaves were of theirs. Indeed, they sometimes called themselves wage slaves. Women before the Civil War The weekly schedule of "drudge" likely included; • laundry on Monday, • ironing and mending on Tuesday, • baking on Wednesday and Saturday, • daily tidying of kitchen and parlor, and thorough cleaning on Thursday and again on Saturday. This was in addition to; • childcare, • three meals a day, • hauling water and keeping the fire burning in the stove, a chore that in itself took at least one hour each day. • Then there was making the family garments and seasonal preserving of fruits, vegetables and meat. • Women also had charge of the farm garden, livestock and poultry • During planting and harvest, if she did not work in the fields herself, she provided room and board for the extra help that did. Northern Culture The North was more devoted to education than was the South. Of the nation's 321 public high schools only 30 were in the South. Women were viewed differently. In the North, women were more active and hard working, a few of them becoming doctors, writers or activists in their church.